
| Filed by the Registrant [X] | ||||
| Filed by a Party other than the Registrant [ ] | ||||
| Check the appropriate box: | ||||
| [ ] | Preliminary Proxy Statement | |||
| [ ] | Confidential, Commission Only (as permitted by Rule 14a-6(e)(2)) | |||
| [X] | Definitive Proxy Statement | |||
| [ ] | Definitive Additional Materials | |||
| [ ] | Soliciting Material Pursuant to §240.14a-12 | |||
| (Name of Registrant as Specified In Its Charter) | ||
| (Name of Person(s) Filing Proxy Statement, if |
| Payment of Filing Fee (Check the appropriate box): | ||||
| [X] | No fee required. | |||
| [ ] | Fee computed on table below per Exchange Act Rules 14a-6(i) | |||
| 1) | Title of each class of securities to which transaction applies: | |||
| 2) | Aggregate number of securities to which transaction applies: | |||
| 3) | Per unit price or other underlying value of transaction computed pursuant to Exchange Act Rule 0-11 (set forth the amount on which the filing fee is calculated and state how it was determined): | |||
| 4) | Proposed maximum aggregate value of transaction: | |||
| 5) | Total fee paid: | |||
| [ ] | Fee paid previously with preliminary | |||
| [ ] | Check box if any part of the fee is offset as provided by Exchange Act Rule 0-11(a)(2) and identify the filing for which the offsetting fee was paid previously. Identify the previous filing by registration statement number, or the | |||
| 1) | Amount | |||
| 2) | Form, Schedule or Registration Statement No.: | |||
| 3) | Filing Party: | |||
| 4) | Date Filed: | |||
__________
PNotice of 2016 Annual Meeting of ShareholdersROXY
NOTICEOF ANNUAL MEETINGOF SHAREHOLDERS
PROXYSTATEMENT
AND
2012 ANNUAL REPORT__________


Fellow Kroger Shareholders:
We beginIt is our 130th anniversary year with confidence.
The ways we listenpleasure to Customersinvite you to join our Board of Directors, senior leadership, and respond to their ever-changing needs have evolved through our history, and yet several clear principles have remained constant forother Kroger associates at The Kroger Co. familyAnnual Meeting of stores.
Our confidence is firmly rooted in Kroger’s strong foundation for growth. About 10 years ago we announced ourCustomer 1Shareholders.st business strategy, which truly puts the Customer at the center of how we manage our business. Through our focus on the Four Keys of our strategy – our people, products, price and the shopping experience –we are connecting with Customers in more powerful ways than ever before. Kroger’s identical store sales trend is the clearest measure of that growing connection. In 2012, Kroger achieved a retail industry-leading 37 consecutive quarters – more than nine years – of positive identical sales growth.
Late in 2012 we announcedaggressive new growth plans to expand Customer 1st into the next decade. The Company is investing in a targeted expansion strategy to increase square footage and store penetration in existing markets and enter new markets. Through additional capital investments in new and existing stores, new store formats, and new ways to connect with our Customers and Associates, including our digital connection, we expect to achieve a higher long-term financial target and increase Shareholder return.
A Year of Record Earnings and Focus on Shareholder Value
Kroger’sunique offering of better service, great products, an enjoyable shopping experienceand low prices and weekly specials continues to resonate with a full range of Customers. As a result, fiscal 2012 sales grew $6.4 billion for total revenue of $96.8 billion, making Krogerone of the largest retailers in the world. Net earnings were $1.5 billion or $2.77 per diluted share; this includes an $0.11 per diluted share benefit of the extra week. We achieved record earnings per share for the year, and grew adjusted net earnings per share by more than 16 percent.
Our outstanding business results allowed Kroger to continue using free cash flow to reward shareholders.We increased our quarterly dividend by 30 percent and returned more than $1.5 billion to shareholders through dividends and stock buybacks in 2012. Since 2006, Kroger has paid nearly $1.6 billion in dividends to Shareholders. We have been able to accomplish this while maintaining our investment-grade credit rating and improving our debt leverage ratio and annual interest expense.Since January 2000, Kroger has returned $9.0 billion to Shareholders through share repurchases.
Now, what makes this best-in-class performance possible? A large part of the answer is simple: Our Great People. Associates in the Kroger family of stores are uniquely and authentically passionate for people and for delivering superior results. This is brought to life through their dedication tomaking the day better for every one of the more than seven million Customers who shop our stores daily – whether through a simple smile, solving a problem or helping Customers on a budget feed their family.
* * *
Celebration of Our Shared Heritage
Barney Kroger opened his first store in Cincinnati, Ohio on July 1, 1883. That his Company not only survived but is thriving 130 years later is an amazing accomplishment. And yet two of our banners have been in business even longer. In 1873, George Ralphs – founder of our Ralphs division – opened his first store in Los Angeles. Ten years earlier, in 1863, John C. Groub – founder of our Jay C division – opened his first store in Rockford, Indiana.
We are celebrating the shared heritage of our entire family of stores – a heritage of transformative growth and innovation that continues to inspire us today.
1
Transformative Growth
Kroger’s heritage is one of impressive growth – from being the first grocer in the nation to operate its own bakery in 1901, to operating 37 manufacturing facilities today; from small grocery stores averaging 3,000 square feet in 1930, to supermarkets averaging 12,000 square feet in 1960, to today’s Marketplace stores averaging 125,000 square feet; and from sales topping $1 billion for the first time in 1952 to sales well over $96 billion in 2012.
Our family of stores has grown by powerful combinations of strong regional banners, giving the Company the benefits of size without losing the local touch.
Innovation
Strengthening our connection with Customers begins with listening to them, and for 130 years Kroger has developed innovative ways to listen and respond. In 1959, Kroger executives began conducting “Kroger Calls,” door-to-door interviews with homemakers, to better understand the needs of our Customers. In the 1970s we became the first grocer to formalize Customer research, and last year we listened to nearly 2,000,000 individual Customers and learned important insights that we use to make merchandising decisions.
A more than decade-long partnership with dunnhumbyUSA, the leader in personalizing Customers’ experience of retailers and brands, helps us say that we know our Customers better than anyone. A great example of how we put this into practice is through ourLoyal Customer Mailing, or LCM, which we send to millions of households regularly throughout the year. The most recent LCM reached more than 11 million households, and 97 percent of recipients received an individualized set of coupons for the products they like and buy regularly –almost no two were alike. At redemption rates regularly topping 60 percent, our LCM continues to lead the industry.
Innovation at Kroger also means utilizing new technologies to meet Customer needs. In the early 1970s Kroger was the first retailer in the country to test now-ubiquitous electronic scanners at checkout. In just the last few years, we have pioneered Que Vision, our innovative faster checkout program that has reduced the time a Customer waits in line to check out, on average, from four minutes a few years ago to less than 30 seconds in our stores today.
Innovation is also at the heart of our sustainability efforts, aimed at improving today to protect tomorrow. Kroger created an innovative process to rescue safe, edible fresh products and donate them quickly to local food banks. This innovation has been replicated by other retailers and today fresh products make up more than half of the food distributed nationwide by Feeding America.
We remain committed to delivering always fresh, high quality andsustainably-sourced seafood. We do this in a variety of ways, including support for both wild-caught and farm-raised fishery improvement projects around the world, through our partnership with theWorld Wildlife Fund.
We continue to reduce energy use, which lowers our carbon footprint and helps our bottom line. We have reduced total energy consumption by 32.7 percent since 2000, and are on track to meet our goal of a 35 percent reduction by 2015. We achieve these efficiencies in large ways and small, from designing every new store to earn the U.S. EPA Energy Star rating, to every Associate taking responsibility to turn off lights and check cooler temperatures throughout the day.
You can learn more about our sustainability initiatives by reading our annual sustainability report, available on our websitesustainability.kroger.com.
Kroger is one of the safest companies in our industry. Associate engagement in innovative safety programs hasreduced accident rates in our stores and manufacturing plantsby 76 percent since 1995.
* * *
2
Celebration of Our People
Our shared heritage is the sum total of countless decisions made by Associates through more than a century in business. We invest in our Associates and their families in a variety of ways, including:
A distinct point of pride and celebration for us is the longevity of so many of our Associates. Currently, more than 13,000 of our more than 343,000 Associates have served our Customers for more than 30 years. Nearly 2,000 Associates have served for more than 40 years.
* * *
Enduring Value of Supporting Communities
Over the years, Kroger has undergone several reinventions to meet the changing needs of American families. One thing that has not changed is our ability to make a difference in the lives of our Customers and communities. We partner with local communities through our commitment to feeding the hungry and supporting women’s health, the military and their families, and local organizations and schools.
In 2012, Kroger:
We do these things because our Customers tell us it is important to them and because it strengthens the communities we call home. When you combine the cash, food and product we donate to a variety of causes and programs,Kroger contributed more than $250 million in 2012 to support the communities we serve.
Kroger is a leader in supplier diversity, spending more than$1 billion annually with women- and minority-owned businesses. We proudly remain a member of theBillion Dollar Roundtable and theUnited States Hispanic Chamber of CommerceMillion Dollar Club.
* * *
3
The Year Ahead
Kroger is on pace to deliver another record year. Revenues will approach $100 billion for the first time.
We will continue toexecute our Customer 1st Strategy, coupled with ourrenewed commitment to growth, to make a difference for Customers and create value for Shareholders in 2013. By targeting capital investments to grow our business in new and existing markets and leveraging dunnhumby insights to solve varied Customer needs, we expect to achieve fully diluted earnings per share growth of 8% to 11% plus the dividend over time.
As you can see, the future is bright for Kroger. We are bullish about our ability to sustain the strong momentum that we generated in 2012. In many ways, our fiscal 2012 results served as a great example of our ability to continually grow. We are enthusiastic about all that is to come in the year ahead, which will surely be an exciting and significant one for Kroger.
On behalf of the entire Kroger family, thank you for your continued trust and support.

4
Congratulations to the winners of The Kroger Co. Community Service Award for 2012:
| Where: | School for Creative and Performing Arts | |||||
| Corbett Theater | ||||||
| 108 W. Central Parkway | ||||||
| Cincinnati, OH 45202 | ||||||
| Items of Business: | 1. | To elect eleven director nominees. | ||||
| 2. | ||||||
| 3. | To ratify the selection of our independent auditor for fiscal year 2016. | |||||
5
Notice of Annual Meeting of Shareholders
Cincinnati, Ohio, May 14, 2013
To All Shareholders of The Kroger Co.:
The annual meeting of shareholders of The Kroger Co. will be held at the MUSIC HALL BALLROOM, MUSIC HALL, 1241 Elm Street, Cincinnati, Ohio 45202, on June 27, 2013, at 11 a.m., eastern time, for the following purposes:
| 4. | To | ||
| 5. | To transact other business as may properly come before the meeting. | ||
| Who can Vote: | Holders of Kroger common shares at the close of business on the record date April 27, 2016 are entitled to notice of and to vote at the meeting. | ||
| How to Vote: | Your vote is important! Please vote your proxy in one of the following ways: | ||
| 1. | Via the internet, by visiting www.proxyvote.com. | ||
| 2. | By telephone, by calling the number on your proxy card, voting instruction form or notice. | ||
| 3. | By mail, by marking, signing, dating and mailing your proxy card if you requested printed materials, or your voting instruction form. No postage is required if mailed in the United States. | ||
| 4. | In person, by attending the meeting in Cincinnati. | ||
| Attending the Meeting: | |||
| Webcast of the | If you are unable to attend the meeting, you may listen to a live webcast of the meeting by visiting ir.kroger.com at 11:00 a.m. eastern time on June 23, 2016. | ||
all as set forthWe appreciate your continued confidence in the Proxy Statement accompanying this Notice. Holders of common shares of recordKroger, and we look forward to seeing you at the close of business on April 30, 2013, will be entitled to vote at the meeting.
Attendance
Only shareholders and persons holding proxies from shareholders may attend the meeting.If you are attending the meeting, please bring the notice of the meeting that was separately mailed to you or the top portion of your proxy card, either of which will serve as your admission ticket.
YOUR MANAGEMENT DESIRES TO HAVE A LARGE NUMBER OF SHAREHOLDERS REPRESENTED AT THE MEETING, IN PERSON OR BY PROXY. PLEASE VOTE YOUR PROXY ELECTRONICALLY VIA THE INTERNET OR BY TELEPHONE. IF YOU HAVE ELECTED TO RECEIVE PRINTED MATERIALS, YOU MAY SIGN AND DATE THE PROXY AND MAIL IT IN THE SELF-ADDRESSED ENVELOPE PROVIDED. NO POSTAGE IS REQUIRED IF MAILED WITHIN THE UNITED STATES.
If you are unable to attend the annual meeting, you may listen to a live webcast of the meeting, which will be accessible through our website, ir.kroger.com, at 11 a.m., eastern time.
| By | |
| May 12, 2016 | |
| Cincinnati, Ohio |
6
Proxy Statement
Cincinnati, Ohio, May 14, 201312, 2016
YourWe are providing this notice, proxy is solicitedstatement and annual report to the shareholders of The Kroger Co. (“Kroger”) in connection with the solicitation of proxies by the Board of Directors for use at the Annual Meeting of TheShareholders to be held on June 23, 2016, at 11:00 a.m. eastern time, at the School for Creative and Performing Arts, Corbett Theater, 108 W. Central Parkway, Cincinnati, Ohio 45202, and at any adjournments thereof.
Our principal executive offices are located at 1014 Vine Street, Cincinnati, Ohio 45202-1100. Our telephone number is 513-762-4000. This notice, proxy statement and annual report, and the accompanying proxy card were first furnished to shareholders on May 12, 2016.
Who can vote?
You can vote if as of the close of business on April 27, 2016, you were a shareholder of record of Kroger Co.,common shares.
Who is asking for my vote, and who pays for this proxy solicitation?
Your proxy is being solicited by Kroger’s Board of Directors. Kroger is paying the cost of solicitation. We have hired D.F. King & Co., Inc., 48 Wall Street, New York, New York, a proxy solicitation firm to assist us in soliciting proxies and we will be borne by Kroger. pay them a fee estimated not to exceed $15,000.
We also will reimburse banks, brokers, nominees, and other fiduciaries for postage and reasonable expenses incurred by them in forwarding the proxy material to their principals. Kroger has retained D.F. King & Co., Inc., 48 Wall Street, New York, New York, to assist in the solicitationbeneficial owners of proxies and will pay that firm a fee estimated at present not to exceed $15,000. our common shares.
Proxies may be solicited personally, by telephone, electronically via the Internet, or by mail.
David B. Dillon, John T. LaMacchia, and Bobby S. Shackouls, all of whomWho are Kroger directors, have been namedthe members of the Proxy Committee.Committee?
Robert D. Beyer, W. Rodney McMullen, and Ronald L. Sargent, all Kroger Directors, are the members of the Proxy Committee for our 2016 Annual Meeting.
How do I vote my proxy?
You can vote your proxy in one of the following ways:
| 1. | Via the internet,by visiting www.proxyvote.com. | |
| 2. | By telephone,by calling the number on your proxy card, voting instruction form, or notice. | |
| 3. | By mail,by marking, signing, dating and mailing your proxy card if you requested printed materials, or your voting instruction form. No postage is required if mailed in the United States. | |
| 4. | In person,by attending the meeting in Cincinnati. | |
What do I need to attend the meeting in person in Cincinnati?
If you plan to attend the meeting, you must bring either: (1) the notice of meeting that was separately mailed to you or (2) the top portion of your proxy card, either of which will be your admission ticket.
You must also bring valid photo identification, such as a driver’s license or passport.
Can I change or revoke my proxy?
The principal executive offices of The Kroger Co. are locatedcommon shares represented by each proxy will be voted in the manner you specified unless your proxy is revoked before it is exercised. You may change or revoke your proxy by providing written notice to Kroger’s Secretary at 1014 Vine Street, Cincinnati, Ohio 45202-1100. Our telephone number is 513-762-4000. This Proxy Statement45202-1100, in person at the meeting or by executing and Annual Report, and the accompanying proxy, were first furnished to shareholders on May 14, 2013.sending us a subsequent proxy.
How many shares are outstanding?
As of the close of business on April 30, 2013,27, 2016, the record date, our outstanding voting securities consisted of 520,063,320953,786,557 common shares,shares.
1
How many votes per share?
Each common share outstanding on the holders of whichrecord date will be entitled to one vote per share aton each of the annual meeting. The shares represented by11 director nominees and one vote on each proxy will be voted unless the proxy is revoked before it is exercised. Revocation may be in writing to Kroger’s Secretary, or in person at the meeting, or by appointment of a subsequent proxy.other proposal. Shareholders may not cumulate votes in the election of directors.
What voting instructions can I provide?
You may instruct the proxies to vote “For” or “Against” each proposal. Or you may instruct the proxies to “Abstain” from voting.
What happens if proxy cards or voting instruction forms are returned without instructions?
If you are a registered shareholder and you return your proxy card without instructions, the Proxy Committee will vote in accordance with the recommendations of the Board of Directors.
If you hold shares in street name and do not provide your broker with specific voting instructions on proposals 1, 2, 4, 5, 6 or 7, which are considered non-routine matters, your broker does not have the authority to vote on those proposals. This is generally referred to as a “broker non-vote.” Proposal 3, ratification of auditors, is considered a routine matter and, therefore, your broker may vote your shares according to your broker’s discretion.
The vote required, including the effect of broker non-votes and abstentions onfor each of the matters presented for shareholder vote, is as follows:set forth below.
ItemWhat are the voting requirements for each of the proposals?
Proposal No. 1, Election of Directors – An affirmative vote of the majority of the total number of votes cast “for”“For” or “against”“Against” a director nominee is required for the election of a director in an uncontested election. Accordingly, brokerA majority of votes cast means that the number of shares voted “For” a director nominee must exceed the number of votes “Against” such director. Broker non-votes and abstentions will have no effect on this proposal.
ItemProposal No. 2, Advisory Vote to Approve Executive Compensation – ApprovalAdvisory approval by shareholders of executive compensation requires the affirmative vote of the majority of shares participating in the voting. Accordingly, brokerBroker non-votes and abstentions will have no effect on this proposal.
ItemProposal No. 3, SelectionRatification of Independent Auditors – Ratification by shareholders of the selection of independent public accountants requires the affirmative vote of the majority of shares participating in the voting. Accordingly, abstentionsAbstentions will have no effect on this proposal.
ItemProposal Nos. 4, 5, 6 and 7, Shareholder Proposals– The affirmative vote of athe majority of shares participating in the voting on a shareholder proposal is required for its adoption.such proposal to pass. Accordingly, broker non-votes and abstentions will have no effect on these proposals. Proxies will be voted AGAINSTagainst these proposals unless the Proxy Committee is otherwise instructed on a proxy properly executed and returned. Broker non-votes and abstentions will have no effect on these proposals.
How does the Board of Directors recommend that I vote?
| Proposal | Board Recommendation | |
| Item No. 1, Election of Directors | FOR | |
| See pages 4-7 | ||
| Item No. 2, Advisory Vote to Approve Executive Compensation | FOR | |
| See page 49 | ||
| Item No. 3, Ratification of Independent Auditors | FOR | |
| See pages 54-55 | ||
| Item Nos. 4, 5, 6 and 7, Shareholder Proposals | AGAINST | |
| See pages 57-63 |
2
Kroger’s Corporate Governance Practices
Kroger is committed to strong corporate governance. We believe that strong governance builds trust and promotes the long-term interests of our shareholders. Highlights of our corporate governance practices include the following:
| ✓ | All director nominees are independent, except for the CEO. | ||
| ✓ | All five Board Committees are fully independent. | ||
| ✓ | Annual election of all directors. | ||
| ✓ | All directors are elected with a simple majority standard for all uncontested director elections, with cumulative voting available in contested director elections. | ||
| ✓ | Commitment to Board refreshment and diversity. | ||
| ✓ | Regular engagement with shareholders to understand their perspectives and concerns. | ||
| ✓ | Regular executive sessions of the independent directors, at board and committee level. | ||
| ✓ | Strong independent lead director with clearly defined roles and responsibilities. | ||
| ✓ | Annual Board and Committee self-assessments. | ||
| ✓ | Annual evaluation of the Chairman and CEO by the independent directors. | ||
| ✓ | High degree of Board interaction with management to ensure successful oversight and succession planning. | ||
| ✓ | Stock ownership guidelines align executive and director interests with those of shareholders. | ||
| ✓ | Prohibition on all hedging, short sales and pledging. | ||
| ✓ | No poison pill (shareholder rights plan). | ||
| ✓ | Shareholders have the right to call a special meeting. | ||
| ✓ | Robust code of ethics. | ||
| ✓ | Strong Board oversight of enterprise risk. |
3
Proposals to Shareholders
Item 1. Election of Directors(Item No. 1)
You are being asked to elect 11 director nominees for a one-year term. The Board of Directors as now authorized,recommends that you vote FOR the election of all director nominees.
As of the date of this proxy statement, the Kroger Board of Directors consists of fourteentwelve members. David B. Lewis will be retiring from the Board of Directors immediately prior to the 2016 annual meeting, in accordance with Kroger’s director retirement policy, and will not be standing for re-election. The number of directors will be reduced to eleven by the Board. All members are to benominees, if elected at the 2016 annual meeting, towill serve until the annual meeting in 2014,2017, or until their successors have been elected by the shareholders or by the Board of Directors pursuant to Kroger’s Regulations, and qualified.
Kroger’s Articles of Incorporation provide that the vote required for election of a director nominee by the shareholders, except in a contested election or when cumulative voting is in effect, will beis the affirmative vote of a majority of the votes cast for or against the election of a nominee.
The experience, qualifications, attributes, and skills that led the Corporate Governance Committee and the Board to conclude that the following individuals should serve as directors are set forth opposite each individual’s name. The committee memberships stated below are those in effect as of the date of this proxy statement. It is intended that, except to the extent that authority is withheld, proxies will be votedExcept as noted, each nominee has been employed by his or her present employer (or a subsidiary thereof) in an executive capacity for the electionat least five years.
Nominees for Directors for Terms of the following persons:Office Continuing until 2017
| Name | Professional Occupation (1) | Age | Director Since | |||
Nominees for Director for Terms of Office | ||||||
Reuben V. Anderson | Mr. Anderson is a Senior Partner in the Jackson, Mississippi office of Phelps Dunbar, a regional law firm based in New Orleans. Prior to joining this law firm, he was a justice of the Supreme Court of Mississippi. Mr. Anderson is a director of AT&T Inc., and during the past five years was a director of Trustmark Corporation. He is a member of the Corporate Governance and Public Responsibilities Committees. Mr. Anderson has extensive litigation experience, and he served as the first African-American Justice on the Mississippi Supreme Court. His knowledge and judgment gained through years of legal practice are of great value to the Board. In addition, as former Chairman of the Board of Trustees of Tougaloo College and a resident of Mississippi, he brings to the Board his insights into the African-American community and the southern region of the United States. Mr. Anderson has served on numerous board committees, including audit, public policy, finance, executive, and nominating committees. | 70 | 1991 |
Nora A. Aufreiter Age 56 Director Since 2014 Committees: | Ms. Aufreiter is a Director Emeritus of McKinsey & Company, a global management consulting firm. She retired in June 2014 after more than 27 years with McKinsey, most recently as a director and senior partner. During that time, she worked extensively in the U.S., Canada, and internationally with major retailers, financial institutions and other consumer-facing companies. Before joining McKinsey, Ms. Aufreiter spent three years in financial services working in corporate finance and investment banking. She is a member of the Board of Directors of The Bank of Nova Scotia, The Neiman Marcus Group, and Cadillac Fairview, one of North America’s largest owners, operators and developers of commercial real estate. Ms. Aufreiter also serves on the boards of St. Michael’s Hospital and the Canadian Opera Company, and is a member of the Dean’s Advisory Board for the Ivey Business School in Ontario, Canada. Ms. Aufreiter has over 30 years of broad business experience in a variety of retail sectors. Her vast experience in leading McKinsey’s North American Retail Practice, North American Branding service line and the Consumer Digital and Omnichannel service line is of particular value to the Board. She also brings to the Board valuable insight on commercial real estate. |
84
| Name | Professional Occupation (1) | Age | Director Since | |||
Robert D. Beyer | Mr. Beyer is Chairman of Chaparal Investments LLC, a private investment firm and holding company that he founded in 2009. From 2005 to 2009, Mr. Beyer served as Chief Executive Officer of The TCW Group, Inc., a global investment management firm. From 2000 to 2005, he served as President and Chief Investment Officer of Trust Company of the West, the principal operating subsidiary of TCW. Mr. Beyer is a member of the Board of Directors of The Allstate Corporation. He is vice chair of the Corporate Governance Committee and a member of the Financial Policy Committee. Mr. Beyer brings to Kroger his experience as CEO of TCW, a global investment management firm serving many of the largest institutional investors in the U.S. He has exceptional insight into Kroger’s financial strategy, and his experience qualifies him to serve as a member of the Financial Policy Committee. While at TCW, he also conceived and developed the firm’s risk management infrastructure, an experience that is useful to the Kroger Board in performing its risk management oversight functions. His abilities and service as a director were recognized by his peers, who selected Mr. Beyer as an Outstanding Director in 2008 as part of the Outstanding Directors Program of theFinancial Times. | 53 | 1999 | |||
David B. Dillon | Mr. Dillon was elected Chairman of the Board of Kroger in 2004, Chief Executive Officer in 2003, and President and Chief Operating Officer in 2000. He served as President in 1999, and as President and Chief Operating Officer from 1995 to 1999. Mr. Dillon was elected Executive Vice President of Kroger in 1990 and President of Dillon Companies, Inc. in 1986. He is a director of DIRECTV, and during the past five years was a director of Convergys Corporation. Mr. Dillon brings to Kroger his extensive knowledge of the supermarket business, having over 30 years of experience with Kroger and Dillon Companies. In addition to his depth of knowledge of Kroger and the fiercely competitive industry in which Kroger operates, he has gained a wealth of experience by serving on audit, compensation, finance, and governance committees of other boards. | 62 | 1995 |
Robert D. Beyer, Age 56 Director Since 1999 Committees: | Mr. Beyer is Chairman of Chaparal Investments LLC, a private investment firm and holding company that he founded in 2009. From 2005 to 2009, Mr. Beyer served as Chief Executive Officer of The TCW Group, Inc., a global investment management firm. From 2000 to 2005, he served as President and Chief Investment Officer of Trust Company of the West, the principal operating subsidiary of TCW. Mr. Beyer is a member of the Board of Directors of The Allstate Corporation and Leucadia National Corporation. Mr. Beyer has decided not to seek re-election to Allstate’s board of directors at its annual meeting in May 2016, after ten years of service on its board. Mr. Beyer brings to Kroger his experience as CEO of TCW, a global investment management firm serving many of the largest institutional investors in the U.S. He has exceptional insight into Kroger’s financial strategy, and his experience qualifies him to serve as a member of the Board. While at TCW, he also conceived and developed the firm’s risk management infrastructure, an experience that is useful to Kroger’s Board in performing its risk management oversight functions. His abilities and service as a director were recognized by his peers, who selected Mr. Beyer as an Outstanding Director in 2008 as part of the Outstanding Directors Program of the Financial Times. His strong insights into corporate governance form the foundation of his leadership role as Lead Director on the Board. | |
Anne Gates Age 56 Director Since 2015 Committees: | Ms. Gates is President of MGA Entertainment, Inc., a privately-held developer, manufacturer and marketer of toy and entertainment products for children, a position she has held since 2014. Ms. Gates held roles of increasing responsibility with The Walt Disney Company from 1992-2012. Her roles included executive vice president, managing director and chief financial officer for Disney Consumer Products and senior vice president of operations, planning and analysis. Prior to joining Disney, Ms. Gates worked for PepsiCo and Bear Stearns. Ms. Gates has over 15 years of experience in the retail and consumer products industry. She brings to Kroger financial expertise gained while serving as President of MGA and CFO of a division of the Walt Disney Company. Ms. Gates has a broad business background in marketing, strategy and business development, including international business. Her expertise in toy and entertainment products is of particular value to the Board. Ms. Gates has been designated an Audit Committee financial expert. | |
Susan J. Kropf Age 67 Director Since 2007 Committees: | Ms. Kropf was President and Chief Operating Officer of Avon Products Inc., a manufacturer and marketer of beauty care products, from 2001 until her retirement in January 2007. She joined Avon in 1970 and, during her tenure at Avon, Ms. Kropf also served as Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer, Avon North America and Global Business Operations from 1998 to 2000 and President, Avon U.S. from 1997 to 1998. Ms. Kropf was a member of Avon’s Board of Directors from 1998 to 2006. She currently is a director of Avon Products Inc., Coach, Inc., and Sherwin Williams Company. In the past five years she also served as a director of MeadWestvaco Corporation. Ms. Kropf has unique and valuable consumer insight, having led a major, publicly-traded retailer of beauty and related consumer products. She has extensive experience in manufacturing, marketing, supply chain operations, customer service, and product development, all of which assist her in her role as a member of Kroger’s Board. Ms. Kropf has a strong financial background, and has significant boardroom experience through her service on the boards of various public companies, including experience serving on compensation, audit, and corporate governance committees. She was inducted into the YWCA Academy of Women Achievers. |
95
| Name | Professional Occupation (1) | Age | Director Since | |||
Susan J. Kropf | Ms. Kropf was President and Chief Operating Officer of Avon Products Inc., a manufacturer and marketer of beauty care products, from 2001 until her retirement in January 2007. She joined Avon in 1970. Prior to her most recent assignment, Ms. Kropf had been Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer, Avon North America and Global Business Operations from 1998 to 2000. From 1997 to 1998 she was President, Avon U.S. Ms. Kropf was a member of Avon’s Board of Directors from 1998 to 2006. She currently is a member of the Board of Directors of Coach, Inc., MeadWestvaco Corporation, and Sherwin Williams Company. She is a member of the Audit and Financial Policy Committees. Ms. Kropf has gained a unique consumer insight, having led a major beauty care company. She has extensive experience in manufacturing, marketing, supply chain operations, customer service, and product development, all of which assist her in her role as a member of Kroger’s Board. Ms. Kropf has a strong financial background, and has served on compensation, audit, and corporate governance committees of other boards. She was inducted into the YWCA Academy of Women Achievers. | 64 | 2007 | |||
John T. LaMacchia | Mr. LaMacchia served as Chairman of the Board of Tellme Networks, Inc., a provider of voice application networks, from September 2001 to May 2007. From September 2001 through December 2004 he was also Chief Executive Officer of Tellme Networks. From May 1999 to May 2000 Mr. LaMacchia was Chief Executive Officer of CellNet Data Systems, Inc., a provider of wireless data communications. From October 1993 through February 1999, he was President and Chief Executive Officer of Cincinnati Bell Inc. He is a member of the Compensation and Corporate Governance Committees. Mr. LaMacchia brings to Kroger his tenure leading both large and small companies. He has developed expertise in compensation and governance issues through his experience on compensation and corporate governance committees of Kroger and other boards. | 71 | 1990 | |||
David B. Lewis | Mr. Lewis is a shareholder and director of Lewis & Munday, a Detroit based law firm with offices in Washington, D.C. and New York City. He is a director of H&R Block, Inc. and STERIS Corporation. He is a member of the Financial Policy Committee and vice chair of the Public Responsibilities Committee. In addition to his background as a practicing attorney and expertise in bond financing, Mr. Lewis brings to Kroger’s Board his financial expertise gained while earning his MBA in Finance as well as his service and leadership on Kroger’s audit committee and the board committees of other publicly traded companies. Mr. Lewis has served on the Board of Directors of Conrail, Inc., LG&E Energy Corp., M.A. Hanna, TRW, Inc., and Comerica, Inc. He is a former chairman of the National Association of Securities Professionals. | 68 | 2002 |
W. Rodney McMullen, Age 55 Director Since 2003 | Mr. McMullen was elected Chairman of the Board in January 2015 and Chief Executive Officer of Kroger in January 2014. Mr. McMullen served as Kroger’s President and Chief Operating Officer from August 2009 to December 2013. Prior to that role, Mr. McMullen was elected to various roles at Kroger including Vice Chairman in 2003, Executive Vice President in 1999 and Senior Vice President in 1997. Mr. McMullen is a director of Cincinnati Financial Corporation and VF Corporation. Mr. McMullen has broad experience in the supermarket business, having spent his career spanning over 37 years with Kroger. He has a strong financial background, having served as our CFO, and played a major role as architect of Kroger’s strategic plan. His service on the compensation, executive, and investment committees of Cincinnati Financial Corporation and the audit and nominating and governance committees of VF Corporation add depth to his extensive retail experience. | |
Jorge P. Montoya Age 69 Director Since 2007 Committees: | Mr. Montoya was President of The Procter & Gamble Company’s Global Snacks & Beverage division, and President of Procter & Gamble Latin America, from 1999 until his retirement in 2004. Prior to that, he was an Executive Vice President of Procter & Gamble, a provider of branded consumer packaged goods, from 1995 to 1999. Mr. Montoya is a director of The Gap, Inc. Mr. Montoya brings to Kroger’s Board over 30 years of leadership experience at a premier consumer products company. He has a deep knowledge of the Hispanic market, as well as consumer products and retail operations. Mr. Montoya has vast experience in marketing and general management, including international business. He was named among the 50 most important Hispanics in Business & Technology, inHispanic Engineer & Information Technology Magazine. | |
Clyde R. Moore Age 62 Director Since 1997 Committees: | Mr. Moore was the Chairman of First Service Networks, a national provider of facility and maintenance repair services, until his retirement in 2015. Prior to that he was Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of First Service Networks from 2000 to 2014. Mr. Moore has over 30 years of general management experience in public and private companies. He has sound experience as a corporate leader overseeing all aspects of a facilities management firm and numerous manufacturing companies. Mr. Moore’s expertise broadens the scope of the Board’s experience to provide oversight to Kroger’s facilities, digital and manufacturing businesses. | |
Susan M. Phillips Age 71 Director Since 2003 Committees: | Dr. Phillips is Professor Emeritus of Finance at The George Washington University School of Business. She joined The George Washington University School of Business as a Professor and Dean in 1998. Dr. Phillips retired from her position as Dean in 2010, and retired from her position as Professor the following year. She was a member of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System from December 1991 through June 1998. Before her Federal Reserve appointment, Dr. Phillips served as Vice President for Finance and University Services and Professor of Finance in The College of Business Administration at the University of Iowa from 1987 through 1991. She is a director of CBOE Holdings, Inc., State Farm Mutual Automobile Insurance Company, State Farm Companies Foundation, the Chicago Board Options Exchange, and Agnes Scott College. Dr. Phillips also was a director of the National Futures Association and State Farm Life Insurance Company until early 2016. Dr. Phillips brings to the Board strong financial acumen, along with a deep understanding of, and involvement with, the relationship between corporations and the government. Her experience in academia brings a unique and diverse viewpoint to the Board’s deliberations. Dr. Phillips has been designated an Audit Committee financial expert. |
106
| Name | Professional Occupation (1) | Age | Director Since | |||
W. Rodney McMullen | Mr. McMullen was elected President and Chief Operating Officer of Kroger in August 2009. Prior to that he was elected Vice Chairman in 2003, Executive Vice President in 1999, and Senior Vice President in 1997. Mr. McMullen is a director of Cincinnati Financial Corporation. Mr. McMullen has broad experience in the supermarket business, having spent his career spanning over 30 years with Kroger. He has a strong financial background and played a major role as architect of Kroger’s strategic plan. Mr. McMullen is actively involved in the day-to-day operations of Kroger. His service on the compensation, executive, and investment committees of Cincinnati Financial Corporation adds depth to his extensive retail experience. | 52 | 2003 | |||
Jorge P. Montoya | Mr. Montoya was President of The Procter & Gamble Company’s Global Snacks & Beverage division, and President of Procter & Gamble Latin America, from 1999 until his retirement in 2004. Prior to that, he was an Executive Vice President of Procter & Gamble, a provider of branded consumer packaged goods, from 1995 to 1999. Mr. Montoya is a director of The Gap, Inc. He is chair of the Public Responsibilities Committee and a member of the Compensation Committee. Mr. Montoya brings to Kroger’s Board over 30 years of leadership experience at a premier consumer products company. He has a deep knowledge of the Hispanic market, as well as consumer products and retail operations. Mr. Montoya has vast experience in marketing and general management, including international business. He was named among the 50 most important Hispanics in Business & Technology, inHispanic Engineer & Information Technology Magazine. | 66 | 2007 | |||
Clyde R. Moore | Mr. Moore is the Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of First Service Networks, a national provider of facility and maintenance repair services. He is a director of First Service Networks. Mr. Moore is chair of the Compensation Committee and a member of the Corporate Governance Committee. Mr. Moore has over 25 years of general management experience in public and private companies. He has sound experience as a corporate leader overseeing all aspects of a facilities management firm and a manufacturing concern. Mr. Moore’s expertise broadens the scope of the Board’s experience to provide oversight to Kroger’s facilities and manufacturing businesses. | 59 | 1997 |
11
| Name | Professional Occupation (1) | Age | Director Since | |||
Susan M. Phillips | Dr. Phillips is Professor Emeritus of Finance at The George Washington University School of Business. She joined that university as a Professor and Dean in 1998. She retired as Dean of the School of Business as of June 30, 2010, and as Professor the following year. She was a member of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System from December 1991 through June 1998. Before her Federal Reserve appointment, Dr. Phillips served as Vice President for Finance and University Services and Professor of Finance in The College of Business Administration at the University of Iowa from 1987 through 1991. She is a director of CBOE Holdings, Inc., State Farm Mutual Automobile Insurance Company, State Farm Life Insurance Company, State Farm Companies Foundation, National Futures Association, the Chicago Board Options Exchange, and Agnes Scott College. Dr. Phillips also was a trustee of the Financial Accounting Foundation until the end of 2010. She is a member of the Audit and Compensation Committees. Dr. Phillips brings to the Board strong financial acumen, along with a deep understanding of, and involvement with, the relationship between corporations and the government. Her experience in academia brings a unique and diverse viewpoint to the deliberations of the Board. Dr. Phillips has been designated an Audit Committee financial expert. | 68 | 2003 | |||
Steven R. Rogel | Mr. Rogel was elected Chairman of the Board of Weyerhaeuser Company, a forest products company, in 1999 and was President and Chief Executive Officer and a director thereof from December 1997 to January 1, 2008 when he relinquished the role of President. He relinquished the CEO role in April of 2008 and retired as Chairman as of April 2009. Before that time Mr. Rogel was Chief Executive Officer, President and a director of Willamette Industries, Inc. He served as Chief Operating Officer of Willamette Industries, Inc. until October 1995 and, before that time, as an executive and group vice president for more than five years. Mr. Rogel is a director of Union Pacific Corporation and a director and non-executive Chairman of the Board of EnergySolutions, Inc. He is a member of the Corporate Governance and Financial Policy Committees. Mr. Rogel has extensive experience in management of large corporations at all levels. He brings to the Board a unique perspective, having led a national supplier of paper products prior to his retirement. Mr. Rogel previously served as Kroger’s Lead Director, and has served on compensation, finance, audit, and governance committees of other corporations. | 70 | 1999 |
12
| Name | Professional Occupation (1) | Age | Director Since | |||
James A. Runde | Mr. Runde is a special advisor and a former Vice Chairman of Morgan Stanley, a financial services provider, where he has been employed since 1974. He was a member of the Board of Directors of Burlington Resources Inc. prior to its acquisition by ConocoPhillips in 2006. Mr. Runde serves as a Trustee Emeritus of Marquette University and the Pierpont Morgan Library. He is a member of the Compensation Committee and chair of the Financial Policy Committee. Mr. Runde brings to Kroger’s Board a strong financial background, having led a major financial services provider. He has served on the compensation committee of a major corporation. | 66 | 2006 | |||
Ronald L. Sargent | Mr. Sargent is Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Staples, Inc., a consumer products retailer, where he has been employed since 1989. Prior to joining Staples, Mr. Sargent spent 10 years with Kroger in various positions. In addition to serving as a director of Staples, Mr. Sargent is a director of Five Below, Inc. During the past five years, he was a director of Mattel, Inc. and The Home Depot, Inc. Mr. Sargent is chair of the Audit Committee and a member of the Public Responsibilities Committee. Mr. Sargent has over 30 years of retail experience, first with Kroger and then with increasing levels of responsibility and leadership at Staples, Inc. His efforts helped carve out a new market niche for the international retailer that he leads. His understanding of retail operations and consumer insights are of particular value to the Board. Mr. Sargent has been designated an Audit Committee financial expert. | 57 | 2006 | |||
Bobby S. Shackouls | Until the merger of Burlington Resources Inc. and ConocoPhillips, which became effective in 2006, Mr. Shackouls was Chairman of the Board of Burlington Resources Inc., a natural resources business, since July 1997 and its President and Chief Executive Officer since December 1995. He had been a director of that company since 1995 and President and Chief Executive Officer of Burlington Resources Oil and Gas Company (formerly known as Meridian Oil Inc.), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Burlington Resources, since 1994. Mr. Shackouls is a director of PNGS GP LLC, the general partner of PAA Natural Gas Storage, L.P., and Oasis Petroleum Inc. During the past five years, Mr. Shackouls was a director of ConocoPhillips. He has been appointed by Kroger’s Board to serve as Lead Director. Mr. Shackouls is chair of the Corporate Governance Committee and a member of the Audit Committee. Mr. Shackouls brings to the Board the critical thinking that comes with a chemical engineering background. His guidance of a major natural resources company, coupled with his corporate governance expertise, forms the foundation of his leadership role on Kroger’s Board. | 62 | 1999 |
James A. Runde Age 69 Director Since 2006 Committees: | Mr. Runde is a special advisor and a former Vice Chairman of Morgan Stanley, a financial services provider, where he was employed from 1974 until his retirement in 2015. He was a member of the Mr. Runde brings to Kroger’s Board a strong financial background, having led a major financial services provider. He has served on the compensation committee of a major corporation. | |
Ronald L. Sargent Age 60 Director Since 2006 Committees: | Mr. Sargent is Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Staples, Inc., a business products retailer, where he has been employed Mr. Sargent has over 35 years of retail experience, first with Kroger and then with increasing levels of responsibility and leadership at Staples, Inc. His efforts helped carve out a new market niche for the international retailer that he leads. His understanding of retail operations and consumer insights are of particular value to the Board. Mr. Sargent has been designated an Audit Committee financial expert. | |
Bobby S. Shackouls Age 65 Director Since 1999 Committees: | Mr. Shackouls was Chairman of the Board of Burlington Resources Inc., a natural resources business, from July 1997 until its merger with ConocoPhillips in 2006 and its President and Chief Executive Officer from December 1995 until 2006. Mr. Shackouls was also the President and Chief Executive Officer of Burlington Resources Oil and Gas Company (formerly known as Meridian Oil Inc.), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Burlington Resources, from 1994 to 1995. Mr. Shackouls is a director of Plains GP Holdings, L.P. and Oasis Petroleum Inc. During the past five years, Mr. Shackouls was a director of ConocoPhillips and PNGS GP LLC, the general partner of PAA Natural Gas Storage, L.P. Mr. Shackouls previously served as Kroger’s Lead Director. Mr. Shackouls brings to the Board the critical thinking that comes with a chemical engineering background, as well as his |
13The Board of Directors Recommends a VoteFor Each Director Nominee.
7
Information Concerning the Board of Directors
Committees of the Board Leadership Structure and Lead Independent Director
The Board is currently composed of Directorseleven independent non-employee directors and one management director, Mr. McMullen, the Chairman and CEO. Kroger has a number of standing committees including Audit, Compensation,balanced governance structure in which independent directors exercise meaningful and Corporate Governance Committees. All standing committees are composed exclusively of independent directors. All Board committees have charters that can be found on our corporate website at ir.kroger.com undervigorous oversight.
In addition, as provided in theGuidelines on Issues of Corporate Governance. During 2012, (the Audit Committee met five times,“Guidelines”), the Compensation Committee met four times,Board has designated one of the independent directors as Lead Director. The Lead Director works with the Chairman to share governance responsibilities, facilitate the development of Kroger’s strategy and grow shareholder value. The Lead Director serves a variety of roles, consistent with current best practices, including:
| ● | reviewing and approving Board meeting agendas, materials and schedules to confirm theappropriate topics are reviewed and sufficient time is allocated to each; |
| ● | serving as the principal liaison between the Chairman, management and the non-managementdirectors; |
| ● | presiding at the executive sessions of independent directors and at all other meetings of the Boardat which the Chairman is not present; |
| ● | calling meetings of independent directors at any time; and |
| ● | serving as the Board’s representative for any consultation and direct communication, following arequest, with major shareholders. The Lead Director carries out these responsibilities in numerous ways, including: |
| ● | facilitating communication and collegiality among the Board; |
| ● | soliciting direct feedback from non-executive directors; |
| ● | overseeing the succession process, including site visits and meeting with a wide range of corporateand division management associates; |
| ● | meeting with the CEO frequently to discuss strategy; |
| ● | serving as a sounding board and advisor to the CEO; and |
| ● | discussing Company matters with other directors between meetings. |
Unless otherwise determined by the Board, the chair of the Corporate Governance Committee met two times.is designated as the Lead Director. Robert Beyer, an independent director and the chair of the Corporate Governance Committee, memberships are shownis currently the Lead Director. Mr. Beyer is an effective Lead Director for Kroger due to, among other things, his independence, his deep strategic and operational understanding of Kroger obtained while serving as a Kroger director, his insight into corporate governance, his experience on pages 8the boards of other large publicly traded companies, and his commitment and engagement to carrying out the roles and responsibilities of the Lead Director.
With respect to the roles of Chairman and CEO, theGuidelines provide that the Board will determine when it is in the best interests of Kroger and our shareholders for the roles to be separated or combined, and the Board exercises its discretion as it deems appropriate in light of prevailing circumstances. Upon retirement of our former Chairman, David B. Dillon, on December 31, 2014, the Board determined that it is in the best interests of Kroger and our shareholders for one person to serve as the Chairman and CEO, as was the case from 2004 through 132013. The Board believes that this leadership structure improves the Board’s ability to focus on key policy and operational issues and helps the Company operate in the long-term interests of shareholders. Additionally, this structure provides an effective balance between strong Company leadership and appropriate safeguards and oversight by independent directors. The Board believes that the combination or separation of these positions should continue to be considered as part of the succession planning process, as was the case in 2003 and 2014 when the roles were separated.
8
The Board and each of its committees conduct an annual self-evaluation to determine whether the Board is functioning effectively at each level. As part of this Proxy Statement.annual self-evaluation, the Board assesses whether the current leadership structure continues to be appropriate for Kroger and its shareholders. The Audit Committee reviews financial reporting and accounting matters pursuantGuidelines provide the flexibility for the Board to its charter and selectsmodify our independent accountants. The Compensation Committee recommends for determinationleadership structure in the future as appropriate. We believe that Kroger, like many U.S. companies, has been well-served by the independent members of our Board the compensationthis flexible leadership structure.
Committees of the Chief Executive Officer, determinesBoard of Directors
To assist the compensationBoard in undertaking its responsibilities, and to allow deeper engagement in certain areas of Kroger’s other senior management,company oversight, the Board has established five standing committees: Audit, Compensation, Corporate Governance, Financial Policy and administers somePublic Responsibilities. All committees are composed exclusively of independent directors, as determined under the NYSE listing standards. The current charter of each Board committee is available on our incentive programs. Additional information on the Compensation Committee’s processes and procedures for consideration of executive compensation are addressed in the Compensation Discussion and Analysis below. website at ir.kroger.com under Corporate Governance – Committee Composition.
| Name of Committee, Number of Meetings, and Current Members | Committee Functions | |
Audit Committee Meetings in 2015:5 Members: | ●Oversees the Company’s financial reporting and accounting matters, including review of the Company’s financial statements and the audit thereof, the Company’s financial reporting and accounting process, and the Company’s systems of internal control over financial reporting ●Selects, evaluates and oversees the compensation and work of the independent registered public accounting firm and reviews its performance, qualifications, and independence ●Oversees and evaluates the Company’s internal audit function, including review of its audit plan, policies and procedures and significant findings ●Oversees risk assessment and risk management, including review of legal or regulatory matters that could have a significant effect on the Company ●Reviews and monitors the Company’s compliance programs, including the whistleblower program | |
Compensation Committee Meetings in 2015:5 Members: | ●Recommends for approval by the independent directors the compensation of the CEO, and determines the compensation of other senior management and directors ●Administers the Company’s executive compensation policies and programs, including determining grants of equity awards under the plans ●Has sole authority to retain and direct the committee’s compensation consultant ●Assists the full Board with senior management succession planning |
9
| Name of Committee, Number of Meetings, and Current Members | Committee Functions |
Corporate Governance Committee | ●Oversees the Company’s corporate governance policies and procedures ●Develops criteria for selecting and retaining directors and identifies and recommends qualified candidates to be director nominees ●Designates membership and chairs of Board committees ●Reviews the Board’s performance and director independence ●Reviews, along with the other independent directors, the performance of the CEO |
Financial Policy Committee | ●Reviews and recommends financial policies and practices ●Oversees management of the Company’s financial resources ●Reviews the Company’s annual financial plan, significant capital investments, plans for major acquisitions or sales, issuance of new common or preferred stock, dividend policy, creation of additional debt and other capital structure considerations including additional leverage or dilution in ownership ●Monitors the investment management of assets held in pension and profit sharing plans administered by the Company |
Public Responsibilities Committee | ●Reviews the Company’s policies and practices affecting its social and public responsibility as a corporate citizen, including: community relations, charitable giving, supplier diversity, sustainability, government relations, political action, consumer and media relations, food and pharmacy safety and the safety of customers and employees ●Reviews and examines the Company’s evaluation of and response to changing public expectations and public issues affecting the business |
Director Nominee Selection Process
The Corporate Governance Committee develops criteriais responsible for selecting and retaining members ofrecommending to the Board seeks out qualified candidatesa slate of nominees for the Board, and reviews the performanceelection at each annual meeting of the Board and, along with the other independent board members, the CEO.
shareholders. The Corporate Governance Committee will consider shareholderrecruits candidates for Board membership through its own efforts and through recommendations for nominees for membership on the Board of Directors. Recommendations relating to our annual meeting in June 2014, together with a description of the proposed nominee’s qualifications, backgroundfrom other directors and experience, must be submitted in writing to Paul W. Heldman, Secretary, and received at our executive offices not later than January 14, 2014. The shareholder also should indicate the number of shares beneficially owned by the shareholder. The Secretary will forward the information toshareholders. In addition, the Corporate Governance Committee for its consideration. The Committee will usehas retained an independent search firm to assist in identifying and recruiting director candidates who meet the same criteria in evaluating candidates submitted by shareholders as it uses in evaluating candidates identifiedestablished by the Corporate Governance Committee.
These criteria are:
| ● | Demonstrated ability in fields considered to be of value in the deliberation and long-term planningof the Board, including business management, public service, education, technology, law andgovernment; |
| ● | Highest standards of personal character and conduct; |
| ● | Willingness to fulfill the obligations of directors and to make the contribution of which he or she iscapable, including regular attendance and participation at Board and committee meetings, andpreparation for all meetings, including review of all meeting materials provided in advance of the meeting;and |
| ● | Ability to understand the perspectives of Kroger’s customers, taking into consideration the diversityof our customers, including regional and geographic differences. |
10
Racial,The Corporate Governance Committee considers racial, ethnic and gender diversity is anto be important elementelements in promoting full, open and balanced deliberations of issues presented to the Board, and is considered by theBoard. The Corporate Governance Committee.Committee considers director candidates that help the Board reflect the diversity of our shareholders, associates, customers and the communities in which we operate. Some consideration also is given to the geographic location of director candidates in order to provide a reasonable distribution of members from Kroger’s operating areas.
At least annually, the operating areas of the Company.
Corporate Governance Committee actively engages in Board succession planning. The Corporate Governance Committee typically recruitstakes into account the Board and committee evaluations regarding the specific backgrounds, skills, and experiences that would contribute to overall Board and committee effectiveness as well as the future needs of the Board and its committees in light of Kroger’s current and future business strategies and the skills and qualifications of directors who are expected to retire in the future.
Candidates Nominated by Shareholders
The Corporate Governance Committee will consider shareholder recommendations for nominees for membership on the Board of Directors. If shareholders wish to nominate a person or persons for election to the Board at our 2017 annual meeting, written notice must be submitted to Kroger’s Secretary, and received at our executive offices, in accordance with Kroger’s Regulations, not later than March 28, 2017. Such notice should include the name, age, business address and residence address of such person, the principal occupation or employment of such person, the number of Kroger common shares owned of record or beneficially by such person and any other information relating to the person that would be required to be included in a proxy statement relating to the election of directors. The Secretary will forward the information to the Corporate Governance Committee for its consideration. The Corporate Governance Committee will use the same criteria in evaluating candidates for Board membership through its own efforts and through suggestions from other directors and shareholders. The Committee on occasion has retained an outside search firm to assistsubmitted by shareholders as it uses in identifying and recruiting Boardevaluating candidates who meet the criteria establishedidentified by the Committee.Corporate Governance Committee, as described above.
Corporate Governance Guidelines
The Board of Directors has adopted theGuidelines on Issues of Corporate Governance. TheseTheGuidelines, which include copies of the current charters for each of the Audit, Compensation, and Corporate Governance Committees, and the otherfive standing committees of the Board, of Directors, are available on our corporate website at ir.kroger.com.ir.kroger.com under Corporate Governance – Highlights. Shareholders may obtain a copy of theGuidelines by making a written request to Kroger’s Secretary at our executive offices.
14Independence
Independence
The Board of Directors has determined that all of the non-employee directors with the exception of Messrs. Dillon and McMullen, have no material relationships with Kroger and, therefore, are independent for purposes of the New York Stock Exchange listing standards. The Board made its determination based on information furnished by all members regarding their relationships with Kroger.Kroger and its management, and other relevant information. After reviewing the information, the Board determined that all of the non-employee directors were independent because (i) because:
| ● | they all satisfied the criteria for independence set forth in Rule 303A.02 of the NYSE ListedCompany Manual, |
| ● | the value of any business transactions between Kroger and entities with which the directors areaffiliated falls below the thresholds identified by the NYSE listing standards, and |
| ● | none had any material relationships with Kroger except for those arising directly from theirperformance of services as a director for Kroger. |
In determining that Mr. Sargent is independent, the independence standards set forth in Rule 10A-3 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, (ii) they all satisfied the criteria for independence set forth in Rule 303A.02 of the New York Stock Exchange Listed Company Manual, and (iii) other than businessBoard considered transactions during fiscal 2015 between Kroger and entities with whichStaples, Inc. (where Mr. Sargent is Chairman and CEO) and determined that the directors are affiliated, the valueamount of which fallsbusiness fell below the thresholds identifiedset by the New York Stock ExchangeNYSE listing standards, none had any material relationships with us except for those arising directly from their performancestandards. The transactions involved the purchase of services asgoods by Kroger in the ordinary course of business totaling approximately $12 million and represented less than 0.06% of Staples’ annual consolidated gross revenue. Kroger periodically employs a director for Kroger.
Lead Director
Kroger’s Lead Director serves in a variety of roles, including reviewing and approving all Board meeting agendas, meeting materials and schedules to ensure that the appropriate topics are reviewed and that sufficient time is allocated to each; serving as a liaison between the chairman of the Board, management, and the non-management directors; presiding at the executive sessions of independent directors (held after each Board meeting) and at all other meetings of the Board at which the chairman is not present; calling an executive session of the independent directors at any time; and serving as the Board’s representative for any consultation and direct communication,bidding process or negotiations following a request, with major shareholders. Unless otherwise determined bybenchmarking of costs of products from various vendors for the Board,items purchased from Staples and awards the chairbusiness based on the results of the Corporate Governance Committee is designated as the Lead Director.that process.
11
Audit Committee Expertise
The Board of Directors has determined that Anne Gates, Susan M. Phillips and Ronald L. Sargent, independent directors who are members of the Audit Committee, are “audit committee financial experts” as defined by applicable SEC regulations and that all members of the Audit Committee are “financially literate” as that term is used in the NYSE listing standards.standards and are independent in accordance with Rule 10A-3 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
Code of Ethics
The Board of Directors has adoptedThe Kroger Co. Policy on Business Ethics, applicable to all officers, employees and members of the Board of Directors,directors, including Kroger’s principal executive, financial and accounting officers. ThePolicy is available on our corporate website at ir.kroger.com.ir.kroger.com under Corporate Governance – Highlights. Shareholders may also obtain a copy of thePolicy by making a written request to Kroger’s Secretary at our executive offices.
Communications with the Board
The Board has established two separate mechanisms for shareholders and interested parties to communicate with the Board. Any shareholder or interested party who has concerns regarding accounting, improper use of Kroger assets or ethical improprieties may report these concerns via the toll-free hotline (800-689-4609) or email address (helpline@kroger.com) established by the Board’s Audit Committee. The concerns are investigated by Kroger’s Vice President of Auditing and reported to the Audit Committee as deemed appropriate by the Vice President of Auditing.
Shareholders or interested parties also may communicate with the Board in writing directed to Kroger’s Secretary at our executive offices. The Secretary will consider the nature of the communication and determine whether to forward the communication to the chair of the Corporate Governance Committee. Communications relating to personnel issues or our ordinary business operations, or seeking to do business with us, will be forwarded to the business unit of Kroger that the Secretary deems appropriate. All other communications will be forwarded to the chair of the Corporate Governance Committee for further consideration. The chair of the Corporate Governance Committee will take such action as he or she deems appropriate, which may include referral to the full Corporate Governance Committee or the entire Board.
15Attendance
Attendance
The Board of Directors held sevenfive meetings in 2012.fiscal year 2015. During 2012,fiscal year 2015, all incumbent directors attended at least 75% of the aggregate number of meetings of the Board and committees on which that director served. Members of the Board are expected to use their best efforts to attend all annual meetings of shareholders. All fourteeneleven members ofthen serving on the Board attended last year’s annual meeting.
Independent Compensation Consultants
The Compensation Committee directly engages a compensation consultant from Mercer Human Resource Consulting to advise the Compensation Committee in the design of compensation forKroger’s executive officers.compensation. In 2012,2015, Kroger paid that consultant $135,573$390,767 for work performed for the Compensation Committee. Kroger, on management’s recommendation, retained the parent and affiliated companies of Mercer Human Resource Consulting to provide other services for Kroger in 2012,2015, for which Kroger paid $2,541,660.$2,339,577. These other services primarily related to insurance claims (for which Kroger was reimbursed by insurance carriers as claims were adjusted), insurance brokerage and bonding commissions provided by Marsh USA Inc., and pension consulting.plan compliance and actuary services provided by Mercer Inc. Kroger also made payments to affiliated companies for insurance premiums that were collected by the affiliated companies on behalf of insurance carriers, but these amounts are not included in the totals referenced above, as the amounts were paid over to insurance carriers for services provided by those carriers.
12
Although neither the Compensation Committee nor the Board expressly approved the other services, after taking into consideration the NYSE’s independence standards and the SEC rules, the Compensation Committee determined that the consultant is independent because (a) he was first engaged by the Committee before he became associated with Mercer; (b) he works exclusively for the Committee and his work has not for our management; (c) he does not benefit from the other work that Mercer’s parent and affiliated companies perform for Kroger; and (d) raised any conflict of interest because:
| ● | the consultant was first engaged by the Compensation Committee before he became associatedwith Mercer; |
| ● | the consultant works exclusively for the Compensation Committee and not for our management; |
| ● | the consultant does not benefit from the other work that Mercer’s parent and affiliated companiesperform for Kroger; and |
| ● | neither the consultant nor the consultant’s team perform any other services for Kroger. |
The Compensation Committee may engage an additional compensation consultant from time to time as it deems advisable.
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
No member of the Compensation Committee was an officer or employee of Kroger during fiscal 2015, and no member of the Compensation Committee is a former officer of Kroger or was a party to any disclosable related person transaction involving Kroger. During fiscal 2015, none of our executive officers served on the board of directors or on the compensation committee of any other services on behalfentity that has or had executive officers serving as a member of Kroger.Kroger’s Board of Directors or Compensation Committee of the Board.
Board Oversight of Enterprise Risk
While risk management is primarily the responsibility of Kroger’s management team, the Board of Directors is responsible for thestrategic planning and overall supervision of our risk management activities. The Board’s oversight of the material risks faced by Kroger occurs at both the full Board level and at the committee level.
The Board’s Audit Committee has oversight responsibility not only for financial reporting of Kroger’s major financial exposures and the steps management has taken to monitor and control those exposures, but also for the effectiveness of management’s processes that monitor and manage key business risks facing Kroger, as well as the major areas of risk exposure and management’s efforts to monitor and control that exposure. The Audit Committee also discusses with management its policies with respect to risk assessment and risk management.
Management, including Kroger’s Chief Ethics and Compliance Officer, provides regular updates throughout the year to the respective committees regarding the management of the risks they oversee, and each of these committees reports on risk to the full Board at each regular meeting of the Board.
In addition to the reports from the committees, the Board receives presentations throughout the year from various department and business unit leaders that include discussion of significant risks as necessary. At each Board meeting, the Chairman and CEO addresses matters of particular importance or concern, including any significant areas of risk that require Board attention. Additionally, through dedicated sessions focusing entirely on corporate strategy, the full Board reviews in detail Kroger’s short- and long-term strategies, including consideration of significant risks facing Kroger and their potential impact. The independent directors, in executive sessions led by the Lead Director, address matters of particular concern, including significant areas of risk, that warrant further discussion or consideration outside the presence of Kroger employees. At the committee level, reports are given by management subject matter experts to each committee on risks within the scope of their charters.
The Audit Committee has oversight responsibility not only for financial reporting of Kroger’s major financial exposures and the steps management has taken to monitor and control those exposures, but also for the effectiveness of management’s processes that monitor and manage key business risks facing Kroger, as well as the major areas of risk exposure and management’s efforts to monitor and control that exposure. The Audit Committee also discusses with management its policies with respect to risk assessment and risk management.
Management, including our Chief Ethics and Compliance Officer, provides regular updates throughout the year to the respective Board committees regarding management of the risks they oversee, and each of these committees reports on risk to the full Board at each regular meeting of the Board.
We believe that our approach to risk oversight, as described above, optimizes our ability to assess interrelationshipsinter-relationships among the various risks, make informed cost-benefit decisions, and approach emerging risks in a proactive manner for Kroger. We also believe that our risk structure complements our current Board leadership structure, as it allows our independent directors, through the five fully independent Board committees, and
16
in executive sessions of independent directors led by an independentthe Lead Director, to exercise effective oversight of the actions of management, led by Mr. DillonMcMullen as Chairman of the Board and CEO, in identifying risks and implementing effective risk management policies and controls.
Board Leadership Structure13
Compensation Discussion and Analysis
Our Board is composed of twelve independent directorsExecutive Summary
Named Executive Officers
This Compensation Discussion and two management directors, Mr. Dillon, the Chairman of the BoardAnalysis provides a discussion and Chief Executive Officer, and Mr. McMullen, President and Chief Operating Officer. In addition, as provided in ourGuidelines on Issues of Corporate Governance, the Board has designated one of the independent directors as Lead Director. The Board has established five standing committees — audit, compensation, corporate governance, financial policy, and public responsibilities. Each of the Board committees is composed solely of independent directors, each with a different independent director serving as committee chair. We believe that the mix of experienced independent and management directors that make up our Board, along with the independent roleanalysis of our Lead Directorcompensation program for our named executive officers (“NEOs”). For the 2015 fiscal year ended January 30, 2016, the NEOs were:
| Name | Title | |
| W. Rodney McMullen | Chairman and Chief Executive Officer | |
| J. Michael Schlotman | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | |
| Michael J. Donnelly | Executive Vice President of Merchandising | |
| Christopher T. Hjelm | Executive Vice President and Chief Information Officer | |
| Frederick J. Morganthall II | Executive Vice President of Retail Operations |
Messrs. Schlotman, Donnelly, Hjelm and Morganthall were each promoted to the position of Executive Vice President effective September 1, 2015.
Executive Compensation in Context: Our Growth Plan, Financial Strategy and Fiscal Year 2015 Results
Kroger’s growth plan includes four key performance indicators: positive identical supermarket sales without fuel (“ID Sales”) growth, slightly expanding non-fuel first in, first out (“FIFO”) operating margin, growing return on invested capital (“ROIC”), and annual market share growth. In 2015, we met or exceeded our independent Board committees, benefitsgoals for each of these performance indicators:
| ● | ID Sales.ID Sales increased 5.0% from 2014. Through 2015, we have achieved 49 consecutivequarters of positive ID Sales growth. |
| ● | ROIC.Our ROIC for 2015 was 13.93%, compared to 13.76% for 2014, excluding Roundy’s (acquiredin December 2015). |
| ● | Non-Fuel FIFO Operating Margin.We exceeded our commitment to slightly expand FIFO operatingmargin, excluding fuel and Roundy’s on a rolling four quarters basis. |
| ● | Market Share.Our market share grew for an eleventh consecutive year. |
| Other highlights of the year include: | |
| ● | Net earnings per diluted share were $2.06. |
| ● | We exceeded our long-term, net earnings per diluted share growth rate of 8-11% in 2015. |
| ● | We reduced operating costs excluding fuel as a percentage of sales for the eleventh consecutive year. |
| Also during 2015, we met all of our objectives with regard to our financial strategy: | |
| ● | Maintain our current investment grade debt rating.Our net total debt to adjusted EBITDA ratiodecreased, even while investing approximately $870 million in our merger with Roundy’s late inthe year. |
| ● | Repurchase shares. In 2015, we repurchased $703 million in Kroger common shares. |
| ● | Fund the dividend. We returned $385 million to shareholders through our dividend in 2015, and weincreased our dividend for the ninth consecutive year since we reinstated our dividend in 2006. |
| ● | Increase capital investments. Our 2015 cash flow generation was strong, allowing us to make$3.3 billion in capital investments during the year, excluding mergers, acquisitions and purchases ofleased facilities. |
The compensation of our NEOs in 2015 reflects Kroger’s short-term and long-term goals and outcomes. Total compensation for the year is an indicator of how well Kroger and its shareholders.
The Board believes that it is beneficialperformed compared to Kroger and its shareholdersour business plan, reflecting how our compensation program responds to designate one of the directors as a Lead Director. The Lead Director serves a variety of roles, including reviewing and approving Board agendas, meeting materials and schedules to confirm the appropriate topics are reviewed and sufficient time is allocated to each; serving as liaison between the Chairman of the Board, management,business challenges and the non-management directors; presiding at the executive sessionsmarketplace.
14
Summary of independent directorsKey Compensation Practices
| What we do: | What we do not do: |
✓Align pay and performance ✓Significant share ownership guidelines of 5x salary for our CEO ✓Multiple performance metrics under our short- and long-term performance-based plans discourage excessive risk taking ✓Balance between short-term and long-term compensation discourages short-term risk taking at the expense of long-term results ✓Engagement of an independent compensation consultant ✓Robust clawback policy ✓Ban on hedging and pledging of Kroger securities ✓Limited perquisites | ×No employment contracts with executives ×No special severance or change of control programs applicable only to executive officers ×No gross-up payments were made to executives under Kroger plans ×No re-pricing or backdating of options ×No guaranteed salary increases or bonuses ×No payment of dividends or dividend equivalents until performance units are earned ×No single-trigger cash severance benefits upon a change in control |
Summary of Fixed and at all other meetingsAt-Risk Pay Elements
The fixed and at-risk pay elements of the Board of Directors at which the Chairman of the Board is not present; calling an executive session of independent directors at any time and serving as the Board’s representative for any consultation and direct communication, following a request, with major shareholders. Bobby Shackouls, an independent director and the chair of the Corporate Governance Committee, is currently our Lead Director. Mr. Shackouls is an effective Lead Director for Kroger due to, among other things, his independence, his deep strategic and operational understanding of Kroger obtained while serving as a Kroger director, his corporate governance knowledge acquired during his tenure as a member of our Corporate Governance Committee, his previous experience on other boards, and his prior experience as a CEO of a Fortune 500 company.
With respect to the roles of Chairman and CEO, theGuidelines provide that the Board believes that it isNEO compensation are reflected in the best interests of Krogerfollowing table and its shareholders for one person to serve as Chairman and CEO.charts. The Board recognizes that there may be circumstances in which it isamounts used in the best interests of Kroger and its shareholders forcharts are based on the roles to be separated, and the Board exercises its discretion as it deems appropriate in light of prevailing circumstances. The Board believes that the combination or separation of these positions should continue to be considered as part of the succession planning process, as was the case in 2003 when the roles were separated. Since 2004, the roles have been combined.
Our Board and each of its committees conduct an annual evaluation to determine whether they are functioning effectively. As part of this annual self-evaluation, the Board assesses whether the current leadership structure continues to be appropriate for Kroger and its shareholders. OurGuidelines provide the flexibility for our Board to modify our leadership structureamounts reported in the future as appropriate. We believe that Kroger, like many U.S. companies, has been well-served by this flexible leadership structure.Summary Compensation Table for 2015, excluding the Change in Pension Value and Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Earnings column.
| Fixed | At-Risk | ||||
| ‹—————————— Annual ————— | ———————› | ‹—————— Long-Term ——————› | |||
| Pay | Base Salary | All Other | Annual Cash | Long-Term | Restricted Stock |
| Element | Compensation | Bonus | Cash Bonus and | and Stock Options | |
| Performance Units | (time-based | ||||
| (the “Long-Term | equity awards) | ||||
| Incentive Plan”) | |||||
Description | ●Fixed cash compensation ●Reviewed annually ●No automatic or guaranteed increases | ●Insurance premiums paid by the Company ●Dividends paid on unvested restricted stock ●Matching and automatic contributions to defined contribution benefit plans | ●Variable cash compensation ●Payout depends on actual performance against annually established goals | ●Variable compensation payable as long-term cash bonus and performance units ●3-year performance period ●Payout depends on actual performance against established goals | ●Stock options vest over 5 years ●Exercise price of stock options is closing price on day of grant ●Restricted stock vests over 3 or 5 years |
1715
| Fixed | At-Risk | ||||
| ‹———————————— Annual ———— | ———————› | ‹—————— Long-Term ——————› | |||
Purpose | ●Provide a base level of cash compensation ●Recognize individual performance, scope of responsibility and experience | ●Provide benefits competitive with peers | ●Metrics and targets align with annual business goals ●Rewards and incentivizes approximately 13,000 Kroger employees, including NEOs, for annual performance on key financial and operational measures | ●Metrics and targets align with long-term business strategy ●Rewards and incentivizes approximately 160 key employees, including the NEOs, for long-term performance on key financial and operational measures ●Drives sustainable performance that ties to long-term value creation for shareholders | ●Retain executive talent ●Align the interests of executives with long-term shareholder value ●Provide direct alignment to stock price appreciation |
CEO
87% of CEO pay is At Risk | Average of Other NEOs 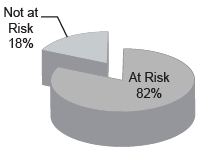 82% of Other NEO pay is At Risk | |
CEO
68% of CEO pay is Long-Term | Average of Other NEOs 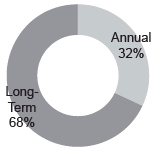 68% of Other NEO pay is Long-Term |
16
60% of CEO pay is Equity | Average of Other NEOs
55% of Other NEO pay is Equity |
ExecutiveThe following discussion and analysis addresses the compensation of the NEOs and the factors considered by the Compensation – OverviewCommittee in setting compensation for the NEOs and, in the case of the CEO’s compensation, making recommendations to the independent directors. Additional detail is provided in the compensation tables and the accompanying narrative disclosures that follow this discussion and analysis.
Our Compensation Philosophy and Objectives
As one of the largest retailers in the world, our executive compensation philosophy remainsis to attract and retain the best management talent and motivatingto motivate these employees to achieve our business and financial goals. Kroger’s incentive plans are designed to reward the actions that lead to long-term value creation. The Compensation Committee believes that there is a strong link between our business strategy, the performance metrics in our short-term and long-term incentive programs, and the business results that drive shareholder value.
We believe thatour strategy creates value for shareholders in a manner consistent with our focus on our core values: honesty, integrity, respect, inclusion, diversity and safety.
To achieve our objectives, ourthe Compensation Committee seeks to ensure that compensation is competitive and that there is a direct link between pay and performance. To do so, it is guided by the following principles:
The compensation of our senior executives in fiscal year 2012 once again reflected these principles. Total compensation for the year reflects how well Kroger performed compared to our business plan, reflecting how our compensation program responds to business challenges and the marketplace. We have continued to deliver sales growth and positive earnings results.
The Committee believes our management produced excellent results in 2012, measured against increasingly aggressive business plan objectives for sales, earnings, and our strategic plan. The compensation paid to our named executive officers reflected this fact as the annual performance-based cash bonus paid out at 85.881% of bonus potentials. The strong link between pay and performance is illustrated by a comparison of the 2011 annual cash bonus, with a 138.666% payout. In 2011, we exceeded our business plan goals for identical sales and EBITDA. In 2012, although our results were very strong, we did not achieve all of our business plan objectives.
In keeping with our overall compensation philosophy, we endeavor to ensure that our compensation practices conform to best practices. In particular, over the past several years we have:
| ● | A significant portion of pay should be performance-based, with the percentage of total pay tied to performance increasing proportionally with an executive’s level of responsibility. |
| ● | Compensation should include incentive-based pay to drive performance, providing superior pay for superior performance, including both a short- and long-term focus. |
| ● | Compensation policies should include an opportunity for, and a requirement of, equity ownership to align the interests of executives and shareholders. |
| ● | Components of compensation should be tied to an evaluation of business and individual performance measured against metrics that directly drive our business strategy. The Compensation Committee has three related objectives regarding compensation: |
| ● | First, the Compensation Committee believes that compensation must be designed to attract and retain those best suited to fulfill the challenging roles that officers play at Kroger. |
| ● | Second, a majority of compensation should help align the interests of our officers with the interests of our shareholders. |
| ● | Third, compensation should create strong incentives for the officers to achieve the annual business plan targets established by the Board, and to achieve Kroger’s long-term strategic objectives. |
1817
In addition, beginning in 2010, fifty percent of the time-based equity awards that otherwise would have been granted to the named executive officers as restricted stock have been replaced with performance units that are earned only to the extent that performance objectives are achieved. Equity compensation awards continue to play an important role in rewarding named executive officers for the achievement of long-term business objectives and providing incentives for the creation of shareholder value.
The Compensation Committee of the Board has the primary responsibility for establishing the compensation of Kroger’s executive officers, including the named executive officers, with the exception of the Chief Executive Officer. The Committee’s role regarding the CEO’s compensation is to make recommendations to the independent members of the Board; those independent Board members establish the CEO’s compensation.
The following discussion and analysis addresses the compensation of the named executive officers, and the factors considered by the Committee in setting compensation for the named executive officers and making recommendations to the independent Board members in the case of the CEO’s compensation. Additional detail is provided in the compensation tables and the accompanying narrative disclosures that follow this discussion and analysis.
Executive Compensation – Objectives
The Committee has several related objectives regarding compensation. First, the Committee believes that compensation must be designed to attract and retain those best suited to fulfill the challenging roles that executive officers play at Kroger. Second, some elements of compensation should help align the interests of the officers with your interests as shareholders. Third, compensation should create strong incentives for the officers (a) to achieve the annual business plan targets established by the Board, and (b) to achieve Kroger’s long-term strategic objectives. In developing compensation programs and amounts to meet these objectives, the Committee exercises judgment to ensure that executive officer compensation is appropriate and competitive in light of Kroger’s performance and the needs of the business.
To meet these objectives, the Committee has taken a number of steps over the last several years, including the following:
19
Results of 2012 Advisory Vote to Approve Executive Compensation
At the 2012 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, we held our second annual advisory vote on executive compensation. Approximately 96% of the votes cast were in favor of the advisory proposal in 2012. The Committee considered this overwhelmingly favorable outcome and believes it conveys our shareholders’ support of the Committee’s decisions and the existing executive compensation programs. As a result, the Committee made no material changes in the structure of our compensation programs or pay for performance philosophy. At the 2013 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, in keeping with our shareholders’ request for an annual advisory vote, we will again hold a vote to approve executive compensation (see page 46). The Committee will continue to consider the results from this year’s and future advisory votes on executive compensation.
Establishing Executive Compensation
The independent members of the Board have the exclusive authority to determine the amount of the CEO’s salary; the bonus potential for the CEO; the nature and amount of any equity awards made to the CEO; and any other compensation questions related to the CEO. In setting the annual bonus potential for the CEO, the independent directors determine the dollar amount that will be multiplied by the percentage payout under the annual bonus plan generally applicable to all corporate management, including the named executive officers. The independent directors retain discretion to reduce the percentage payout the CEO would otherwise receive. The independent directors thus make a separate determination annually concerning both the CEO’s bonus potential and the percentage of bonus paid.
The Committee performs the same function and exercises the same authority as to the other named executive officers. The Committee’s annual review of compensation for the named executive officers includes the following:
In considering each of the factors above, the Committee does not make use of a formula, but rather subjectively reviews each in making its compensation determination.
The Committee’s Compensation Consultants and Benchmarking
As referenced earlier in this proxy statement, the Committee directly engages a compensation consultant from Mercer Human Resource Consulting to advise the Committee in the design of compensation for executive officers.
20
The Mercer consultant conducts an annual competitive assessment of executive positions at Kroger for the Committee. The assessment is one of several bases, as described above, on which the Committee determines compensation. The consultant assesses:
This peer group is the same group as was used in 2011. The make-up of the compensation peer group is reviewed annually and modified as circumstances warrant. Industry consolidation and other competitive forces will change the peer group used over time. The consultant also provides the Committee data from companies in “general industry,” a representation of major publicly-traded companies. These data are reference points, particularly for senior staff positions where competition for talent extends beyond the retail sector.
In 2009, the Committee directly engaged an additional compensation consultant to conduct a review of Kroger’s executive compensation. This consultant, from Frederic W. Cook & Co., Inc., examined the compensation philosophy, peer group composition, annual cash bonus, and long-term incentive compensation including equity awards. The consultant concluded that Kroger’s executive compensation program met the Committee’s objectives, and that it provides a strong linkage between pay and performance. The Committee expects to engage an additional compensation consultant from time to time as it deems advisable.
Considering the size of Kroger in relation to other peer group companies, the Committee believes that salaries paid to our executive officers should be at or above the median paid by competitors for comparable positions. The committee also aims to provide an annual bonus potential to our executive officers that, if the increasingly more challenging annual business plan objectives are achieved, would cause total cash compensation to be meaningfully above the median.
Components of Executive Compensation at Kroger
Compensation for our named executive officersNEOs is comprised of the following:
| ●Annual Compensation: | |
| ➢ | Salary |
| ➢ | Performance-Based Annual Cash Bonus |
| ●Long-Term Compensation: | |
| ➢ | Performance-Based Long-Term Incentive Plan (consisting of a long-term cash bonus andperformance units) |
| ➢ | Non-qualified stock options |
| ➢ | Restricted stock |
●Retirement and other benefits ● Limited perquisites | |
The annual and long-term performance-based compensation awards described herein were made pursuant to our 2011 Long-Term Incentive and Cash Bonus (annual, non-equity incentive pay);
Annual Compensation (long-term, cash and performance unit incentivecompensation);
21
– Salary
WeOur philosophy with respect to salary is to provide a sufficient and stable source of fixed cash compensation. All of our named executive officerscompensation cannot be at-risk or long-term. It is important to provide a meaningful annual salary to attract and other employeesretain a fixed amounthigh caliber leadership team, and to have an appropriate level of cash compensation – salary – for their work. that is not variable.
Salaries for named executive officersthe NEOs (with the exception of the CEO) are established each year by the Committee.Compensation Committee, in consultation with the CEO. The CEO’s salary is established by the independent directors. Salaries for the named executive officers wereNEOs are reviewed annually in June.
The amount of each executive’sNEO’s salary is influenced by numerous factors including:
| ● | An assessment of individual contribution in the judgment of the CEO and the CompensationCommittee (or, in the case of the CEO, of the Compensation Committee and the rest of theindependent directors); |
| ● | Benchmarking with comparable positions at peer group companies; |
| ● | Tenure in role; and |
| ● | Relationship to other Kroger executives’ salaries. |
The assessment of individual contribution is a qualitative determination, based on a subjective determination, without the use of performance targets, in the following areas:factors:
| ● | Leadership; |
| ● | Contribution to the officer group; |
| ● | Achievement of established objectives, to the extent applicable; |
| ● | Decision-making abilities; |
| ● | Performance of the areas or groups directly reporting to the officer; |
| ● | Increased responsibilities; |
| ● | Strategic thinking; and |
| ● | Furtherance of Kroger’s core values. |
18
The amounts shown below reflect the salaries of the named executive officers in effect followingNEOs effective at the annual review of their compensation in Juneend of each fiscal year.
| Salaries | |||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | |||||||
| David B. Dillon | $ | 1,260,000 | $ | 1,290,000 | $ | 1,330,000 | |||
| J. Michael Schlotman | $ | 610,000 | $ | 650,000 | $ | 671,100 | |||
| W. Rodney McMullen | $ | 890,000 | $ | 910,000 | $ | 939,600 | |||
| Paul W. Heldman | $ | 724,000 | $ | 739,000 | $ | 763,000 | |||
| Kathleen S. Barclay* | — | — | $ | 677,300 | |||||
| Salary | ||||||||
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen(1) | $ | 1,100,000 | $ | 1,200,000 | $ | 1,240,000 | ||
| J. Michael Schlotman(2) | $ | 735,000 | $ | 760,000 | $ | 840,000 | ||
| Michael J. Donnelly(2) | $ | 643,560 | $ | 662,900 | $ | 750,000 | ||
| Christopher T. Hjelm(2)(3) | $ | 700,000 | ||||||
| Frederick J. Morganthall II(2)(3) | $ | 670,000 | ||||||
| (2) | Messrs. Schlotman, Donnelly, Hjelm and Morganthall were each promoted to the position of Executive Vice President effective September 1, 2015. | |
| (3) | Messrs. Hjelm and Morganthall became | |
Annual Compensation – Performance-Based Annual Cash Bonus
A large percentageThe NEOs, along with approximately 13,000 of our employees at all levels, including the named executive officers, are eligible to receivetheir fellow Kroger associates, participate in a performance-based annual cash bonus plan. Approximately 7,000 of those associates are eligible for the same plan as the NEOs. The remaining associates are eligible for an annual cash bonus plan of which 40% is based on the Kroger corporate plan and 60% is based on the metrics and targets for their respective supermarket division or operating unit of the Company.
Over time, the Compensation Committee and our independent directors have placed an increased emphasis on our strategic plan by making the targets more difficult to achieve. The annual cash bonus plan is structured to encourage high levels of performance. A threshold level of performance must be achieved before any payouts are earned, while a payout of up to 200% of target can be achieved for superior performance.
The amount of annual cash bonus that the NEOs earn each year is based upon Kroger’s performance compared to targets established by the Compensation Committee and the independent directors based on the business unit performance. plan adopted by the Board of Directors.
The annual cash bonus plan is designed to encourage decisions and behavior that drive the annual operating results and the long-term success of the Company. Kroger’s success is based on a combination of factors, and accordingly the Compensation Committee believes that it is important to encourage behavior that supports multiple elements of our business strategy.
Establishing Annual Cash Bonus Potentials
The Compensation Committee establishes annual cash bonus potentials for each executive officer,NEO, other than the CEO, whose annual cash bonus potential is established by the independent directors. Actual payouts, which can exceed 100% of the potential amounts but may not exceed 200% of the potential amounts, represent the extent to which performance meets or exceeds the thresholdsgoals established by the Compensation Committee. Actual payouts may be as low as zero if performance does not meet the goals established by the Compensation Committee.
The Compensation Committee considers severalmultiple factors in making its determination or recommendation as to annual cash bonus potentials. First, the individual’s level within the organization is a factor in that the Committee believes that more senior executives should have a substantial part of their compensation dependent upon Kroger’s performance. Second, the individual’s salary is a factor so that a substantial portion of a named executivepotentials:
| ● | The individual’s level within the organization, as the Compensation Committee believes that moresenior executives should have a more substantial part of their compensation dependent uponKroger’s performance; |
| ● | The individual’s salary, as the Compensation Committee believes that a significant portion of aNEO’s total cash compensation should be dependent upon Kroger’s performance; |
2219
| ● | The officer’s level in the organization and the internal relationship of annual cash bonus potentialswithin Kroger; |
| ● | Individual performance; |
| ● | The recommendation of the CEO for all NEOs other than the CEO; and |
| ● | The compensation consultant’s benchmarking report regarding annual cash bonus potential andtotal compensation awarded by our peer group. |
officer’s total cash compensation is dependent upon Kroger’s performance. Finally, the Committee considers the reports of its compensation consultants to assess the bonus potential of the named executive officers in light of total compensation paid to comparable executive positions in the industry.
The annual cash bonus potential in effect at the end of the fiscal year for each named executive officerNEO is shown below. Actual annual cash bonus payouts are prorated to reflect changes, if any, to bonus potentials during the year.
| Annual Bonus Potential | |||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | |||||||
| David B. Dillon | $ | 1,500,000 | $ | 1,500,000 | $ | 1,500,000 | |||
| J. Michael Schlotman | $ | 525,000 | $ | 525,000 | $ | 550,000 | |||
| W. Rodney McMullen | $ | 1,000,000 | $ | 1,000,000 | $ | 1,000,000 | |||
| Paul W. Heldman | $ | 550,000 | $ | 550,000 | $ | 550,000 | |||
| Kathleen S. Barclay* | — | — | $ | 550,000 | |||||
| Annual Cash Bonus Potential | ||||||||
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen(1) | $ | 1,500,000 | $ | 1,600,000 | $ | 1,650,000 | ||
| J. Michael Schlotman(2) | $ | 550,000 | $ | 550,000 | $ | 600,000 | ||
| Michael J. Donnelly(2) | $ | 425,000 | $ | 550,000 | $ | 600,000 | ||
| Christopher T. Hjelm(2)(3) | $ | 600,000 | ||||||
| Frederick J. Morganthall II(2)(3) | $ | 600,000 | ||||||
| (2) | Messrs. Schlotman, Donnelly, Hjelm and Morganthall were each promoted to the position of Executive Vice President effective September 1, 2015. | |
| (3) | Messrs. Hjelm and Morganthall became NEOs in 2015. | |
Annual Cash Bonus Plan Metrics and Connection to our Business Plan
The annual cash bonus plan has the following measurable performance metrics, all of which are interconnected, and individually necessary to sustain our business model and achieve our growth strategy:
| Metric | Weight | Rationale for Use |
ID Sales | 30% | ●ID Sales represent sales, without fuel, at our supermarketsthat have been open without expansion or relocation for fivefull quarters. ●We believe this is the best measure of the real growth ofour sales across the enterprise. A key driver of our model isstrong ID Sales; it is the engine that fuels our growth. |
EBITDA without Fuel(1) | 30% | ●EBITDA is an important way for us to evaluate our earningsfrom operating the business; we cannot achieve solidEBITDA without a ●Unlike earnings per share, which can be affected bymanagement decisions on share buybacks, this measureof earnings is relevant for all of our approximately 13,000associates who are eligible for the annual cash bonus plan. |
20
| Metric | Weight | Rationale for Use |
Customer 1st Strategy | 30% | ●Kroger’s Customer 1stStrategy is the focus, in ●This proprietary metric measures the improvement in howKroger is perceived by customers in each of the Four Keys. ●Annual cash bonus payout is based on certain elements ofthe Customer 1stPlan, to highlight annual objectives that areintended to receive the most focused attention in that year. |
Total Operating Costs as a Percentage of Sales, without Fuel(2) | 10% | ●An essential part of Kroger’s model is to increaseproductivity and efficiency, and to take costs out of thebusiness in a sustainable way. ●We strive to be disciplined, so that as the Company grows,expenses are properly managed. |
Total of 4 Metrics | 100% | |
Fuel Bonus | 5% “Kicker” | ●An additional 5% is earned if Kroger achieves three goalswith respect to its supermarket fuel operations: targeted fuelEBITDA, an increase in total gallons sold, and additionalfuel centers placed in service. ●The fuel bonus was added to the annual cash bonus planas an incentive to encourage the addition of fuel centersat a faster rate, while maintaining fuel EBITDA and fuelgallon growth. ●The fuel bonus of 5% is only available if all three measuresare met. If any of the three fuel goals are not met, no portionof the fuel bonus is earned. |
| (1) | EBITDA is calculated as operating profit plus depreciation and amortization, excluding fuel and consolidated variable interest entities. | |
| (2) | Total Operating Costs is calculated as the sum of (i) operating, general and administrative expenses, depreciation and amortization, and rent expense, without fuel, and (ii) warehouse and transportation costs, shrink, and advertising expenses, for our supermarket operations, without fuel. | |
Over timeThe use of these four primary metrics creates checks and balances on the Committee has placed an increased emphasisvarious behaviors and decisions that impact the long-term success of the Company. The ID Sales, EBITDA without fuel and Customer 1st Strategy metrics are weighted equally to highlight the need to simultaneously achieve all three metrics in order to maintain our growth.
We aligned the weighting of ID Sales and EBITDA without fuel metrics to emphasize sales growth balanced with the focus on profit. Kroger’s business is not sustainable if we merely increase our strategic plan by makingID Sales, but do not have a corresponding increase in earnings. Furthermore, payouts in the ID Sales and EBITDA without fuel segments are interrelated. Achieving the goal for both the ID Sales and EBITDA without fuel results in a higher percentage payout on both elements. Achieving the target more difficulton one, but not the other will limit the payout percentage on both.
By supporting the Customer 1st Strategy and the Four Keys, we will better connect with our customers. Our unique competitive advantage is our ability to achieve. The bonus plan allows for minimal bonusdeliver on the Four Keys, which are the items that matter most to be earned at relatively low levels to provide incentive for achieving even higher levels of performance.our customers, and it is that multi-faceted achievement that we believe drives our ID Sales growth.
As we strive to achieve our aggressive growth targets, we also continuously aim to reduce our operating costs as a percentage of sales, without fuel. Productivity improvements and other reductions in operating costs allow us to reduce costs in areas that do not matter to our customers so that we can
21
invest money in the areas that matter the most to our customers, like the Four Keys. We carefully manage operating cost reductions to ensure a consistent delivery of the customer experience. This again shows the need to have multiple metrics, to create checks and balances on the various behavior and decisions that are influenced by the design of the bonus plan.
Results of 2015 Annual Cash Bonus Plan
The amount of bonus that the named executive officers earn each year is determined by Kroger’s performance compared to targets2015 goals established by the Compensation Committee, based on the business plan adopted byactual 2015 results and the Board of Directors. In 2012, one-thirdbonus percentage earned for each of the bonus was based on a target for identical supermarket sales without fuel; one-third was based on a target for EBITDA without fuel; and one-third was based on implementation and results of a set of measures under our strategic plan. An additional 5% would be earned if Kroger achieved three goals with respect to its supermarket fuel operations: achievementperformance metrics of the targeted fuel EBITDA, increase of at least 3% in total gallons sold, and achievement of the planned number of fuel centers placed in service.annual cash bonus plan were as follows:
| Actual | ||||||||||||
| Performance | ||||||||||||
| Goals | Compared to | Amount | ||||||||||
| Target | Actual | Target | Weight | Earned | ||||||||
| Performance Metrics | Minimum | (100%) | Performance(1) | (A) | (B) | (A) x (B) | ||||||
| ID Sales | 2.1% | 4.1% | 5.0% | 134.3% | 30% | 40.3% | ||||||
| EBITDA without Fuel | $4.4384 | $5.2217 | $5.2351 | |||||||||
| Billion | Billion | Billion | 126.3%(2) | 30% | 37.9% | |||||||
| Customer 1stStrategy(3) | * | * | * | * | 30% | 39.0% | ||||||
| Over | Over | Over | 45.0% | 10% | 4.5% | |||||||
| Total Operating Costs as | budget by | budget by | budget by | |||||||||
| Percentage of Sales, | 25 basis | 5 basis | 16 basis | |||||||||
| without Fuel(4) | points | points | points | |||||||||
| 0% | 5.0% | |||||||||||
| Fuel Bonus(5) | [As described in the footnote below] | or 5% | ||||||||||
| Total Earned | 126.7% | |||||||||||
| (1) | Actual performance results exclude Roundy’s because the merger occurred after the performance goals were established. | |
| (2) | Under the terms of the plan, if ID Sales results exceed the target and EBITDA results exceed the target, then the payout percentage for reaching the EBITDA target is 125% rather than 100%. | |
| (3) | The Customer 1stStrategy component also was established by the Compensation Committee at the beginning of the year, but is not disclosed as it is competitively sensitive. | |
| (4) | Total Operating Costs without fuel were budgeted at 26.07% as a percentage of sales for fiscal year 2015. | |
| (5) | An additional 5% is earned if Kroger achieves three goals with respect to its supermarket fuel operations: achievement of the targeted fuel EBITDA of $242 million, an increase in total gallons sold of 3%,and achievement of 50 additional fuel centers placed in service. Actual results were: fuel EBITDA of $450 million; an increase in total gallons sold of 8.53%; and 57 additional fuel centers placed in service. | |
Following the close of the year, the Compensation Committee reviewed Kroger’s performance against each of the identical sales without fuel, EBITDA without fuel, and strategic plan objectivesmetrics outlined above and determined the extent to which Kroger achieved those objectives. Kroger’s EBITDA without fuel for 2012 was $4.118 billion and Kroger’s identical supermarket sales without fuel for 2012 were 3.5%. In 2012, Kroger’s supermarket fuel EBITDA was $215.818 million, which exceeded the goal of $153.425 million necessary to earn a bonus for the fuel component. Kroger’s sale of fuelThe Compensation Committee believes our management produced outstanding results in supermarket fuel centers was 4.250 billion gallons, or 9.7% over the prior year. We operated 1,169 supermarket fuel centers as of the end of 2012, exceeding our goal of 1,150 centers. As a result, the payout percentage included the additional 5% fuel bonus.2015, measured against increasingly aggressive business plan objectives. Due to our performance when compared to the targetsgoals established by the Compensation Committee, and based on the business plan adopted by the Board, of Directors, the named executive officers earned 85.881% of their bonus potentials This is the same bonus percentage payout received byNEOs and all other participants in the corporate annual corporatecash bonus plan.plan earned 126.7% of their bonus potentials.
The 2012 targets established by the Committee for annual bonus amounts based on identical sales and EBITDA results, the actual 2012 results, and the bonus percentage earned in each of the components of named executive officer bonus, were as follows:
| Targets | ||||||||||
| Component | Minimum | 100% | Result | Amount Earned | ||||||
| Identical Sales without fuel | 1.6% | 3.6% | 3.5% | 31.170% | ||||||
| EBITDA without fuel | $3.589 Billion | $4.222 Billion* | $4.118 Billion | 16.871% | ||||||
| Strategic Plan | ** | ** | ** | 32.840% | ||||||
| Fuel Bonus | [as described in the text above] | 5.000% | ||||||||
| Total Earned | 85.881% | |||||||||
23
In 2012,2015, as in all years, the Compensation Committee retained discretion to reduce the annual cash bonus payout for all executive officers, including the named executive officers,NEOs, if the Compensation Committee determined for any reason that the bonus payouts were not appropriate.appropriate given their assessment of Company performance. The independent directors retained that discretion for the CEO’s bonus. Those bodiesThe Compensation Committee and the independent directors also retained discretion to adjust the targets goals for each metric
22
under the plan should unanticipated developments arise during the year. No adjustments were made to the targets.goals in 2015. The Compensation Committee, and the independent directors in the case of the CEO, determined that the annual cash bonus payouts forearned appropriately reflected the named executive officersCompany’s strong performance in 2015 and therefore should remain the same as other participants.not be adjusted.
The actual annual cash bonus percentage paidpayout for 20122015 represented goodexcellent performance that fell shortexceeded our business plan objectives, with the exception of meetingoperating costs as a percentage of sales, without fuel. The strong link between pay and performance is illustrated by a comparison of earned amounts under our annual cash bonus plan in previous years, such as 2009, 2010 and 2012, when payouts were less than 100%. In those years, we did not achieve all of our business plan objectives. objectives.A comparison of actual annual cash bonus percentages for the named executive officerspercentage payouts in prior years demonstrates the variability of annual cash bonus incentive compensation:compensation and its strong link to our performance:
| Annual Cash Bonus | Annual Cash Bonus | |||||||
| Fiscal Year | Percentage | Payout Percentage | ||||||
| 2015 | 126.7 | % | ||||||
| 2014 | 121.5 | % | ||||||
| 2013 | 104.9 | % | ||||||
| 2012 | 85.881 | % | 85.9 | % | ||||
| 2011 | 138.666 | % | 138.7 | % | ||||
| 2010 | 53.868 | % | 53.9 | % | ||||
| 2009 | 38.450 | % | 38.5 | % | ||||
| 2008 | 104.948 | % | 104.9 | % | ||||
| 2007 | 128.104 | % | 128.1 | % | ||||
| 2006 | 141.118 | % | 141.1 | % | ||||
| 2005 | 132.094 | % | ||||||
| 2004 | 55.174 | % | ||||||
| 2003 | 24.100 | % | ||||||
As described above, the annual cash bonus payout percentage is applied to each NEO’s bonus potential, which is determined by the Compensation Committee, and the independent directors in the case of the CEO. The actual amounts of performance-based annual performance-based cash bonuses paid to the named executive officersNEOs for 20122015 are reported in the Summary Compensation Table underin the heading “Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation” column and footnote 4. These amounts represent the bonus potentials for each named executive officer multiplied by the 85.881% payout percentage earned in 2012. In no event can any participant receive a performance-based annual cash bonus in excess of $5,000,000. The maximum amount4 to that a participant, including each named executive officer, can earn is further limited to 200% of the participant’s bonus potential amount.
The performance-based annual cash bonus for 2013 will be determined based on Kroger’s performance against the identical sales, EBITDA, and strategic plan objectives established by the Committee. Each of these metrics will again be weighted the same to indicate to the organization the equal importance that each measure has to Kroger’s overall strategy. The underlying strategy metrics have been revised from prior years to focus on shorter-term measures, as the long-term bonus emphasizes long-term performance. The 2013 plan also provides for an additional 5% payout if our goals for supermarket fuel EBITDA, supermarket fuel gallons sold, and targeted number of fuel centers in operation at the fiscal year end are achieved.table.
Long-Term IncentivesCompensation
The Compensation Committee continues to believebelieves in the importance of providing an incentive to the named executive officersNEOs to achieve the long-term goals established by the BoardBoard. As such, a majority of Directors by conditioning a significant portion of compensation is conditioned on the achievement of those goals.
In 2006, the Committee adopted the first in a series ofCompany’s long-term performance based plans designed to reward participants for improving thegoals and is delivered via four long-term performance of Kroger. These earlier plans provided for overlapping four year performance periods that allowed for the earning of a long-term cash bonus. In 2010, Kroger’s long-term incentive program was redesigned to combine the total value of ourcompensation vehicles: long-term cash bonus, performance units, stock options and equity programs into a cohesive, strategic reward for eligible executivesrestricted stock. Long-term compensation promotes long-term value creation and discourages the over-emphasis of attaining short-term goals at the Vice President level and above. Approximately fifty percentexpense of long-term growth.
The Compensation Committee considers several factors in determining the target value of long-term compensation awarded to the NEOs or, in the case of the planCEO, recommending to the independent directors the amount awarded. These factors include:
| ● | The compensation consultant’s benchmarking report regarding long-term compensation awarded by our peer group; |
| ● | The officer’s level in the organization and the internal relationship of long-term compensation awards within Kroger; |
| ● | Individual performance; and |
| ● | The recommendation of the CEO, for all NEOs other than the CEO. |
23
Long-term incentives are structured to be a combination of performance- and time-based compensation that reflects elements of financial and stock performance to provide both retention value is performance-based, delivered inand alignment with company performance. Long-term cash bonus and performance units,unit payouts are contingent on the achievement of certain strategic performance measures. The other fifty percent ofand financial measures and incentivize recipients to promote long-term value creation and enhance shareholder wealth by supporting the Company’s long-term strategic goals. Stock options and restricted stock are linked to stock performance creating alignment between executives and company shareholders. Options have no initial value and recipients only realize benefits if the value of our stock increases following the date of grant.
A majority of long-term compensation is time-based and delivered inequity-based (performance units, stock options, and restricted shares.stock) and is tied to the future value of our common shares, further aligning the interests of our NEOs with our shareholders. All four components of long-term compensation are intended to focus executive behaviors on our long-term strategy. Each component is described in more detail below.
24
Performance Based Long-Term Compensation
TheAmounts of long-term incentive plan adopted in 2010 provides the modelcompensation awards issued and outstanding for the new combinedNEOs are set forth in the tables that follow this discussion and analysis.
Long-Term Incentive Plan Design
In contrast to the performance-based annual cash bonus plan, structure. Subsequent plans have been adopted in 2011, 2012described above, which has approximately 13,000 participants, our performance-based Long-Term Incentive Plan has approximately 160 participants, including the NEOs. Each year we adopt a similar Long-Term Incentive Plan, which provides for overlapping three year performance periods. The Long-Term Incentive Plan consists of a performance-based long-term cash bonus and 2013. Each of these plansperformance units which has the following characteristics:
| ● | The long-term cash bonus | ||
| ● | |||
In addition, a fixed number of performance units is awarded to each | |||
| ● | The actual long-term cash bonus and number of performance units earned are each determined based on our performance against the same metrics established by the Compensation Committee (the independent directors, for the CEO) at the beginning of the performance period. | ||
| ● | Performance at the end of the three-year period is measured against the baseline of each performance metric established at the beginning of the performance period. | ||
| ● | The payout percentage, based on the extent to which the performance metrics are achieved, is applied to both the long-term cash bonus potential and the number of performance units awarded. | ||
| ● | Actual payouts cannot exceed 100% of the long-term cash bonus potential or 100% of the number of performance units awarded. |
The Compensation Committee anticipates adopting a new Long-Term Incentive Plan each year, measuring improvement over successive three-year periods. Each year when establishing the performance metric baselines and percentage payouts per unit of improvement, the Compensation Committee considers the difficulty of achieving compounded improvement over time. During 2015, Kroger awarded 503,276 performance units to approximately 160 employees, including the NEOs.
24
Long-Term Incentive Plan Metrics and Connection to our Business Strategy
| Metric | Rationale for Use | |
| Customer 1stStrategy | ● | Kroger’s Customer 1stStrategy is the focus, in all of Kroger’s decision-making, on the customer. The Four Keys of Kroger’s Customer 1stStrategy are People, Products, Shopping Experience and Price. |
| ● | This proprietary metric measures the improvement in how Kroger is perceived by customers in each of the Four Keys. | |
| ● | Long-Term Incentive Plan payout is based on all of the elements of the Customer 1stStrategy, to maintain our top executives’ consistent focus on the entirety of the Customer 1stStrategy. This is in contrast to the annual cash bonus payout which is based on certain elements of the Customer 1stPlan, to highlight annual objectives that are intended to receive the most focused attention in that year. | |
| Improvement in Associate Engagement | ● | Kroger measures associate engagement in an annual survey of associates. |
| ● | This metric is included in the Long-Term Incentive Plan as an acknowledgement that our Company’s success is directly tied to our associates connecting with and serving our customers every day, whether in our stores, manufacturing plants, distribution centers or offices. | |
| Reduction in Operating Costs(1)as a Percentage of Sales, without Fuel | ● | An essential part of Kroger’s model is to increase productivity and efficiency, and to take costs out of the business in a sustainable way. |
| ● | We strive to be disciplined, so that as the Company grows, expenses are properly managed. | |
| ● | This metric is included in both the annual cash bonus plan and Long-Term Incentive Plans. Operating costs, without fuel, can be improved temporarily on an annual basis, but it is more difficult to maintain these reductions over time. | |
| ● | It is the role of the approximately 160 employees in the Long-Term Incentive Plan to continue to reduce operating costs as a percentage of sales,without fuel, over time and to ensure such reductions are sustainable over the long-term. Including this metric in the Long-term Incentive Plan, incentivizes these key employees to implement policies for sustainable improvement over a long period of time. | |
| ROIC(2) | ● | Part of our long-term growth strategy is to increase capital investments over time. We have a pipeline of high quality projects and new store openings, and we continue to increase the square footage in our fill-in markets. |
| ● | With increased capital spend,it is essential that we achieve the proper returns on our investments. | |
| ● | This measure is intended to hold executives accountable for the returns on the increased capital investments. | |
| (1) | Operating Costs is calculated as the sum of (i) operating, general and administrative expenses, depreciation and amortization, and rent expense, without fuel, and (ii) warehouse and transportation costs, shrink, and advertising expenses, for our supermarket operations, without fuel. Operating costs will exclude one-time expenses incurred in lieu of future anticipated obligations. Future expenses that are avoided by virtue of the incurrence of the one-time expense will be deemed to be total operating expenses in the year in which they otherwise would have been incurred. |
Compensation under the plans is earned based on our performance against metrics established by theCommittee at the beginning of the performance period.25
| (2) | Return on invested capital is calculated by dividing adjusted operating profit for the prior four quarters by the average invested capital. Adjusted operating profit is calculated by excluding certain items included in operating profit, and adding our LIFO charge, depreciation and amortization, and rent. Average invested capital will be calculated as the sum of (i) the average of our total assets, (ii) the average LIFO reserve, (iii) the average accumulated depreciation and amortization, and (iv) a rent factor equal to total rent for the last four quarters multiplied by a factor of eight; minus (i)the average taxes receivable, (ii) the average trade accounts payable, (iii) the average accrued salaries and wages, and (iv) the average other current liabilities, excluding accrued income taxes. |
The following table summarizes each of the long-term performance based plansLong-Term Incentive Plans adopted for the years shown:
| Performance Period | 2013 to 2015 | 2014 to 2016 | 2015 to 2017 | |||||||||
| Payout Date | March | March | March | |||||||||
| Long-term Cash | Salary at end of | Salary at end of | Salary at end of | |||||||||
| Bonus Potential | fiscal year | fiscal year | fiscal year | |||||||||
| Performance Metrics | ||||||||||||
| 2% payout per unit | 2% payout per unit | 4% payout per unit | ||||||||||
| improvement | improvement | improvement | ||||||||||
| | improvement | improvement | improvement | |||||||||
| Reduction in Operating Cost as a | 0.50% payout per | 0.50% payout per | ||||||||||
| Percentage of Sales, | 0.01% reduction | 0.01% reduction | 0.01% reduction | |||||||||
| without Fuel | in operating costs | in operating costs | in operating costs | |||||||||
| Baseline: 26.69% | Baseline: 26.68% | Baseline: 26.41% | ||||||||||
| ROIC | 1% payout per | 1% payout per | 1% payout per | |||||||||
| 0.01% improvement | 0.01% improvement | 0.01% improvement | ||||||||||
| in ROIC | in ROIC | in ROIC | ||||||||||
| Baseline: | Baseline: 13.29% | Baseline: 13.76% | ||||||||||
| * | Or date of plan entry, if later. |
The Compensation Committee has made adjustments to the percentage payouts for the components of the Long-Term Incentive Plans over time to account for the increasing difficulty of achieving compounded improvement.
During 2015, Kroger awarded 503,276 performance units to approximately 160 employees, including the NEOs.
2526
Results of 2013 Long-Term Incentive Plan
The long-term performance based plan adopted in 2010,2013 Long-Term Incentive Plan, which measured improvements through fiscalover the three year 2012,period from 2013 to 2015, paid out in March 20132016 and was calculated as follows:
| Percentage | ||||||||||||||||
| Component | Baseline | Result | Improvement | Multiplier | Earned | |||||||||||
| Strategic Plan | * | * | 0 units of improvement | 1 | % | 0.00 | % | |||||||||
| Associate Engagement | * | * | 3 units of improvement | 2 | % | 6.00 | % | |||||||||
| Operating Costs, as a Percentage of | ||||||||||||||||
| Sales, Excluding Fuel | 27.59% | 26.84% | 75 basis point improvement | 0.25 | % | 18.75 | % | |||||||||
| Total Earned | 24.75 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Payout per | Percentage | ||||||||||||
| Improvement | Improvement | Earned | |||||||||||
| Metric | Baseline | Result(1) | (A) | (B) | (A) x (B) | ||||||||
| Customer 1st | 12 units of | ||||||||||||
| Strategy(2) | * | * | improvement | 2.00% | 24.00 | % | |||||||
| Improvement | |||||||||||||
| in Associate | 2 units of | ||||||||||||
| Engagement(2) | * | * | improvement | 4.00% | 8.00 | % | |||||||
| Reduction in Operating | |||||||||||||
| Cost as a Percentage | 56 basis point | ||||||||||||
| of Sales, without Fuel | 26.69% | 26.13% | improvement | 0.50% | 28.00 | % | |||||||
| Return on Invested | 66 basis point | ||||||||||||
| Capital | 13.27% | 13.93% | improvement | 1.00% | 66.00 | % | |||||||
| Total | 126.00 | % | |||||||||||
| Total Earned: Payout is | |||||||||||||
| capped at 100% | 100.00 | % | |||||||||||
| Results exclude Harris Teeter and Roundy’s because the mergers occurred after the performance goals were established. | ||
| (2) | The | |
Accordingly, each named executive officerNEO received a long-term cash bonus in an amount equal to 24.75%100% of that executive’s long-term cash bonus base,potential, and was issued the number of Kroger common shares equal to 24.75%100% of the number of performance units awarded to that executive, along with a cash amount equal to the dividends paid on that number of common shares during the three year performance period. ThePayout for the cash components of the 2010 plan payout2013 Long-Term Incentive Plan are reportreported in the “Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation” columnand “All Other Compensation” columns of the Summary Compensation Table and footnotefootnotes 4 and 6 to that table, and the common shares issued under the plan are reported in the Options Exercised2015 Option Exercises and Stock Vested Table and footnote 2 to that table.
At the time of adopting new long-term plans, the Committee has made adjustmentsStock Options and Restricted Stock
Stock options and restricted stock continue to the percentage payoutsplay an important role in rewarding NEOs for the componentsachievement of the long-term plans to accountbusiness objectives and providing incentives for the increasing difficultycreation of achieving compounded improvement.
The Committee anticipates adopting a new plan each year, measuring improvement over successive three-year periods.
Equity Awards
Awardsshareholder value.Awards based on Kroger’s common shares are granted periodicallyannually to the named executive officersNEOs and a large number of other employees. Equity participation alignsKroger historically has distributed time-based equity awards widely, aligning the interests of employees with your interest as shareholders, and Kroger historically has distributed equity awards widely. shareholders.
In 2012,2015, Kroger granted 4,068,8153,425,720 stock options to approximately 8,0311,222 employees, including the named executive officers.NEOs. The options permit the holder to purchase Kroger common shares at an option price equal to the closing price of Kroger common shares on the date of the grant.
During 2015, Kroger awarded 3,228,270 shares of restricted stock to approximately 8,280 employees, including the NEOs.
Options are granted only on one of the four dates of Compensation CommitteeBoard meetings conducted after Kroger’s public release of its quarterly earnings results.
Kroger’s long-term incentive plans also provide The Compensation Committee determines the vesting schedule for other equity-based awards, includingstock options and restricted stock.
During 2012, Kroger awarded 2,623,742 shares of2015, the Compensation Committee granted to the NEOs: (a) stock options with a five-year vesting schedule; and (b) restricted stock to approximately 18,346 employees, including the named executive officers, under Kroger’s 2012 long-term incentive plan.
The Committee considers several factors in determining the amount of options, restricted shares, and performance units awarded to the named executive officerswith a three- or in the case of the CEO, recommending to the independent directors the amount awarded. These factors include:
The Committee has long recognized that the amount of compensation provided to the named executive officers through equity-based pay is often below the amount paid by our competitors. Lower equity-based awards for the named executive officers and other senior management permit a broader base of Kroger employees to participate in equity awards.five-year vesting schedule.
2627
AmountsAs discussed below under Stock Ownership Guidelines, covered individuals, including the NEOs, must hold 100% of equity awardscommon shares issued and outstandingpursuant to performance units earned, the shares received upon the exercise of stock options or upon the vesting of restricted stock, except those necessary to pay the exercise price of the options and/or applicable taxes, until applicable stock ownership guidelines are met, unless the disposition is approved in advance by the CEO, or by the Board or Compensation Committee for the named executive officers are set forth in the tables that follow this discussion and analysis.CEO.
Retirement and Other Benefits
Kroger maintains a defined benefit and several defined contribution retirement plans for its employees. The named executive officersNEOs participate in one or more of these plans, as well as one or more excess plans designed to make up the shortfall in retirement benefits created by limitations under the Internal Revenue Code on benefits to highly compensated individuals under qualified plans. Additional details regarding certain retirement benefits available to the named executive officersNEOs can be found below in the 20122015 Pension Benefits tableTable and the accompanying narrative description that follows this discussion and analysis.
Kroger also maintains an executive deferred compensation plan in which some of the named executive officersNEOs participate. This plan is a nonqualified plan under which participants can elect to defer up to 100% of their cash compensation each year. CompensationAdditional details regarding our nonqualified deferred bears interest, until paid out, atcompensation plans available to the rate representing Kroger’s cost of ten-year debtNEOs can be found below in the yearNonqualified Deferred Compensation Table and the rate is set, as determined by Kroger’s CEO, and reviewed with the Committee, prior to the beginning of each deferral year. In 2012, that rate was 4.23%. Deferred amounts are paid out only in cash, in accordance with a deferral option selected by the participant at the time the deferral election is made.accompanying narrative.
We adoptedKroger also maintains The Kroger Co. Employee Protection Plan or KEPP, during fiscal year 1988. That plan was amended and restated in 2007. All(“KEPP”), which covers all of our management employees and administrative support personnel who have provided services to Kroger for at least one year and whose employment is not covered by a collective bargaining agreement, with at least one year of service, are covered.agreement. KEPP provides for severance benefits and extended Kroger-paid health care, as well as the continuation of other benefits as described in the plan, when an employee is actually or constructively terminated without cause within two years following a change in control of Kroger (as defined in the plan)KEPP). Participants are entitled to severance pay of up to 24 months’ salary and bonus. The actual amount is dependent upon pay level and years of service. KEPP can be amended or terminated by the Board at any time prior to a change in control.
StockPerformance-based long-term cash bonus, performance unit, stock option, and restricted stock and performance unit agreements with participants in Kroger’s long-term incentive plansaward recipients provide that those awards “vest,” with options becoming immediately exercisable, restrictions on restricted stock lapsing, and50% of the long-term cash bonus potential being paid, common shares equal to 50% of the performance units being awarded, options becoming immediately exercisable, and restrictions on restricted stock lapsing upon a change in control as described in the grant agreements.
None of the named executive officersNEOs is party to an employment agreement.
Perquisites
TheNEOs receive limited perquisites because the Compensation Committee does not believe that it is necessary for the attraction or retention of management talent to provide the named executive officersNEOs a substantial amount of compensation in the form of perquisites. In 2012,2015, the only perquisites available to our named executive officersNEOs were:
| ● | premiums paid on life insurance policies; |
| ● | premiums paid on accidental death and dismemberment insurance; and |
| ● | premiums paid on long-term disability insurance policies. |
The life insurance benefitBecause he was offered beginning several years ago to replace a split-dollar life insurance benefit thatan officer of Harris Teeter during 2015, Mr. Morganthall also was substantially more costly to Kroger. Currently, 136 active executives, including the named executive officers, and 73 retired executives, receive this benefit.
In addition, the named executive officers are entitled toeligible for the following benefit that does not constitute a perquisite as defined by SEC rules: personal use of Kroger aircraft, which officers may lease from Kroger and pay the average variable cost of operating the aircraft, making officers more available and allowing for a more efficient use of their time.Harris Teeter perquisites:
| ● | premiums paid on executive bonus insurance policies; and |
| ● | tax reimbursements for the taxes due on insurance premiums paid by Harris Teeter. |
The total amount of perquisites furnished to the named executive officersNEOs is shown in the Summary Compensation Table and described in more detail in footnote 6 to that table.
2728
Process for Establishing Executive Compensation
The Compensation Committee of the Board has the primary responsibility for establishing the compensation of our executive officers, including the NEOs, with the exception of the Chief Executive Officer. The Compensation Committee’s role regarding the CEO’s compensation is to make recommendations to the independent members of the Board; those members of the Board establish the CEO’s compensation.
The Compensation Committee directly engages a compensation consultant from Mercer Human Resource Consulting to advise the Compensation Committee in the design of compensation for executive officers.
The Mercer consultant conducts an annual competitive assessment of executive positions at Kroger for the Compensation Committee. The assessment is one of several bases, as described above, on which the Compensation Committee determines compensation. The consultant assesses:
| ● | Base salary; |
| ● | Target performance-based annual cash bonus; |
| ● | Target annual cash compensation (the sum of salary and annual cash bonus potential); |
| ● | Annualized long-term compensation, such as performance-based long-term cash bonus potential and performance units, stock options and restricted stock; and |
| ● | Total direct compensation (the sum of target annual cash compensation and annualized long-term compensation). |
The consultant compares these elements against those of other companies in a group of publicly-traded food and drug retailers. For 2015, our peer group consisted of:
| Costco Wholesale | SUPERVALU |
| CVS Health, formerly CVS Caremark | Target |
| Rite Aid | Wal-Mart |
| Safeway | Walgreens Boots Alliance, formerly Walgreen |
This peer group is the same group as was used in 2014. Median 2015 revenue for the peer group was $92.5 billion, compared to our revenue of $109.8 billion. The make-up of the compensation peer group is reviewed annually and modified as circumstances warrant. Industry consolidation and other competitive forces will result in changes to the peer group over time.
The consultant also provides the Compensation Committee data from “general industry” companies, a representation of major publicly-traded companies of similar size and scope from outside the retail industry. This data serves as reference points, particularly for senior staff positions where competition for talent extends beyond the retail sector.
Considering the size of Kroger in relation to other peer group companies, the Compensation Committee believes that salaries paid to our NEOs should be at or above the median paid by peer group companies for comparable positions. The Compensation Committee also aims to provide an annual cash bonus potential to our NEOs that, if the increasingly more challenging annual business plan objectives are achieved at superior levels, would cause total cash compensation to be meaningfully above the median. Actual payouts may be as low as zero if performance does not meet the baselines established by the Compensation Committee.
The independent members of the Board have the exclusive authority to determine the amount of the CEO’s compensation. In setting total compensation, the independent directors consider the median compensation of the peer group’s CEOs. With respect to the annual bonus, the independent directors make two determinations: (1) they determine the annual cash bonus potential that will be multiplied by the annual cash bonus payout percentage earned that is generally applicable to all corporate management, including the NEOs and (2) the independent directors determine the annual cash bonus amount paid to the CEO by retaining discretion to reduce the annual cash bonus percentage payout the CEO would otherwise receive under the formulaic plan.
29
The Compensation Committee performs the same function and exercises the same authority as to the other NEOs. In its annual review of compensation for the NEOs the Compensation Committee:
| ● | Conducts an annual review of all components of compensation, quantifying total compensation for the NEOs on tally sheets. The review includes a summary for each NEO of salary; performance-based annual cash bonus; long-term performance-based cash and performance unit compensation; stock options; restricted stock; accumulated realized and unrealized stock option gains and restricted stock and performance unit values; the value of any perquisites; retirement benefits; company paid health and welfare benefits; banked vacation; severance benefits available under KEPP; and earnings and payouts available under Kroger’s nonqualified deferred compensation program. |
| ● | Considers internal pay equity at Kroger to ensure that the CEO is not compensated disproportionately. The Compensation Committee has determined that the compensation of the CEO and that of the other NEOs bears a reasonable relationship to the compensation levels of other executive positions at Kroger taking into consideration performance and differences in responsibilities. |
| ● | Reviews a report from the Compensation Committee’s compensation consultants comparing NEO and other senior executive compensation with that of other companies, including both our peer group of competitors and a larger general industry group, to ensure that the Compensation Committee’s objectives of competitiveness are met. |
| ● | Takes into account a recommendation from the CEO (except in the case of his own compensation) for salary, annual cash bonus potential and long-term compensation awards for each of the senior officers including the other NEOs. The CEO’s recommendation takes into consideration the objectives established by and the reports received by the Compensation Committee as well as his assessment of individual job performance and contribution to our management team. |
In considering each of the factors above, the Compensation Committee does not make use of a formula, but rather quantitatively reviews each factor in setting compensation.
Advisory Vote to Approve Executive Compensation
At the 2015 annual meeting, we held our fifth annual advisory vote on executive compensation. Over 95% of the votes cast were in favor of the advisory proposal in 2015. The Compensation Committee believes it conveys our shareholders’ support of the Compensation Committee’s decisions and the existing executive compensation programs. As a result, the Compensation Committee made no material changes in the structure of our compensation programs or our pay for performance philosophy.
At the 2016 annual meeting, in keeping with our shareholders’ request for an annual advisory vote, we will again hold an advisory vote to approve executive compensation (see page 49). The Compensation Committee will continue to consider the results from this year’s and future advisory votes on executive compensation in their evaluation and administration of our compensation program.
Stock Ownership Guidelines
To more closely align the interests of our officers and directors with your interests as shareholders, the Board has adopted stock ownership guidelines. These guidelines require non-employee directors, executive officers, and other key executives to acquire and hold a minimum dollar value of Kroger common shares as set forth below:
| Position | Multiple | |
| Chief Executive Officer | 5 times base salary | |
| Vice Chairman, President and Chief Operating Officer | 4 times base salary | |
| Executive Vice Presidents and Senior Vice Presidents | 3 times base salary | |
| Other Key Executives | 2 times base salary | |
| Non-employee Directors | 3 times annual base cash retainer |
30
Covered individuals are expected to achieve the target level within five years of appointment to their position. If the requirements are not met, individuals, including the NEOs, must hold 100% of common shares issued pursuant to performance units earned,shares received upon the exercise of stock options and upon the vesting of restricted stock, except those necessary to pay the exercise price of the options and/or applicable taxes, and must retain all Kroger shares unless the disposition is approved in advance by the CEO, or by the Board or Compensation Committee for the CEO.
Executive Compensation Recoupment Policy (Clawback)
If a material error of facts results in the payment to an executive officer at the level of Group Vice President or higher of an annual cash bonus or a long-term cash bonus in an amount higher than otherwise would have been paid, as determined by the Compensation Committee, then the officer, upon demand from the Compensation Committee, will reimburse Kroger for the amounts that would not have been paid if the error had not occurred. This recoupment policy applies to those amounts paid by Kroger within 36 months prior to the detection and public disclosure of the error. In enforcing the policy, the Compensation Committee will take into consideration all factors that it deems appropriate, including:
| ● | The materiality of the amount of payment involved; |
| ● | The extent to which other benefits were reduced in other years as a result of the achievement of performance levels based on the error; |
| ● | Individual officer culpability, if any; and |
| ● | Other factors that should offset the amount of overpayment. |
Compensation Policies as They Relate to Risk Management
As part of the amountCompensation Committee’s review of payment involved;
Prohibition on Hedging and Pledging
After considering best practices related to ownership of company shares, the Board has adopted a policy regarding hedging, pledging and short sales of Kroger securities. Kroger directors and officers are prohibited from engaging, directly or indirectly, in other yearshedging transactions in, or short sales of, Kroger securities. In addition, the policy was further revised as a result of the achievement ofperformance levels based on the error;
Section 162(M)162(m) of the Internal Revenue Code
Tax laws place a deductibility limit of $1,000,000 on the amount of some types of compensation for the CEO and the next four most highly compensated officers (other than the chief financial officer) reported in this proxy by virtue of beingbecause they are among the four highest compensated officers (“covered employees”) that. In Kroger’s case, this group of individuals is tax deductible by Kroger.not identical to the group of NEOs. Compensation that is deemed to be “performance-based” is excluded for purposes of the calculation and is tax deductible. Awards under Kroger’s long-term incentive plans,Long-Term Incentive Plans, when payable upon achievement of stated performance criteria, should be considered performance-based and the compensation paid under those plans should be tax deductible. Generally, compensation expense related to stock options awarded to the CEO and the next four most highly compensated officers should be deductible. On the other hand, Kroger’s awards of restricted stock that vest solely upon the passage of time are not performance-based. As a result,
31
compensation expense for those awards to the covered employees is not deductible, to the extent that the related compensation expense, plus any other expense for compensation that is not performance-based, exceeds $1,000,000.
Kroger’s bonus plans rely on performance criteria, andwhich have been approved by shareholders. As a result, bonuses paid under the plans to the covered employees willshould be deductible by Kroger. In Kroger’s case, this group of individuals is not identical to the group of named executive officers.
Kroger’s policy is, primarily, to design and administer compensation plans that support the achievement of long-term strategic objectives and enhance shareholder value. Where it is material and supports Kroger’s compensation philosophy, the Compensation Committee also will attempt to maximize the amount of compensation expense that is deductible by Kroger.
| Compensation Committee Report |
The Compensation Committee has reviewed and discussed with management of the Company the Compensation Discussion and Analysis contained in this proxy statement. Based on its review and discussions with management, the Compensation Committee has recommended to the Company’s Board of Directors that the Compensation Discussion and Analysis be included in the Company’s proxy statement and incorporated by reference into its annual reportAnnual Report on Form 10-K.
Compensation Committee:
Clyde R. Moore, Chair John T. LaMacchia
Jorge P. Montoya
Susan M. Phillips
James A. Runde
2832
Executive Compensation Tables
Summary Compensation Table
The following table showsand footnotes provide information regarding the compensation of the Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and each of the Company’s three most highly compensated executive officers other than the CEO and CFO (the “named executive officers”) duringNEOs for the fiscal years presented:presented.
| Change in | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Value and | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nonqualified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Equity | Deferred | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock | Option | Incentive Plan | Compensation | All Other | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name and Principal | Salary | Bonus | Awards | Awards | Compensation | Earnings | Compensation | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Position | Year | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| David B. Dillon | 2012 | $ | 1,328,320 | — | $ | 3,332,852 | $ | 1,342,088 | $ | 1,619,419 | $ | 3,380,527 | $ | 143,084 | $ | 11,146,290 | ||||||||||||||
| Chairman and CEO | 2011 | $ | 1,273,871 | — | $ | 3,130,540 | $ | 1,716,693 | $ | 2,699,153 | $ | 3,088,686 | $ | 115,600 | $ | 12,024,543 | ||||||||||||||
| 2010 | $ | 1,256,548 | — | $ | 2,070,880 | $ | 1,201,240 | $ | 808,020 | $ | 2,156,625 | $ | 58,027 | $ | 7,551,340 | |||||||||||||||
| J. Michael Schlotman | 2012 | $ | 669,787 | — | $ | 609,908 | $ | 245,602 | $ | 604,250 | $ | 822,669 | $ | 37,543 | $ | 2,989,759 | ||||||||||||||
| Senior Vice President | 2011 | $ | 631,371 | — | $ | 503,801 | $ | 276,269 | $ | 1,002,310 | $ | 990,524 | $ | 31,255 | $ | 3,435,530 | ||||||||||||||
| and CFO | 2010 | $ | 590,295 | — | $ | 225,096 | $ | 130,570 | $ | 277,368 | $ | 578,541 | $ | 13,815 | $ | 1,815,685 | ||||||||||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen | 2012 | $ | 937,732 | — | $ | 1,087,655 | $ | 437,983 | $ | 1,084,975 | $ | 1,415,003 | $ | 44,619 | $ | 5,007,967 | ||||||||||||||
| President and COO | 2011 | $ | 899,113 | — | $ | 1,009,368 | $ | 553,506 | $ | 1,821,903 | $ | 1,768,792 | $ | 38,957 | $ | 6,091,639 | ||||||||||||||
| 2010 | $ | 887,562 | — | $ | 630,268 | $ | 365,595 | $ | 538,680 | $ | 953,159 | $ | 20,875 | $ | 3,396,139 | |||||||||||||||
| Paul W. Heldman | 2012 | $ | 761,501 | — | $ | 551,418 | $ | 222,048 | $ | 650,595 | $ | 1,266,466 | $ | 83,175 | $ | 3,535,203 | ||||||||||||||
| Executive Vice | 2011 | $ | 730,682 | — | $ | 479,075 | $ | 262,710 | $ | 1,110,126 | $ | 1,374,309 | $ | 68,346 | $ | 4,025,248 | ||||||||||||||
| President, Secretary | 2010 | $ | 716,044 | — | $ | 270,115 | $ | 156,684 | $ | 296,274 | $ | 875,646 | $ | 33,777 | $ | 2,348,540 | ||||||||||||||
| and General Counsel | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kathleen S. Barclay(1) | 2012 | $ | 675,972 | — | $ | 491,998 | $ | 148,512 | $ | 630,375 | $ | — | $ | 71,753 | $ | 2,018,610 | ||||||||||||||
| Senior Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name and Principal Position(1) | Fiscal Year | Salary | Stock Awards ($)(2) | Option | Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation ($)(4) | Change in | All Other Compensation ($)(6) | Total ($) | ||||||||||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen | 2015 | 1,216,665 | 4,332,252 | 2,300,092 | 2,999,693 | 618,033 | 279,656 | 11,746,391 | ||||||||||||||
| Chairman and Chief | 2014 | 1,118,726 | 3,740,251 | 1,951,394 | 2,441,546 | 3,498,396 | 232,602 | 12,982,915 | ||||||||||||||
| Executive Officer | 2013 | 962,731 | 5,062,435 | 907,862 | 1,722,946 | 63,518 | 166,329 | 8,885,821 | ||||||||||||||
| J. Michael Schlotman | 2015 | 793,825 | 2,489,148 | 1,040,847 | 1,394,752 | 44,163 | 148,104 | 5,910,839 | ||||||||||||||
| Executive Vice President | 2014 | 745,313 | 1,490,700 | 520,372 | 1,103,750 | 1,922,821 | 113,922 | 5,896,878 | ||||||||||||||
| and Chief Financial | 2013 | 688,599 | 1,564,689 | 509,088 | 1,004,220 | — | 85,176 | 3,851,772 | ||||||||||||||
| Officer | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Michael J. Donnelly | 2015 | 700,684 | 1,919,013 | 585,529 | 1,274,152 | 321,545 | 175,112 | 4,976,035 | ||||||||||||||
| Executive Vice President | 2014 | 651,315 | 748,051 | 390,279 | 1,024,261 | 341,775 | 100,305 | 3,255,986 | ||||||||||||||
| of Merchandising | 2013 | 565,136 | 1,099,201 | 236,283 | 803,052 | 3,744 | 81,557 | 2,778,973 | ||||||||||||||
| Christopher T. Hjelm | 2015 | 653,368 | 1,992,003 | 780,633 | 1,302,852 | 168 | 98,992 | 4,828,016 | ||||||||||||||
| Executive Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| and Chief Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Officer | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Frederick J. Morganthall II | 2015 | 619,944 | 1,595,918 | 390,414 | 1,453,450 | — | 297,335 | 4,357,061 | ||||||||||||||
| Executive Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| of Retail Operations | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | ||
| (2) | ||
| Name | Restricted Stock | Performance Units | ||||
| Mr. McMullen | $3,300,021 | $1,032,231 | ||||
| Mr. Schlotman | $1,979,946 | $509,202 | ||||
| Mr. Donnelly | $1,632,562 | $286,451 | ||||
| Mr. Hjelm | $1,610,062 | $381,941 | ||||
| Mr. Morganthall | $1,404,958 | $190,960 | ||||
The grant date fair value of the performance units reflected in the stock awards column and in the table above is computed based on the probable outcome of the performance conditions as of the grant date. This amount is consistent with the estimate of aggregate compensation cost to be recognized by the Company over the three-year performance period of the award determined as of the grant date under FASB ASC Topic 718, excluding the effect of estimated forfeitures. The assumptions used in calculating the valuations are set forth in Note 12 to the consolidated financial statements in Kroger’s 10-K for fiscal year 2015.
33
Assuming that the highest level of performance conditions is achieved, the aggregate fair value of the 2015 performance unit awards at the grant date is as follows:
| Value of Performance Units | |||||
| Name | Assuming Maximum Performance | ||||
| Mr. McMullen | $ | 2,064,462 | |||
Mr. Schlotman | $ | 1,018,403 | |||
| Mr. Donnelly | $ | 572,901 | |||
| Mr. Hjelm | $ | 763,881 | |||
| Mr. Morganthall | $ | 381,921 | |||
| (3) | These amounts represent the aggregate grant date fair value of option awards computed in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718. The assumptions used in calculating the valuations are set forth in Note 12 to the consolidated financial statements in Kroger’s 10-K for fiscal year 2015. |
| (4) | Non-equity incentive plan compensation earned for 2015 consists of amounts earned under the 2015 performance-based annual cash bonus program and the 2013 Long-Term Incentive Plan. The amount reported for Mr. Morganthall also includes the 2015 amount earned under the Harris Teeter Merger Cash Bonus Plan (described below). |
| Long-Term Cash | Harris Teeter | |||||||||||||
| Name | Annual Cash Bonus | Bonus | Merger Bonus | |||||||||||
| Mr. McMullen | $ | 2,060,093 | $ | 939,600 | N/A | |||||||||
| Mr. Schlotman | $ | 723,652 | $ | 671,100 | N/A | |||||||||
| Mr. Donnelly | $ | 723,652 | $ | 550,500 | N/A | |||||||||
| Mr. Hjelm | $ | 723,652 | $ | 579,200 | N/A | |||||||||
| Mr. Morganthall | $ | 645,010 | $ | 369,083 | $439,357 | |||||||||
In accordance with the terms of the 2015 performance-based annual cash bonus program, Kroger paid 126.7% of bonus potentials for the participants, including the NEOs. These amounts were earned with respect to performance in 2015 and paid in March 2016. Mr. Morganthall’s annual cash bonus payout was calculated by using the Harris Teeter formula for the 17 weeks he was a Harris Teeter officer and the Kroger formula for the remainder of the year when he was a Kroger officer.
The long-term cash bonus awarded under the 2013 Long-Term Incentive Plan is a performance-based bonus plan designed to reward participants for improving the long-term performance of the Company. The plan covered performance during fiscal years 2013, 2014 and 2015 and amounts earned under the plan were paid in March 2016. In accordance with the terms of the plan, participants earned and Kroger paid 100% of long-term cash bonus potentials. The long-term cash bonus potential equaled the participant’s salary in effect on the last day of fiscal 2012, and for Mr. Morganthall, the day he became eligible for the plan.
Amounts for Mr. Morganthall also include $439,357 for 2015 performance under The Harris Teeter Merger Cash Bonus Plan. This plan is a performance-based bonus plan designed to reward participants for achieving synergies over the three year period following the merger between Harris Teeter and Kroger, fiscal years 2014, 2015 and 2016. Payouts are made following the end of each fiscal year of amounts earned based on that year’s performance, subject to a maximum payout over the three-year period of 200% of the participant’s bonus potential. The bonus potential is equal to the participant’s salary in effect on the date of the merger. In March 2016, Mr. Morganthall received $439,357 for 2015 performance.
34
| (5) | For 2015, the amounts reported consist of the aggregate change in the actuarial present value of the NEO’s accumulated benefit under a defined benefit pension plan (including supplemental plans), which applies to all eligible NEOs, and preferential earnings on nonqualified deferred compensation, which applies to Messrs. McMullen, Donnelly and Hjelm: |
| Change in | Preferential Earnings on Nonqualified | ||||||||||
| Name | Pension Value | Deferred Compensation | |||||||||
| Mr. McMullen | $ | 537,941 | $ | 80,092 | |||||||
| Mr. Schlotman | $ | 44,163 | N/A | ||||||||
| Mr. Donnelly | $ | 316,969 | $ | 4,576 | |||||||
| Mr. Hjelm | $ | (1,142 | ) | $ | 168 | ||||||
| Mr. Morganthall | $ | (429,556 | ) | N/A | |||||||
The change in value of the accumulated pension benefit for each of Messrs. Hjelm and Morganthall are not included in the table because the value decreased.
Amounts reported for 2015 and 2014 include the change in the actuarial present value of accumulated pension benefits and preferential earnings on nonqualified deferred compensation. Amounts reported for 2013 include only preferential earnings on nonqualified deferred compensation because the changes in pension value were negative, which are not required to be reported in the table in accordance with SEC rules. Pension values may fluctuate significantly from year to year depending on a number of factors, including age, years of service, average annual earnings and the assumptions used to determine the present value, such as the discount rate. The change in the actuarial present value of accumulated pension benefits for 2014 was significantly greater than 2013 primarily due to a lower discount rate and revised mortality assumptions. The change in the actuarial present value of accumulated pension benefits for 2015 is primarily due to a lower discount rate. Please see the Pension Benefits section for further information regarding the assumptions used in calculating pension benefits.
Messrs. McMullen, Donnelly and Hjelm participate in Kroger’s nonqualified deferred compensation plan. Under the plan, deferred compensation earns interest at a rate representing Kroger’s cost of ten-year debt, as determined by the CEO and approved by the Compensation Committee prior to the beginning of each deferral year. For each participant, a separate deferral account is created each year and the interest rate established for that year is applied to that deferral account until the deferred compensation is paid out. If the interest rate established by Kroger for a particular year exceeds 120% of the applicable federal long-term interest rate that corresponds most closely to the plan rate, the amount by which the plan rate exceeds 120% of the corresponding federal rate is deemed to be above-market or preferential. In thirteen of the twenty-two years in which at least one NEO deferred compensation, the rate set under the plan for that year exceeds 120% of the corresponding federal rate. For each of the deferral accounts in which the plan rate is deemed to be above-market, Kroger calculates the amount by which the actual annual earnings on the account exceed what the annual earnings would have been if the account earned interest at 120% of the corresponding federal rate, and discloses those amounts as preferential earnings. Amounts deferred in 2015 earn interest at a rate lower than 120% of the corresponding federal rate; accordingly there are no preferential earnings on these amounts. In 2015, Mr. Morganthall participated in the Harris Teeter Supermarkets, Inc.Flexible Deferral Plan (the “HT Flexible Deferral Plan”), which does not provide above-market or preferential earnings on deferred compensation.
35
| (6) | Amounts reported in the “All Other Compensation” column for 2015 include: the dollar value of premiums paid by the Company for life insurance, Company contributions to defined contribution retirement plans, dividend equivalents paid on earned performance units, dividends paid on unvested restricted stock and other benefits. The following table identifies the perquisites and other compensation for 2015 that are required to be quantified by SEC rules. |
| Name | Life Insurance Premiums | Retirement Plan Contributions(a) | Payment of Dividend Equivalents on Earned Performance Units | Dividends Paid on Unvested Restricted Stock | Other(b) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mr. McMullen | $ | 76,340 | — | $ | 50,791 | $ | 152,525 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Mr. Schlotman | $ | 60,878 | — | $ | 28,481 | $ | 58,745 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Mr. Donnelly | $ | 54,525 | $ | 69,169 | $ | 13,219 | $ | 38,199 | — | ||||||||||||||
| Mr. Hjelm | $ | 36,781 | $ | 12,867 | $ | 13,219 | $ | 36,125 | — | ||||||||||||||
| Mr. Morganthall | $ | 20,940 | $ | 34,466 | $ | 6,689 | $ | 61,583 | $ | 173,657 | |||||||||||||
| (a) | Retirement plan contributions.The Company makes automatic and matching contributions to NEOs’ accounts under the applicable defined contribution plan on the same terms and using the same formulas as |
●Mr. Donnelly – $13,603 to the Dillon Companies, Inc. Employees’ Profit Sharing Plan and $55,566 to the Dillon Companies, Inc. Excess Benefit Profit Sharing Plan; | |
●Mr. Hjelm – $12,867 to The Kroger Co. 401(k) Retirement Savings Account Plan, which includes a $2,000 automatic Company contribution; and | |
●Mr. Morganthall – $20,991 to the Harris Teeter Supermarkets, Inc. Retirement and Savings Plan, which includes a $13,000 automatic Company contribution, and $13,475 to the Harris Teeter Supermarkets, Inc. Flexible Deferral Plan. | |
| (b) | Other.For each of Messrs. McMullen, Schlotman, Donnelly and Hjelm the total amount of other benefits provided was less than $10,000. |
| For Mr. Morganthall, this amount includes the dollar value of insurance premiums paid by the | |
36
2015 Grants of Plan-Based Awards
The following table provides information about equity and non-equity incentive awards granted to the NEOs in 2015.
| Name | Grant Date | Estimated Future Payouts Under Non-Equity Incentive Plan Awards | Estimated Future Payouts Under Equity Incentive Plan Awards | All Other Stock Awards: Number of Shares of Stock or Units (#)(4) | All Other Option Awards: Number of Securities Underlying Options (#)(5) | Exercise or Base Price of Option Awards ($/Sh) | Grant Date Fair Value of Stock and Option Awards | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Target ($) | Maximum ($) | Target | Maximum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| W. Rodney | $ | 1,625,962 | (1) | $ | 3,251,924 | (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| McMullen | $ | 600,000 | (2) | $ | 1,200,000 | (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 86,095 | $ | 3,300,021 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 235,415 | $ | 38.33 | $ | 2,300,092 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 26,090 | (3) | 52,179 | (3) | $ | 1,032,231 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| J. Michael | $ | 571,154 | (1) | $ | 1,142,308 | (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Schlotman | $ | 380,000 | (2) | $ | 760,000 | (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 38,610 | $ | 1,479,921 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9/17/2015 | 13,334 | $ | 500,025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 106,531 | $ | 38.33 | $ | 1,040,847 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 12,870 | (3) | 25,740 | (3) | $ | 509,202 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Michael J. | $ | 571,154 | (1) | $ | 1,142,308 | (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Donnelly | $ | 331,450 | (2) | $ | 662,900 | (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 29,547 | $ | 1,132,537 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9/17/2015 | 13,334 | $ | 500,025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 59,929 | $ | 38.33 | $ | 585,529 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 7,240 | (3) | 14,480 | (3) | $ | 286,451 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Christopher T. | $ | 571,154 | (1) | $ | 1,142,308 | (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hjelm | $ | 310,000 | (2) | $ | 620,000 | (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 28,960 | $ | 1,110,037 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9/17/2015 | 13,334 | $ | 500,025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 79,898 | $ | 38.33 | $ | 780,633 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 9,654 | (3) | 19,307 | (3) | $ | 381,941 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Frederick J. | $ | 577,769 | (1) | $ | 1,155,538 | (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Morganthall II | $ | 285,117 | (2) | $ | 570,234 | (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 23,609 | $ | 904,933 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9/17/2015 | 13,334 | $ | 500,025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 39,959 | $ | 38.33 | $ | 390,414 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/15/2015 | 4,827 | (3) | 9,653 | (3) | $ | 190,960 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | These amounts relate to the 2015 performance-based annual cash bonus plan. The amount listed under “Target” represents the annual cash bonus potential of the NEO. By the terms of the plan, payouts are limited to no more than 200% of a participant’s annual cash bonus potential; accordingly, the amount listed under “Maximum” equals two times that officer’s annual cash bonus potential amount. In the event that a participant’s annual cash bonus potential is |
37
| (2) | These amounts relate to the long-term cash bonus potential issued under 2015 Long-Term Incentive Plan, which covers performance during fiscal years 2015, 2016 and 2017. The long-term cash bonus potential amount equals the annual base salary of the NEOs as of the last day of fiscal 2014 (or date of plan entry, if later). By the terms of the plan, payouts are limited to no more than 100% of a participant’s long-term cash bonus potential; accordingly, the amount listed under “Maximum” equals the participant’s long-term cash bonus potential. Because the actual payout is based on the level of performance achieved, the target amount is not determinable and therefore the amount listed under “Target” is a representative amount based on the probable outcome of the performance conditions. | |
| (3) | These amounts | |
| (4) | These amounts represent the number of shares of restricted stock granted in 2015. The aggregate grant date fair value reported in the last column is calculated in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718. | |
29
30
| Accidental Death and | ||||||||||||||||
| Life Insurance | Dismemberment | Long-Term Disability | ||||||||||||||
| Premium | Insurance Premium | Insurance Premium | Gift | |||||||||||||
| Mr. Dillon | $ | 142,657 | $228 | — | $ | 199 | ||||||||||
| Mr. Schlotman | $ | 37,116 | $228 | — | $ | 199 | ||||||||||
| Mr. McMullen | $ | 41,414 | $228 | $ | 2,778 | $ | 199 | |||||||||
| Mr. Heldman | $ | 79,970 | $228 | $ | 2,778 | $ | 199 | |||||||||
| Ms. Barclay | $ | 71,326 | $228 | — | $ | 199 | ||||||||||
Grants of Plan-Based Awards
The following table provides information about equity and non-equity awards granted to the named executive officers in 2012:
| Estimated Future | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Payouts Under | Estimated Future | Exercise | Grant | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Equity | Payouts Under | or Base | Date Fair | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Incentive Plan | Equity Incentive | Price of | Value of | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Awards | Plan Awards | Option | Stock and | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Grant | Target | Maximum | Target | Maximum | Awards | Option | ||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Date | ($) | ($) | (#) | (#) | ($/Sh) | Awards | |||||||||||||||||
| David B. Dillon | $ | 1,500,000 | (1) | $ | 3,000,000 | (1) | ||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 1,290,000 | (2) | $ | 1,290,000 | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 111,968 | (3) | $ | 2,458,817 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 298,580 | (4) | $ | 21.96 | (4) | $ | 1,342,088 | |||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 36,949 | (5) | 74,645 | (5) | $ | 874,035 | (5) | |||||||||||||||||
| J. Michael Schlotman | $ | 550,000 | (1) | $ | 1,100,000 | (1) | ||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 650,000 | (2) | $ | 650,000 | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 20,490 | (3) | $ | 449,960 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 54,640 | (4) | $ | 21.96 | (4) | $ | 245,601 | |||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 6,762 | (5) | 13,660 | (5) | $ | 159,948 | (5) | |||||||||||||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen | $ | 1,000,000 | (1) | $ | 2,000,000 | (1) | ||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 910,000 | (2) | $ | 910,000 | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 36,540 | (3) | $ | 802,418 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 97,440 | (4) | $ | 21.96 | (4) | $ | 437,983 | |||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 12,058 | (5) | 24,360 | (5) | $ | 285,237 | (5) | |||||||||||||||||
| Paul W. Heldman | $ | 550,000 | (1) | $ | 1,100,000 | (1) | ||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 739,000 | (2) | $ | 739,000 | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 18,525 | (3) | $ | 406,809 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 49,400 | (4) | $ | 21.96 | (4) | $ | 222,048 | |||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 6,113 | (5) | 12,350 | (5) | $ | 144,609 | (5) | |||||||||||||||||
| Kathleen S. Barclay | $ | 550,000 | (1) | $ | 1,100,000 | (1) | ||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 656,000 | (2) | $ | 656,000 | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 18,000 | (3) | $ | 395,280 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 33,040 | (4) | $ | 21.96 | (4) | $ | 148,512 | |||||||||||||||||
| 7/12/2012 | 4,089 | (5) | 8,260 | (5) | $ | 96,718 | (5) | |||||||||||||||||
31
The Compensation Committee, of the Board of Directors, and the independent members of the Board in the case of the CEO, established the bonus potentials shown in this table as “target”“Target” amounts for the performance-based annual cash bonus awards, and established the amounts shown in this table as “Maximum” amounts for the long-term cash bonus awards forand the named executive officers.performance unit awards. Amounts wereare payable to the extent that performance metmeets specific objectivesperformance goals established by the Compensation Committee at the beginning of the performance period. As described in the Compensation Discussion and Analysis, actual earnings under the annual performance-based cash bonus canplan may exceed the target amountsamount if the Company’s performance exceeds the thresholds.performance goals, but are limited to 200% of the target amount. The Compensation Committee, of the Board of Directors, and the independent members of the Board in the case of the CEO, also determined the number of performance units to be awarded to each named executive officer,NEO, under which common shares are earned to the extent performance meets specific objectives established at the beginning of the performance period. The performance units and the long-term cash bonus awards are more particularly described in the Compensation Discussion and Analysis.
Restrictions on restricted stock awards madeawarded to the named executive officersNEOs normally lapse, asso long as the officer is then in our employ, in equal amounts on each of the first five anniversaries of the grant date, except that the awards granted to Messrs. Schlotman, Donnelly, Hjelm and Morganthall on 9/17/2015 and 9,132 shares of the award is made, except that: (1) 70,000 shares awardedgranted to Mr. McMullen in 2009 vest as follows: 15,000 sharesMorganthall on 6/25/2012, 20,000 shares on 6/25/2013, and 35,000 shares on 6/25/2014; (2) 30,000 shares awarded to Mr. Heldman in 2008 vest as follows: 6,000 shares on 6/26/2011, 12,000 shares on 6/26/2012, and 12,000 shares on 6/26/2013; (3) 111,986 shares awarded to Mr. Dillon in 20127/15/15 vest in equal amounts on each of the four anniversaries of the date the award was made; and (4) 18,000 shares awarded to Ms. Barclay in 2012 vest in equal amounts on each of thefirst three anniversaries of the date the award was made.grant date. Any dividends declared on Kroger common shares are payable on unvested restricted stock. Nonqualified stock options granted to the named executive officersNEOs normally vest, so long as the officer is then in our employ, in equal amounts on each of the first five anniversaries of the date of grant. Those options were granted at the fair market value of Kroger common shares on the date of the grant. Options are granted only on one of the four dates of Compensation Committee meetings conducted after Kroger’s public release of its quarterly earnings results.grant date.
3238
2015 Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End
The following table disclosesprovides information about outstanding equity-based incentive compensation awards for the named executive officersNEOs as of the end of fiscal year 2012. Each outstanding award is shown separately. Option awards made through 2002 included performance-based nonqualified stock options.2015. The vesting schedule for each award is described in the footnotes to this table. MarketThe market value of unvested sharesrestricted stock and unearned performance units is based on Kroger’sthe closing stock price of $27.89Kroger’s common shares of $38.81 on February 1, 2013,January 29, 2016, the last trading day of the 2012 fiscal year.2015.
| Option Awards | Stock Awards | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity | Equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity | Incentive | Incentive | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incentive | Plan | Plan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plan | Awards: | Awards: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Awards: | Market | Number of | Market or | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of | Number of | Number of | Value of | Unearned | Payout Value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Securities | Securities | Securities | Number of | Shares or | Shares, | of Unearned | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Underlying | Underlying | Underlying | Shares or | Units of | Units or | Shares, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unexercised | Unexercised | Unexercised | Option | Units of Stock | Stock That | Other | Units or | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Options | Options | Unearned | Exercise | Option | That Have | Have Not | Rights That | Other Rights | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (#) | (#) | Options | Price | Expiration | Not Vested | Vested | Have | That Have | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Exercisable | Unexercisable | (#) | ($) | Date | (#) | ($) | Not Vested | Not Vested | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| David B. Dillon | 300,000 | $ | 16.39 | 5/5/2015 | 23,000 | (6) | $ | 641,470 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 240,000 | $ | 19.94 | 5/4/2016 | 46,000 | (7) | $ | 1,282,940 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 220,000 | $ | 28.27 | 6/28/2017 | 51,750 | (8) | $ | 1,443,308 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 180,000 | 45,000 | (1) | $ | 28.61 | 6/26/2018 | 85,080 | (9) | $ | 2,372,881 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 135,000 | 90,000 | (2) | $ | 22.34 | 6/25/2019 | 111,968 | (10) | $ | 3,122,788 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 92,000 | 138,000 | (3) | $ | 20.16 | 6/24/2020 | 39,704 | (14) | $ | 1,169,680 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 56,720 | 226,880 | (4) | $ | 24.74 | 6/23/2021 | 36,949 | (15) | $ | 1,093,144 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 298,580 | (5) | $ | 21.96 | 7/12/2022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| J. Michael Schlotman | 17,250 | $ | 17.31 | 5/6/2014 | 2,000 | (6) | $ | 55,780 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40,000 | $ | 16.39 | 5/5/2015 | 4,000 | (7) | $ | 111,560 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20,000 | $ | 19.94 | 5/4/2016 | 5,625 | (8) | $ | 156,881 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20,000 | $ | 28.27 | 6/28/2017 | 13,692 | (9) | $ | 381,870 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16,000 | 4,000 | (1) | $ | 28.61 | 6/26/2018 | 20,490 | (11) | $ | 571,466 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12,000 | 8,000 | (2) | $ | 22.34 | 6/25/2019 | 6,390 | (14) | $ | 188,238 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10,000 | 15,000 | (3) | $ | 20.16 | 6/24/2020 | 6,762 | (15) | $ | 200,045 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9,128 | 36,512 | (4) | $ | 24.74 | 6/23/2021 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 54,640 | (5) | $ | 21.96 | 7/12/2022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen | 75,000 | $ | 17.31 | 5/6/2014 | 7,000 | (6) | $ | 195,230 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 75,000 | $ | 16.39 | 5/5/2015 | 55,000 | (12) | $ | 1,533,950 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 60,000 | $ | 19.94 | 5/4/2016 | 14,000 | (7) | $ | 390,460 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 60,000 | $ | 28.27 | 6/28/2017 | 15,750 | (8) | $ | 439,268 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 52,000 | 13,000 | (1) | $ | 28.61 | 6/26/2018 | 27,432 | (9) | $ | 765,078 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 39,000 | 26,000 | (2) | $ | 22.34 | 6/25/2019 | 36,540 | (11) | $ | 1,019,101 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28,000 | 42,000 | (3) | $ | 20.16 | 6/24/2020 | 12,802 | (14) | $ | 377,135 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18,288 | 73,152 | (4) | $ | 24.74 | 6/23/2021 | 12,058 | (15) | $ | 356,742 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 97,440 | (5) | $ | 21.96 | 7/12/2022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Option Awards | Stock Awards | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options Exercisable (#) | Number of | Option | Option Expiration Date | Number of Shares or Units of Stock That Have Not Vested (#) | Market Value | Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Number of Unearned Shares, Units or Other Rights That Have Not Vested (#) | Equity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| W. Rodney | 120,000 | — | $ | 9.97 | 5/4/2016 | 13,716 | (6) | 532,318 | 73,875 | (16) | 2,952,414 | (16) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| McMullen | 120,000 | — | $ | 14.14 | 6/28/2017 | 29,232 | (7) | 1,134,494 | 26,090 | (17) | 1,044,754 | (17) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 130,000 | — | $ | 14.31 | 6/26/2018 | 43,848 | (8) | 1,701,741 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 130,000 | — | $ | 11.17 | 6/25/2019 | 96,000 | (9) | 3,725,760 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 140,000 | — | $ | 10.08 | 6/24/2020 | 90,000 | (10) | 3,492,900 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 146,304 | 36,576 | (1) | $ | 12.37 | 6/23/2021 | 86,095 | (11) | 3,341,347 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 116,928 | 77,952 | (2) | $ | 10.98 | 7/12/2022 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 77,952 | 116,928 | (3) | $ | 18.88 | 7/15/2023 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 60,000 | 240,000 | (4) | $ | 24.67 | 7/15/2024 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | 235,415 | (5) | $ | 38.33 | 7/15/2025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| J. Michael | 50,000 | — | $ | 10.08 | 6/24/2020 | 6,846 | (6) | 265,693 | 19,700 | (16) | 787,311 | (16) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Schlotman | 73,024 | 18,256 | (1) | $ | 12.37 | 6/23/2021 | 16,392 | (7) | 636,174 | 12,870 | (17) | 515,379 | (17) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 65,568 | 43,712 | (2) | $ | 10.98 | 7/12/2022 | 24,588 | (8) | 954,260 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 43,712 | 65,568 | (3) | $ | 18.88 | 7/15/2023 | 13,000 | (12) | 504,530 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16,000 | 64,000 | (4) | $ | 24.67 | 7/15/2024 | 16,000 | (13) | 620,960 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | 106,531 | (5) | $ | 38.33 | 7/15/2025 | 24,000 | (10) | 931,440 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 38,610 | (11) | 1,498,454 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13,334 | (14) | 517,493 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Michael J. | 40,000 | — | $ | 14.14 | 6/28/2017 | 4,804 | (6) | 186,443 | 14,775 | (16) | 590,483 | (16) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Donnelly | 40,000 | — | $ | 14.31 | 6/26/2018 | 7,608 | (7) | 295,266 | 7,240 | (17) | 289,926 | (17) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40,000 | — | $ | 11.17 | 6/25/2019 | 14,412 | (8) | 559,330 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40,000 | — | $ | 10.08 | 6/24/2020 | 13,000 | (12) | 504,530 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 56,576 | 14,144 | (1) | $ | 12.37 | 6/23/2021 | 18,000 | (10) | 698,580 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30,432 | 20,288 | (2) | $ | 10.98 | 7/12/2022 | 29,547 | (11) | 1,146,719 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20,288 | 30,432 | (3) | $ | 18.88 | 7/15/2023 | 13,334 | (14) | 517,493 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12,000 | 48,000 | (4) | $ | 24.67 | 7/15/2024 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | 59,929 | (5) | $ | 38.33 | 7/15/2025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Christopher T. | 8,000 | — | $ | 14.31 | 6/26/2018 | 3,804 | (6) | 147,633 | 14,775 | (16) | 590,483 | (16) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hjelm | 16,000 | — | $ | 11.17 | 6/25/2019 | 7,608 | (7) | 295,266 | 9,654 | (17) | 386,574 | (17) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24,000 | — | $ | 10.08 | 6/24/2020 | 11,412 | (8) | 442,900 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30,432 | 10,144 | (1) | $ | 12.37 | 6/23/2021 | 13,000 | (12) | 504,530 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30,432 | 20,288 | (2) | $ | 10.98 | 7/12/2022 | 18,000 | (10) | 698,580 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20,288 | 30,432 | (3) | $ | 18.88 | 7/15/2023 | 28,960 | (11) | 1,123,938 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12,000 | 48,000 | (4) | $ | 24.67 | 7/15/2024 | 13,334 | (14) | 517,493 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | 79,898 | (5) | $ | 38.33 | 7/15/2025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Frederick J. | — | 39,959 | (5) | $ | 38.33 | 7/15/2025 | 75,778 | (15) | 2,940,944 | 13,445 | (16) | 537,339 | (16) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Morganthall II | 34,710 | (10) | 1,347,095 | 4,827 | (17) | 193,277 | (17) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9,132 | (8) | 354,413 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14,477 | (11) | 561,852 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13,334 | (14) | 517,493 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3339
| Option Awards | Stock Awards | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity | Equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity | Incentive | Incentive | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incentive | Plan | Plan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plan | Awards: | Awards: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Awards: | Market | Number of | Market or | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of | Number of | Number of | Value of | Unearned | Payout Value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Securities | Securities | Securities | Number of | Shares or | Shares, | of Unearned | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Underlying | Underlying | Underlying | Shares or | Units of | Units or | Shares, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unexercised | Unexercised | Unexercised | Option | Units of Stock | Stock That | Other | Units or | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Options | Options | Unearned | Exercise | Option | That Have | Have Not | Rights That | Other Rights | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (#) | (#) | Options | Price | Expiration | Not Vested | Vested | Have | That Have | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Exercisable | Unexercisable | (#) | ($) | Date | (#) | ($) | Not Vested | Not Vested | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paul W. Heldman | 40,000 | $ | 17.31 | 5/6/2014 | 2,500 | (6) | $ | 69,725 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40,000 | $ | 16.39 | 5/5/2015 | 12,000 | (6) | $ | 334,680 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25,000 | $ | 19.94 | 5/4/2016 | 5,000 | (7) | $ | 139,450 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25,000 | $ | 28.27 | 6/28/2017 | 6,750 | (8) | $ | 188,258 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20,000 | 5,000 | (1) | $ | 28.61 | 6/26/2018 | 13,020 | (9) | $ | 363,128 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15,000 | 10,000 | (2) | $ | 22.34 | 6/25/2019 | 18,525 | (11) | $ | 516,662 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12,000 | 18,000 | (3) | $ | 20.16 | 6/24/2020 | 6,076 | (14) | $ | 178,999 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8,680 | 34,720 | (4) | $ | 24.74 | 6/23/2021 | 6,113 | (15) | $ | 180,861 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 49,400 | (5) | $ | 21.96 | 7/12/2022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kathleen S. Barclay | 25,000 | $ | 20.06 | 12/10/2019 | 5,625 | (8) | $ | 156,881 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10,000 | 15,000 | (3) | $ | 20.16 | 6/24/2020 | 9,912 | (9) | $ | 276,446 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6,608 | 26,432 | (4) | $ | 24.74 | 6/23/2021 | 18,000 | (13) | $ | 502,020 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33,040 | (5) | $ | 21.96 | 7/12/2022 | 4,626 | (14) | $ | 136,270 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4,089 | (15) | $ | 120,964 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Stock options vest on 6/ | |
| (2) | ||
| Stock options vest in equal amounts on 7/12/ | ||
| (3) | Stock options vest in equal amounts on 7/ | |
| (4) | Stock options vest in equal amounts on 7/15/2016, 7/15/2017, 7/15/2018 and 7/15/2019. | |
| (5) | Stock options vest in equal amounts on 7/15/2016, 7/15/2017, 7/15/2018, 7/15/2019 and 7/15/2020. | |
| (6) | Restricted stock vests on 6/23/2016. | |
| (7) | Restricted stock vests in equal amounts on 7/12/2016 and 7/12/2017. | |
| (8) | ||
| Restricted stock vests in equal amounts on 7/ | ||
| Restricted stock vests in equal amounts on 12/12/2016, 12/12/2017 and 12/12/2018. | ||
| (10) | Restricted stock vests in equal amounts on 7/ | |
| (11) | Restricted stock vests in equal amounts on 7/ | |
34
| (12) | Restricted stock vests on 12/12/2016. | |
| (13) | Restricted stock vests as follows: 4,000 shares on 7/15/2016 and 12,000 shares on 7/15/2017. | |
| (14) | Restricted stock vests in equal amounts on 9/17/2016, 9/17/2017 and 9/17/2018. | |
| (15) | Restricted stock vests in equal amounts on 1/30/2017, 1/30/2018 and 1/30/2019. | |
| (16) | Performance units granted under the 2014 Long-Term Incentive Plan are earned as of the last day of fiscal | |
| (17) | Performance units granted under the 2015 Long-Term Incentive Plan are earned as of the last day of fiscal | |
From 1997 through 2002, Kroger granted to the named executive officers performance-based nonqualified stock options. These options, having a term of ten years, vest six months prior to their date of expiration unless earlier vesting because Kroger’s stock price achieved the specified annual rate of appreciation set forth in the stock option agreement. That rate ranged from 13% to 16%. All performance-based options have vested and have expired if not earlier exercised.
2015 Option Exercises and Stock Vested
The following table provides theinformation for 2015 regarding stock options exercised, and restricted stock vested, during 2012, as well asand common shares issued to the executivesNEOs pursuant to performance units awarded in 2010.earned under the 2013 Long-Term Incentive Plan.
| 2012 OPTION EXERCISES AND STOCK VESTED | ||||||||||||||||||
| Option Awards(1) | Stock Awards(2) | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of | Number of | |||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Shares | |||||||||||||||||
| Acquired | Value Realized | Acquired | Value Realized | |||||||||||||||
| on Exercise | on Exercise | on Vesting | on Vesting | |||||||||||||||
| Name | (#) | ($) | (#) | ($) | ||||||||||||||
| David B. Dillon | 510,000 | $ | 4,916,550 | 120,751 | $ | 2,874,530 | ||||||||||||
| J. Michael Schlotman | 22,750 | $ | 199,290 | 12,845 | $ | 306,302 | ||||||||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen | 150,000 | $ | 1,721,700 | 51,439 | $ | 1,208,059 | ||||||||||||
| Paul W. Heldman | 120,000 | $ | 840,400 | 26,861 | $ | 625,328 | ||||||||||||
| Kathleen S. Barclay | — | — | 32,900 | $ | 839,961 | |||||||||||||
| Option Awards(1) | Stock Awards(2) | |||||||||||||||||
| Name | Number of Shares Acquired on Exercise (#) | Value Realized on Exercise ($) | Number of Shares Acquired on Vesting (#) | Value Realized on Vesting ($) | ||||||||||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen | 150,000 | $ | 4,141,875 | 156,668 | $ | 6,019,970 | ||||||||||||
| J. Michael Schlotman | — | — | 70,808 | $ | 2,696,280 | |||||||||||||
| Michael J. Donnelly | 36,000 | $ | 1,124,280 | 43,426 | $ | 1,668,288 | ||||||||||||
| Christopher T. Hjelm | — | — | 41,426 | $ | 1,593,233 | |||||||||||||
| Frederick J. Morganthall II | — | — | 43,034 | $ | 1,656,157 | |||||||||||||
| (1) |
40
| (2) | The Stock Awards columns include vested restricted stock and earned performance units, as follows: |
| Vested Restricted Stock | Earned Performance Units | |||||||||||||
| Name | Number of Shares | Value Realized | Number of Shares | Value Realized | ||||||||||
| Mr. McMullen | 107,948 | $ | 4,181,764 | 48,720 | $ | 1,838,206 | ||||||||
| Mr. Schlotman | 43,488 | $ | 1,665,496 | 27,320 | $ | 1,030,784 | ||||||||
| Mr. Donnelly | 30,746 | $ | 1,189,872 | 12,680 | $ | 478,416 | ||||||||
| Mr. Hjelm | 28,746 | $ | 1,114,817 | 12,680 | $ | 478,416 | ||||||||
| Mr. Morganthall | 33,934 | $ | 1,312,814 | 9,100 | $ | 343,343 | ||||||||
Restricted stock. The table includes the number of shares acquired upon vesting of restricted stock and the value realized on the vesting of restricted stock.
Performance Units. In 2013, participants in the 2013 Long-Term Incentive Plan were awarded performance units that were earned based on performance criteria established by the Compensation Committee at the beginning of the three-year performance period. Actual payouts were based on the level of performance achieved, and were paid in common shares. The number of common shares issued and the value realized based on the closing price of Kroger common shares of $37.73 on March 10, 2016, the date of deemed delivery of the shares, are reflected in the table above.
2015 Pension Benefits
The following table provides information regarding pension benefits for the NEOs as of the last day of 2015.
| Name | Plan Name | Number of Years Credited Service (#) | Present Value of Accumulated Benefit ($)(1) | ||||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen | Kroger Consolidated Retirement Benefit Plan | 30 | $ | 1,070,880 | |||||||
| Kroger Excess Benefit Plan | 30 | $ | 10,276,024 | ||||||||
| J. Michael Schlotman | Kroger Consolidated Retirement Benefit Plan | 30 | $ | 1,169,438 | |||||||
| Kroger Excess Benefit Plan | 30 | $ | 5,457,400 | ||||||||
| Michael J. Donnelly | Kroger Consolidated Retirement Benefit Plan | 36 | $ | 244,532 | |||||||
| Kroger Excess Benefit Plan | 36 | $ | 3,241,033 | ||||||||
| Christopher T. Hjelm | Kroger Consolidated Retirement Benefit Plan | — | (2) | $ | 10,086 | ||||||
| Frederick J. Morganthall II | Harris Teeter Employees’ Pension Plan | 29 | $ | 975,455 | |||||||
| Harris Teeter Supplemental Executive | |||||||||||
| Retirement Plan | 29 | $ | 8,044,875 | ||||||||
| (1) | The discount rate used to determine the present values was 4.66% for the Kroger and Dillon plans, 4.65% for the Harris Teeter Supermarkets, Inc. Employees’ Pension Plan (the “HT Pension Plan”) and 4.40% for the Harris Teeter Supermarkets, Inc. Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (the “HT SERP”), which are the same rates used at the measurement date for financial reporting purposes. Additional assumptions used in calculating the present values are set forth in Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements in Kroger’s 10-K for 2015. |
| (2) | The |
3541
Kroger Pension BenefitsPlan and Excess Plan
The following table provides information on pension benefits as of 2012 year-end for the named executive officers.
| 2012 PENSION BENEFITS | ||||||||||||||
| Number | Present | Payments | ||||||||||||
| of Years | Value of | During | ||||||||||||
| Credited | Accumulated | Last Fiscal | ||||||||||||
| Service | Benefit | Year | ||||||||||||
| Name | Plan Name | (#) | ($) | ($) | ||||||||||
| David B. Dillon | The Kroger Consolidated Retirement Benefit Plan | 17 | $ | 756,583 | $ | 0 | ||||||||
| The Kroger Co. Excess Benefit Plan | 17 | $ | 9,996,939 | $ | 0 | |||||||||
| Dillon Companies, Inc. Excess Benefit Pension Plan | 20 | $ | 9,810,803 | $ | 0 | |||||||||
| J. Michael Schlotman | The Kroger Consolidated Retirement Benefit Plan | 27 | $ | 914,191 | $ | 0 | ||||||||
| The Kroger Co. Excess Benefit Plan | 27 | $ | 3,844,299 | $ | 0 | |||||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen | The Kroger Consolidated Retirement Benefit Plan | 27 | $ | 836,023 | $ | 0 | ||||||||
| The Kroger Co. Excess Benefit Plan | 27 | $ | 6,997,019 | $ | 0 | |||||||||
| Paul W. Heldman | The Kroger Consolidated Retirement Benefit Plan | 30 | $ | 1,343,141 | $ | 0 | ||||||||
| The Kroger Co. Excess Benefit Plan | 30 | $ | 7,020,108 | $ | 0 | |||||||||
Messrs. Dillon,McMullen, Schlotman, McMullenDonnelly and HeldmanHjelm participate in The Kroger Consolidated Retirement Benefit Plan (the “Consolidated“Kroger Pension Plan”), which is a qualified defined benefit pension plan. Messrs. McMullen, Schlotman and Donnelly also participate in The ConsolidatedKroger Co. Excess Benefit Plan (the “Excess Plan”), which is a nonqualified deferred compensation plan as defined in Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code. The purpose of the Excess Plan is to make up the shortfall in retirement benefits caused by the limitations on benefits to highly compensated individuals under the qualified defined benefit pension plans in accordance with the Internal Revenue Code.
Although participants generally receive credited service beginning at age 21, certain participants in the Kroger Pension Plan and the Excess Plan who commenced employment prior to 1986, including Messrs. McMullen and Schlotman, began to accrue credited service after attaining age 25 and one year of service. The Kroger Pension Plan and the Excess Plan generally determinesdetermine accrued benefits using a cash balance formula, but retainsretain benefit formulas applicable under prior plans for certain “grandfathered participants” who were employed by Kroger on December 31, 2000. Each of the above listed named executive officersMessrs. McMullen, Schlotman and Donnelly is eligible for these grandfathered benefits. Mr. Hjelm is not a grandfathered participant, and therefore, his benefits underare determined using the Consolidated Plan. Their benefits, therefore,cash balance formula.
Grandfathered Participants
Benefits for grandfathered participants are determined using formulas applicable under prior plans, including the Kroger formula covering service to The Kroger Co. and the Dillon Companies, Inc. Pension Plan formula covering service to Dillon Companies, Inc.
As “grandfathered participants”, Messrs. Dillon,McMullen, Schlotman McMullen and Heldman also are eligible to receive benefits under The Kroger Co. Excess Benefit Plan (the “Kroger Excess Plan”), and Mr. Dillon is also eligible to receive benefits under the Dillon Companies, Inc. Excess Benefit Pension Plan (the “Dillon Excess Plan”). These plans are collectively referred to as the “Excess Plans.” The Excess Plans are each considered to be nonqualified deferred compensation plans as defined in Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code. The purpose of the Excess Plans is to make up the shortfall in retirement benefits caused by the limitations on benefits to highly compensated individuals under qualified plans in accordance with the Internal Revenue Code.
Each of the above listed named executive officersDonnelly will receive benefits under the ConsolidatedKroger Pension Plan and the Excess Plans,Plan, determined as follows:
| ● | 1½% times years of credited service multiplied by the average of the highest five years of total earnings (base salary and annual cash bonus) during the last ten calendar years of employment, reduced by 1¼% times years of credited service multiplied by the primary social security benefit; |
| ● | normal retirement age is 65; |
| ● | unreduced benefits are payable beginning at age 62; and |
| ● | benefits payable between ages 55 and 62 will be reduced by⅓ of one percent for each of the first 24 months and by ½ of one percent for each of the next 60 months by which the commencement of benefits precedes age 62. |
36
Although participants generally receive credited service beginning at age 21, those participants who commenced employment prior to 1986, including the above listed named executive officers, began to accrue credited service after attaining age 25. In the event of a termination of employment other than death or disability, Messrs. Dillon, HeldmanMcMullen, Schlotman and SchlotmanDonnelly currently are eligible for a reduced early retirement benefit, as they each havehas attained age 55. If a “grandfathered participant” becomes disabled while employed by Kroger and after attaining age 55, the participant will receive the full retirement benefit. If a married “grandfathered participant” dies while employed by Kroger, the surviving spouse will receive benefits as though a retirement occurred on such date, based on the greater of: actual benefits payable to the participant if he was over age 55, or the benefits that would have been payable to the participant assuming he was age 55 on the date of death.
Cash Balance Participants
Mr. DillonHjelm began participating in the Kroger Pension Plan in August 2005 as a cash balance participant. Until the plan was frozen on December 31, 2006, cash balance participants received an annual pay credit equal to 5% of that year’s eligible earnings plus an annual interest credit equal to the account balance at the beginning of the plan year multiplied by the annual rate of interest on 30-year Treasury Securities in effect prior to the plan year. Beginning on January 1, 2007, cash balance participants receive an annual interest credit but no longer receive an annual pay credit. Upon retirement, cash balance participants generally are eligible to receive a life annuity which is the actuarial equivalent of his account balance, but may elect in some circumstances to receive a lump sum distribution equal to his account balance. If Mr. Hjelm becomes disabled while employed by Kroger, he will receive the full retirement benefit. If he dies while employed by Kroger, his beneficiary will receive a death benefit equal to the benefit he was eligible to receive if a retirement occurred on such date.
42
Offsetting Benefits
Mr. Donnelly also participates in the Dillon Companies, Inc. Employees’ Profit Sharing Plan, (the “Dillon Plan”). The Dillon Planwhich is a qualified defined contribution plan (the “Dillon Profit Sharing Plan”) under which Dillon Companies, Inc. and its participating subsidiaries may choose to make discretionary contributions each year that are then allocated to each participant’s account. Participation in the Dillon Profit Sharing Plan was frozen effective January 1, 2001. Benefits under the Dillon Plan do not continuein 2001 and participants are no longer able to accruemake employee contributions, but certain participants, including Mr. Donnelly, are still eligible for Mr. Dillon.employer contributions. Participants in the Dillon Plan elect from among a number of investment options and the amounts in their accounts are invested and credited with investment earnings in accordance with their elections. Prior to July 1, 2000, participants could elect to make voluntary contributions under the Dillon Plan, but that option was discontinued effective as of July 1, 2000. Participants can elect to receive their Dillon Plan benefit in the form of either a lump sum payment or installment payments.
Due to offset formulas contained in the Consolidated Plan and the Dillon ExcessKroger Pension Plan, Mr. Dillon’sDonnelly’s accrued benefits under the Dillon Profit Sharing Plan offset a portion of the benefit that would otherwise accrue for themhim under those plansthe Kroger Pension for theirhis service with Dillon Companies, Inc. Although benefits that accrue underThis offset is reflected in the table above.
Harris Teeter Pension Plan
Mr. Morganthall participates in the HT Pension Plan, which is a defined contribution plans are not reportablebenefit pension plan. Participation in the HT Pension Plan was frozen effective October 1, 2005. For participants with age and service points as of December 31, 2005 equal to or greater than 45, which includes Mr. Morganthall, benefit accruals under the accompanying table, we have added narrative disclosureHT Pension Plan after September 30, 2005 will be offset by the actuarial equivalent of the Dillonportion of their account balance under the Harris Teeter Supermarkets, Inc. Retirement and Savings Plan because(the “HT Savings Plan”) that are attributable to automatic retirement contributions made by Harris Teeter after September 30, 2005, plus earnings and losses on such contributions. A participant’s normal annual retirement benefit under the HT Pension Plan at age 65 is an amount equal to 0.8% of his final average earnings multiplied by years of service at retirement, plus 0.6% of his final average earnings in excess of Social Security covered compensation multiplied by the number of years of service up to a maximum of 35 years. A participant’s final average earnings is the average annual cash compensation paid to the participant during the plan year, including salary, incentive compensation and any amount contributed to the HT Savings Plan, for the 5 consecutive years in the last 10 years that produce the highest average.
Harris Teeter SERP
Mr. Morganthall also participates in the HT SERP, which is a nonqualified deferred compensation plan as defined in Section 409A of the offsetting effect thatInternal Revenue Code. The purpose of the HT SERP is to supplement the benefits under that plan has on benefits accruingpayable under the Consolidatedretirement plans. Under the HT SERP, participants who retire at normal retirement age of 60 receive monthly retirement benefits equal to between 55% and 60% of his final average earnings times his accrual fraction and reduced by his (1) assumed HT Pension Plan retirement benefit, and (2) assumed Social Security benefit. The final average earnings are the Dillon Excess Plan.
average annual earnings during the highest 3 calendar years out of the last 10 calendar years preceding termination of employment. The assumptions used in calculatingaccrual fraction is a fraction, the present values are set forth in Note 13 to the consolidated financial statements in Kroger’s Form 10-K for fiscal year 2012 ended February 2, 2013. The discount rate used to determine the present values is 4.29%,numerator of which is the same rate used atyears of credited service, the measurement datedenominator of which is 20, and which may not exceed 1.0. The benefits payable under the HT SERP are payable for financial reporting purposes.the participant’s lifetime with an automatic 75% survivor benefit payable to the participant’s surviving eligible spouse for his or her lifetime. Mr. Morganthall is eligible to receive the full benefit as he has reached age 60. Harris Teeter uses a non-qualified trust to purchase and hold the assets to satisfy Harris Teeter’s obligation under the HT SERP, and participants in the HT SERP are general creditors of Harris Teeter in the event Harris Teeter becomes insolvent.
43
2015 Nonqualified Deferred Compensation
The following table provides information on nonqualified deferred compensation for the named executive officersNEOs for 2012.2015.
| 2012 NONQUALIFIED DEFERRED COMPENSATION | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive | Registrant | Aggregate | Aggregate | Aggregate | ||||||||||||||||
| Contributions | Contributions | Earnings | Withdrawals/ | Balance at | ||||||||||||||||
| in Last FY | in Last FY | in Last FY | Distributions | Last FYE | ||||||||||||||||
| Name | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | |||||||||||||||
| David B. Dillon | $ | 60,000 | (1) | $0 | $ | 68,918 | $0 | $ | 1,037,365 | |||||||||||
| J. Michael Schlotman | $ | 0 | $0 | $ | 0 | $0 | $ | 0 | ||||||||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen | $ | 364,381 | (2) | $0 | $ | 413,093 | $0 | $ | 6,329,976 | |||||||||||
| Paul W. Heldman | $ | 312,716 | (3) | $0 | $ | 74,488 | $0 | $ | 1,368,700 | |||||||||||
| Kathleen S. Barclay | $ | 0 | $0 | $ | 0 | $0 | $ | 0 | ||||||||||||
| Name | Executive Contributions in Last FY | Registrant Contributions in Last FY | Aggregate Earnings in Last FY(1) | Aggregate Balance at Last FYE(2) | ||||||||||||||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen | $ | 7,500 | (3) | — | $ | 532,896 | $ | 8,379,170 | ||||||||||||||
| J. Michael Schlotman | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Michael J. Donnelly | — | — | $ | 24,430 | $ | 372,649 | ||||||||||||||||
| Christopher T. Hjelm | $ | 148,808 | (4) | — | $ | 10,053 | $ | 236,885 | ||||||||||||||
| Frederick J. Morganthall II | $ | 100,000 | (4) | $ | 13,475 | (5) | — | $ | 663,852 | |||||||||||||
| (1) | These amounts include the aggregate earnings on all accounts for each NEO, including any above-market or preferential earnings. The following amounts earned in 2015 are deemed to be preferential earnings and are included in the “Change in Pension Value and Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Earnings” column of the Summary Compensation Table for 2015: Mr. McMullen, $80,092; Mr. Donnelly, $4,576; and Mr. Hjelm, $168. | |
| (2) | The following amounts in the Aggregate Balance column from the table were reported in the Summary Compensation Tables covering fiscal years 2006 – 2014: Mr. McMullen – $2,558,370; and Mr. Donnelly - $14,318. For Messrs. Hjelm and Morganthall, no portion of the Aggregate Balance from the table was reported in the Summary Compensation Table for prior years because they were not NEOs prior to 2015. | |
| (3) | This amount represents the deferral of | |
| These amounts represent the deferral of a portion of the 2014 performance-based annual cash bonus earned in | ||
| This amount is included in the All Other Compensation column of the Summary Compensation Table for | ||
Eligible participantsKroger Executive Deferred Compensation Plan
Messrs. McMullen, Donnelly and Hjelm participate in The Kroger Co. Executive Deferred Compensation Plan, which is a nonqualified deferred compensation plan. Participants may elect to defer up to 100% of the amount of their salary that exceeds the sum of the FICA wage base and pre-tax insurance and other Internal Revenue Code Section 125 plan deductions, as well as up to 100% of their annual and long-term cash bonus compensation. Kroger does not match any deferral or provide other contributions. Deferral account amounts are credited with
37
interest at the rate representing Kroger’s cost of ten-year debt as determined by Kroger’s CEO and reviewedapproved by the Compensation Committee prior to the beginning of each deferral year. The interest rate established for deferral amounts for each deferral year will be applied to those deferral amounts for all subsequent years until the deferred compensation is paid out. Amounts deferred in 2015 earn interest at a rate of 3.65%. Participants can elect to receive lump sum distributions or quarterly installments for periods up to ten years. Participants also can elect between lump sum distributions and quarterly installments to be received by designated beneficiaries if the participant dies before distribution of deferred compensation is completed.
Director CompensationParticipants may not withdraw amounts from their accounts until they leave Kroger, except that Kroger has discretion to approve an early distribution to a participant upon the occurrence of an unforeseen emergency. Participants who are “specified employees” under Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code, which includes the NEOs, may not receive a post-termination distribution for at least six months following separation. If the employee dies prior to or during the distribution period, the remainder of the account will be distributed to his designated beneficiary in lump sum or quarterly installments, according to the participant’s prior election.
44
Harris Teeter Flexible Deferral Plan
Mr. Morganthall participates in the HT Flexible Deferral Plan, which is a nonqualified deferred compensation plan that provides certain highly compensated employees of Harris Teeter, the opportunity to defer the receipt and taxation on a portion of their annual compensation and supplements the benefits under tax qualified retirement plans to the extent that such benefits are subject to limitation under the Internal Revenue Code. Participants may elect to defer up to 50% of their base salary and up to 90% of their non-equity incentive bonus compensation. Harris Teeter provides matching contributions of 50% of the participant’s contribution, up to a maximum of 4% of the participant’s pay, less assumed matching contributions under the HT Savings Plan. These deferred amounts and Company match are credited to the participant’s account. Plan participants may choose deemed investments in the HT Flexible Deferral Plan that represent choices that span a variety of diversified asset classes. Participants may elect to receive a lump sum distribution, annual installment payments for 2-15 years, or a partial lump sum and installment payments. Upon retirement, death, disability, or other separation of service, the participant will receive distributions in accordance with his election, subject to limitations under Section 409A. Mr. Morganthall has reached the retirement age and is eligible for the full benefit. The HT Flexible Deferral Plan also allows for an in-service withdrawal for an unforeseeable emergency based on facts and circumstances that meet Internal Revenue Service and plan guidelines. Harris Teeter uses a non-qualified trust to purchase and hold the assets to satisfy Harris Teeter’s obligation under the HT Flexible Deferral Plan, and participants in the HT Flexible Deferral Plan are general creditors of Harris Teeter in the event Harris Teeter becomes insolvent.
Potential Payments upon Termination or Change in Control
Kroger does not have employment agreements or other contracts, agreements, plans or arrangements that provide for payments to the NEOs in connection with a termination of employment or a change in control of Kroger. However, KEPP, our award agreements for stock options, restricted stock and performance units and our long-term cash bonus plans provide for certain payments and benefits to participants, including the NEOs, in the event of a termination of employment or a change in control of Kroger, as described below. Our pension plans and nonqualified deferred compensation plan also provide for certain payments and benefits to participants in the event of a termination of employment, as described above in the Pension Benefits section and the Nonqualified Deferred Compensation section, respectively.
A “change in control” under KEPP, and our equity and non-equity incentive awards occurs if:
| ● | any person or entity (excluding Kroger’s employee benefit plans) acquires 20% or more of the voting power of Kroger; |
| ● | a merger, consolidation, share exchange, division, or other reorganization or transaction with Kroger results in Kroger’s voting securities existing prior to that event representing less than 60% of the combined voting power immediately after the event; |
| ● | Kroger’s shareholders approve a plan of complete liquidation or winding up of Kroger or an agreement for the sale or disposition of all or substantially all of Kroger’s assets; or |
| ● | during any period of 24 consecutive months, individuals at the beginning of the period who constituted Kroger’s Board of Directors cease for any reason to constitute at least a majority of the Board of Directors. |
KEPP
KEPP applies to all management employees and administrative support personnel who are not covered by a collective bargaining agreement, with at least one year of service, and provides severance benefits when a participant’s employment is terminated actually or constructively within two years following a change in control of Kroger, including the NEOs. The actual amount is dependent on pay level and years of service. The NEOs are eligible for the following benefits:
| ● | a lump sum severance payment equal to up to two times the sum of the participant’s annual base salary and 70% of the greater of the current annual cash bonus potential or the average of the actual annual cash bonus payments for the prior three years; |
45
| ● | a lump sum payment equal to the participant’s accrued and unpaid vacation, including banked vacation; |
| ● | a lump sum payment equal to 1/12th of the sum of the participant’s annual vacation pay plus 70% of the greater of the current year’s annual cash bonus potential or the average of the actual annual cash bonus payments for the prior three years, multiplied by the number of months elapsed in the current calendar year; |
| ● | continued medical and dental benefits for up to 24 months and continued life insurance coverage for up to 6 months; and |
| ● | up to $5,000 as reimbursement for eligible tuition expenses and up to $10,000 as reimbursement for eligible outplacement expenses. |
Payments to executive officers under KEPP will be reduced, to the extent necessary, so that payments will not exceed 2.99 times the officer’s average W-2 earnings over the preceding five years.
Long-Term Compensation Awards
The following table describes the fiscal year 2012treatment of long-term compensation awards following a termination of employment or change in control of Kroger. In each case, the continued vesting, exercisability or eligibility for non-employee directors. Employee directors receive no compensation for their Board service.the incentive awards will end if the participant provides services to a competitor of Kroger.
| 2012 DIRECTOR COMPENSATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change in | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| and | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fees | Nonqualified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Earned | Non-Equity | Deferred | All | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| or Paid | Stock | Option | Incentive Plan | Compensation | Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| in Cash | Awards | Awards | Compensation | Earnings | Compensation | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | (1) | (12) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reuben V. Anderson | $ | 76,008 | $ | 120,780 | (2) | $ | 29,217 | (4) | — | — | (9) | $465 | $ | 226,470 | ||||||||||||||||
| Robert D. Beyer | $ | 81,105 | $ | 120,780 | (3) | $ | 29,217 | (4) | — | $ | 5,972 | (10) | $465 | $ | 237,539 | |||||||||||||||
| Susan J. Kropf | $ | 86,142 | $ | 120,780 | (3) | $ | 29,217 | (5) | — | N/A | $465 | $ | 236,604 | |||||||||||||||||
| John T. LaMacchia | $ | 81,105 | $ | 120,780 | (2) | $ | 29,217 | (4) | — | $ | 415 | (11) | $465 | $ | 231,982 | |||||||||||||||
| David B. Lewis | $ | 76,008 | $ | 120,780 | (2) | $ | 29,217 | (4) | — | N/A | $266 | $ | 226,271 | |||||||||||||||||
| Jorge P. Montoya | $ | 88,169 | $ | 120,780 | (2) | $ | 29,217 | (5) | — | N/A | $465 | $ | 238,631 | |||||||||||||||||
| Clyde R. Moore | $ | 83,073 | $ | 120,780 | (3) | $ | 29,217 | (4) | — | — | (9) | $465 | $ | 233,535 | ||||||||||||||||
| Susan M. Phillips | $ | 86,142 | $ | 120,780 | (2) | $ | 29,217 | (6) | — | $ | 1,995 | (10) | $465 | $ | 238,599 | |||||||||||||||
| Steven R. Rogel | $ | 76,008 | $ | 120,780 | (2) | $ | 29,217 | (4) | — | N/A | $465 | $ | 226,470 | |||||||||||||||||
| James A. Runde | $ | 83,073 | $ | 120,780 | (2) | $ | 29,217 | (7) | — | N/A | $465 | $ | 233,535 | |||||||||||||||||
| Ronald L. Sargent | $ | 98,304 | $ | 120,780 | (3) | $ | 29,217 | (7) | — | $ | 2,058 | (10) | $465 | $ | 250,824 | |||||||||||||||
| Bobby S. Shackouls | $ | 118,573 | $ | 120,780 | (3) | $ | 29,217 | (8) | — | N/A | $266 | $ | 268,836 | |||||||||||||||||
| Triggering Event | Stock Options | Restricted Stock | Performance Units | Performance-Based Long-Term Cash Bonus | |||
Involuntary | Forfeit all unvested options. Previously vested options remain exercisable for the shorter of one year after termination or the remainder of the original 10-year term. | Forfeit all unvested shares | Forfeit all rights to units for which the three year performance period has not ended | Forfeit all rights to long-term cash bonuses for which the three year performance period has not ended | |||
Voluntary - Prior to minimum | Forfeit all unvested options. Previously vested options remain exercisable for the shorter of one year after termination or the remainder of the original 10-year term. | Forfeit all unvested shares | Forfeit all rights to units for which the three year performance period has not ended | Forfeit all rights to long-term cash bonuses for which the three year performance period has not ended | |||
Voluntary - After minimum age | Unvested options continue vesting on the original schedule. All options are exercisable for remainder of the original 10-year term. | Forfeit all unvested shares granted prior to 2013. Vesting continues on the original schedule for awards granted during or after 2013. | Pro rata portion(1) of units earned based on performance results over the full three-year period | Pro rata portion(1) of long-term cash bonuses earned based on performance results over the full three-year period | |||
Death | Unvested options are immediately vested. All options are exercisable for remainder of the original 10-year term. | Unvested shares immediately vest | Pro rata portion(1) of units earned based on performance results through the end of the fiscal year in which death occurs. Award will be paid following the end of such fiscal year. | Pro rata portion(1) of long-term cash bonuses earned based on performance results through the end of the fiscal year in which death occurs. Award will be paid following the end of such fiscal year. | |||
Disability | Unvested options are immediately vested. All options are exercisable for remainder of the original 10-year term. | Unvested shares immediately vest | Pro rata portion(1) of units earned based on performance results over the full three-year period | Pro rata portion(1) of long-term cash bonuses earned based on performance results over the full three-year period | |||
Change in | Unvested options are immediately vested and exercisable | Unvested shares immediately vest | 50% of the maximum units granted at the beginning of the performance period earned immediately | 50% of the maximum bonus granted at the beginning of the performance period earned immediately |
46
| (1) | The prorated amount is equal to the number of weeks of active employment during the performance period divided by the total number of weeks in the performance period. | |
| (2) | The minimum age requirement is age 62 for stock options and restricted stock and age 55 for performance units and the long-term cash bonus. | |
| (3) | These benefits are payable upon a change in control of Kroger with or without a termination of employment. | |
Quantification of Payments upon Termination or Change in Control
The following table provides information regarding certain potential payments that would have been made to the NEOs if the triggering event occurred on the last day of the fiscal year, January 30, 2016, given compensation, age and service levels as of that date and, where applicable, based on the closing market price per Kroger common share on the last trading day of the fiscal year ($38.81 on January 29, 2016). Amounts actually received upon the occurrence of a triggering event will vary based on factors such as the timing during the year of such event, the market price of Kroger common shares, and the officer’s age, length of service and compensation levels.
| Name | Involuntary Termination | Voluntary Termination/ Retirement | Death | Disability | Change in Control without Termination | Change in | ||||||||||||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accrued and Banked Vacation | $ | 763,072 | $ | 763,072 | $ | 763,072 | $ | 763,072 | $ | 763,072 | $ | 763,072 | ||||||||||
| Severance | — | — | — | — | — | 4,790,016 | ||||||||||||||||
| Additional Vacation and Bonus | — | — | — | — | — | 108,173 | ||||||||||||||||
| Continued Health and Welfare Benefits(1) | — | — | — | — | — | 58,326 | ||||||||||||||||
| Stock Options(2) | — | — | 8,973,448 | 8,973,448 | 8,973,448 | 8,973,448 | ||||||||||||||||
| Restricted Stock(3) | — | — | 13,928,560 | 13,928,560 | 13,928,560 | 13,928,560 | ||||||||||||||||
| Performance Units(4) | — | 2,615,463 | 2,615,463 | 2,615,463 | 2,467,908 | 2,467,908 | ||||||||||||||||
| Long-Term Cash Bonus(5) | — | 1,133,340 | 1,133,340 | 1,133,340 | 1,150,000 | 1,150,000 | ||||||||||||||||
| Executive Group Life Insurance | — | — | 4,910,000 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| J. Michael Schlotman | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accrued and Banked Vacation | $ | 516,928 | $ | 516,928 | $ | 516,928 | $ | 516,928 | $ | 516,928 | $ | 516,928 | ||||||||||
| Severance | — | — | — | — | — | 2,581,080 | ||||||||||||||||
| Additional Vacation and Bonus | — | — | — | — | — | 45,622 | ||||||||||||||||
| Continued Health and Welfare Benefits(1) | — | — | — | — | — | 48,995 | ||||||||||||||||
| Stock Options(2) | — | — | 3,962,059 | 3,962,059 | 3,962,059 | 3,962,059 | ||||||||||||||||
| Restricted Stock(3) | — | — | 5,929,004 | 5,929,004 | 5,929,004 | 5,929,004 | ||||||||||||||||
| Performance Units(4) | — | 850,471 | 850,471 | 850,471 | 887,585 | 887,585 | ||||||||||||||||
| Long-Term Cash Bonus(5) | — | 743,335 | 743,335 | 743,335 | 747,500 | 747,500 | ||||||||||||||||
| Executive Group Life Insurance | — | — | 3,064,200 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Michael J. Donnelly | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accrued and Banked Vacation | $ | 245,191 | $ | 245,191 | $ | 245,191 | $ | 245,191 | $ | 245,191 | $ | 245,191 | ||||||||||
| Severance | — | — | — | — | — | 2,345,731 | ||||||||||||||||
| Additional Vacation and Bonus | — | — | — | — | — | 42,451 | ||||||||||||||||
| Continued Health and Welfare Benefits(1) | — | — | — | — | — | 38,794 | ||||||||||||||||
| Stock Options(2) | — | — | 2,252,578 | 2,252,578 | 2,252,578 | 2,252,578 | ||||||||||||||||
| Restricted Stock(3) | — | — | 3,908,361 | 3,908,361 | 3,908,361 | 3,908,361 | ||||||||||||||||
| Performance Units(4) | — | 575,422 | 575,422 | 575,422 | 572,059 | 572,059 | ||||||||||||||||
| Long-Term Cash Bonus(5) | — | 650,008 | 650,008 | 650,008 | 653,230 | 653,230 | ||||||||||||||||
| Executive Group Life Insurance | — | — | 2,770,000 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Christopher T. Hjelm | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accrued and Banked Vacation | $ | 53,848 | $ | 53,848 | $ | 53,848 | $ | 53,848 | $ | 53,848 | $ | 53,848 | ||||||||||
| Severance | — | — | — | — | — | 2,053,342 | ||||||||||||||||
| Additional Vacation and Bonus | — | — | — | — | — | 39,487 | ||||||||||||||||
| Continued Health and Welfare Benefits(1) | — | — | — | — | — | 48,101 | ||||||||||||||||
| Stock Options(2) | — | — | 2,156,403 | 2,156,403 | 2,156,403 | 2,156,403 | ||||||||||||||||
| Restricted Stock(3) | — | — | 3,730,340 | 3,730,340 | 3,730,340 | 3,730,340 | ||||||||||||||||
| Performance Units(4) | — | 637,879 | 637,879 | 637,879 | 665,727 | 665,727 | ||||||||||||||||
| Long-Term Cash Bonus(5) | — | 606,668 | 606,668 | 606,668 | 610,000 | 610,000 | ||||||||||||||||
| Executive Group Life Insurance | — | — | 3,165,000 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
47
| Name | Involuntary Termination | Voluntary | Death | Disability | Change in Control without Termination | Change in Control with Termination | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Frederick J. Morganthall II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accrued and Banked Vacation | $ | 77,310 | $ | 77,310 | $ | 77,310 | $ | 77,310 | $ | 77,310 | $ | 77,310 | ||||||||||||||
| Severance | — | — | — | — | — | 2,180,016 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Additional Vacation and Bonus | — | — | — | — | — | 41,443 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Continued Health and Welfare Benefits(1) | — | — | — | — | — | 27,484 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock Options(2) | — | — | 19,180 | 19,180 | 19,180 | 19,180 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted Stock(3) | — | — | 5,721,797 | 5,721,797 | 5,721,797 | 5,721,797 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Performance Units(4) | — | 478,038 | 478,038 | 478,038 | 452,195 | 452,195 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-Term Cash Bonus(5) | — | 559,162 | 559,162 | 559,162 | 561,930 | 561,930 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive Group Life Insurance | — | — | 2,295,000 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Represents the aggregate present value of continued participation in the Company’s medical, dental and executive term life insurance plans, based on the premiums paid by the Company during the eligible period. The eligible period for continued medical and dental benefits is based on the length of service, which is 22 months for Mr. Hjelm, and 24 months for the other NEOs. The eligible period for continued executive term life insurance coverage is six months for all NEOs. The amounts reported may ultimately be lower if the executive is no longer eligible to receive benefits, which could occur upon obtaining other employment and becoming eligible for substantially equivalent benefits through the new employer. | |
| (2) | Amounts reported in the death, disability and change in control columns represent the intrinsic value of the accelerated vesting of unvested stock options, calculated as the difference between the exercise price of the stock option and the closing price per Kroger common share on January 29, 2016. In accordance with SEC rules, no amount is reported in the voluntary termination/retirement column because vesting is not accelerated, but the awards may continue to vest on the original schedule if the conditions described above are met. | |
| (3) | Amounts reported in the death, disability and change in control columns represent the aggregate value of the accelerated vesting of restricted stock. In accordance with SEC rules, no amount is reported in the voluntary termination/retirement column because vesting is not accelerated, but the awards may continue to vest on the original schedule if the conditions described above are met. | |
| (4) | Amounts reported in the voluntary termination/retirement, death and disability columns represent the aggregate value of the performance units granted in 2014 and 2015, based on the probable outcome of the performance conditions as of January 30, 2016 and prorated for the portion of the performance period completed. Amounts reported in the change in control column represent the aggregate value of 50% of the maximum number of performance units granted in 2014 and 2015 at the beginning of the performance period. Awards under the 2013 Long-Term Incentive Plan were earned as of the last day of 2015 so each NEO was entitled to receive (regardless of the triggering event) the amount actually earned, which is reported in the Stock Awards column of the 2015 Stock Vested Table. | |
| (5) | Amounts reported in the voluntary termination/retirement, death and disability columns represent the aggregate value of the long-term cash bonuses granted in 2014 and 2015, based on the probable outcome of the performance conditions as of January 30, 2016 and prorated for the portion of the performance period completed. Amounts reported in the change in control column represent the aggregate value of 50% of the long-term cash bonus potentials under the 2014 and 2015 Long-Term Incentive Plans. Awards under the 2013 Long-Term Incentive Plan were earned as of the last day of 2015, so each NEO was entitled to receive (regardless of the triggering event) the amount actually earned, which is reported in the Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation column of the Summary Compensation Table. | |
48
Item 2. Advisory Vote on Executive Compensation
You are being asked to vote, on an advisory basis, to approve the compensation of our NEOs. The Board of Directors recommends that you vote FOR the approval of compensation of our NEOs.
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, enacted in July 2010, requires that we give our shareholders the right to approve, on a nonbinding, advisory basis, the compensation of our NEOs as disclosed earlier in this proxy statement in accordance with the SEC’s rules.
As discussed earlier in the Compensation Discussion and Analysis, our compensation philosophy is to attract and retain the best management talent and to motivate these employees to achieve our business and financial goals. Our incentive plans are designed to reward the actions that lead to long-term value creation. To achieve our objectives, we seek to ensure that compensation is competitive and that there is a direct link between pay and performance. To do so, we are guided by the following principles:
| ● | A significant portion of pay should be performance-based, with the percentage of total pay tied to performance increasing proportionally with an executive’s level of responsibility; |
| ● | Compensation should include incentive-based pay to drive performance, providing superior pay for superior performance, including both a short- and long-term focus; |
| ● | Compensation policies should include an opportunity for, and a requirement of, equity ownership to align the interests of executives and shareholders; and |
| ● | Components of compensation should be tied to an evaluation of business and individual performance measured against metrics that directly drive our business strategy. |
The vote on this resolution is not intended to address any specific element of compensation. Rather, the vote relates to the compensation of our NEOs as described in this proxy statement. The vote is advisory. This means that the vote is not binding on Kroger. The Compensation Committee of the Board is responsible for establishing executive compensation. In so doing that Compensation Committee will consider, along with all other relevant factors, the results of this vote.
We ask our shareholders to vote on the following resolution:
“RESOLVED, that the compensation paid to the Company’s NEOs, as disclosed pursuant to Item 402 of Regulation S-K, including the Compensation Discussion and Analysis, compensation tables, and the related narrative discussion, is hereby APPROVED.”
The next advisory vote will occur at our 2017 annual meeting.
The Board of Directors Recommends a VoteFor This Proposal.
49
Director Compensation
2015 Director Compensation
The following table describes the 2015 compensation for non-employee directors. Mr. McMullen does not receive compensation for his Board service.
| Name | Fees Earned or Paid in Cash | Stock Awards(1) | Option Awards(1) | Change in Pension Value and Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Earnings(2) | Total | |||||||||||||||
| Nora A. Aufreiter | $ | 84,772 | $ | 165,586 | — | — | $ | 250,358 | ||||||||||||
| Robert D. Beyer | $ | 124,664 | $ | 165,586 | — | $ | 8,271 | $ | 298,521 | |||||||||||
| Anne Gates(3) | $ | 13,280 | $ | 98,136 | — | — | $ | 111,416 | ||||||||||||
| Susan J. Kropf | $ | 94,745 | $ | 165,586 | — | — | $ | 260,331 | ||||||||||||
| David B. Lewis | $ | 84,772 | $ | 165,586 | — | — | $ | 250,358 | ||||||||||||
| Jorge P. Montoya | $ | 99,731 | $ | 165,586 | — | — | $ | 265,317 | ||||||||||||
| Clyde R. Moore | $ | 104,718 | $ | 165,586 | — | $ | 11,753 | $ | 282,057 | |||||||||||
| Susan M. Phillips | $ | 94,745 | $ | 165,586 | — | $ | 2,701 | $ | 263,032 | |||||||||||
| James A. Runde | $ | 99,731 | $ | 165,586 | — | — | $ | 265,317 | ||||||||||||
| Ronald L. Sargent | $ | 114,691 | $ | 165,586 | — | $ | 2,777 | $ | 283,054 | |||||||||||
| Bobby S. Shackouls | $ | 94,745 | $ | 165,586 | — | — | $ | 260,331 | ||||||||||||
| (1) | Amounts reported in the Stock Awards column represent the aggregate grant date fair value of |
| Name | Options | |
| Ms. Aufreiter | — | |
| Mr. Beyer | 85,000 | |
| Ms. Gates | — | |
| Ms. Kropf | 75,000 | |
| Mr. Lewis | 75,000 | |
| Mr. Montoya | 75,000 | |
| Mr. Moore | 65,000 | |
| Ms. Phillips | 85,000 | |
| Mr. Runde | 85,000 | |
| Mr. Sargent | 85,000 | |
| Mr. Shackouls | 7,800 |
| (2) | ||
38
50
Annual Compensation
Each non-employee director receives an annual cash retainer of $75,000.$85,000. The chairs of each of the Audit Committee and the Compensation Committee receive an additional annual cash retainer of $20,000. The chair of each committeeof the other committees receives an additional annual cash retainer of $12,000.$15,000. Each member of the Audit Committee receives an additional annual cash retainer of $10,000. The director designated as the “Lead Director”Lead Director receives an additional annual cash retainer of $20,000.$25,000.
Approximately $165,000 worth of incentive shares (Kroger common shares) are issued to non-employee directors as a portion of the directors’ overall compensation. On July 12, 2012,15, 2015, each non-employee director, except for Ms. Gates, received 5,5004,320 common shares. Ms. Gates received 2,386 common shares on December 10, 2015 upon joining the Board.
The Board has determined that compensation of restricted stocknon-employee directors must be competitive on an ongoing basis to attract and an award of 6,500 nonqualified stock options.retain directors who meet the qualifications for service on the Board. Non-employee director compensation will be reviewed from time to time as the Corporate Governance Committee deems appropriate.
Pension Plan
Non-employee directors first elected prior to July 17, 1997 receive a major medical plan benefit as well as an unfunded retirement benefit. The retirement benefit equalsequal to the average cash compensation for the five calendar years preceding retirement. Only Mr. Moore is eligible for this benefit. Participants who retire from the Board prior to age 70 will be credited with 50% vesting after five years of service, and 10% for each additional year up to a maximum of 100%. Benefits for participants who retire prior to age 70 begin at the later of actual retirement or age 65.
Nonqualified Deferred Compensation
We also maintain a deferred compensation plan in which allfor non-employee members of the Board are eligible to participate.directors. Participants may defer up to 100% of their cash compensation. Theycompensation and/or the receipt of all (and not less than all) of the annual award of incentive shares.
Cash Deferrals
Cash deferrals are credited to a participant’s deferred compensation account. Participants may elect from either or both of the following two alternative methods of determining benefits:
| ● | interest accrues until paid out at the rate of interest determined prior to the beginning of the deferral year to represent Kroger’s cost of ten-year debt; and/or |
| ● | amounts are credited in “phantom” stock accounts and the amounts in those accounts fluctuate with the price of Kroger common shares. |
In both cases, deferred amounts are paid out only in cash, based on deferral options selected by the participantsparticipant at the time the deferral elections are made. Participants can elect to have distributions made in a lump sum or in quarterly installments, and may make comparable elections for designated beneficiaries who receive benefits in the event that deferred compensation is not completely paid out upon the death of the participant.
The Board has determined that compensationIncentive Share Deferrals
Participants may also defer the receipt of non-employee directors must be competitive on an on-going basis to attract and retain directors who meetall (and not less than all) of the qualifications for service on Kroger’s Board. Non-employee director compensationannual award of incentive shares. Distributions will be reviewed from time to time as the Corporate Governance Committee deems appropriate.
Potential Payments upon Termination or Change in Control
made by delivery of Kroger has no contracts, agreements, plans or arrangements that provide for payments to the named executive officers in connection with resignation, severance, retirement, termination, or change in control, except for those available generally to salaried employees. The Kroger Co. Employee Protection Plan, or KEPP, applies to all management employees and administrative support personnel who are not covered by a collective bargaining agreement, with at least one year of service, and provides severance benefits when a participant’s employment is terminated actually or constructivelycommon shares within two years following a change in control of Kroger. For purposes of KEPP, a change in control occurs if:
39
Assuming that a change in control occurred on the last day of Kroger’s fiscal year 2012, and the named executive officers had their employment terminated, they would receive a maximum payment, or, in the case of group term life insurance, a benefit having a cost to Kroger, in the amounts shown below:
| Accrued | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Additional | and | Group | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Severance | Vacation and | Banked | Term Life | Tuition | Outplacement | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Benefit | Bonus | Vacation | Insurance | Reimbursement | Reimbursement | |||||||||||||||||||||
| David B. Dillon | $ | 4,760,000 | $ | 100,289 | $ | 767,310 | $29 | $ | 5,000 | $ | 10,000 | ||||||||||||||||
| J. Michael Schlotman | $ | 2,112,200 | $ | 38,536 | $ | 412,992 | $29 | $ | 5,000 | $ | 10,000 | ||||||||||||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen | $ | 3,279,200 | $ | 67,368 | $ | 578,208 | $29 | $ | 5,000 | $ | 10,000 | ||||||||||||||||
| Paul W. Heldman | $ | 2,296,000 | $ | 39,420 | $ | 220,095 | $29 | $ | 5,000 | $ | 10,000 | ||||||||||||||||
| Kathleen S. Barclay | $ | 2,124,600 | $ | 37,510 | $ | 65,125 | $29 | $ | 5,000 | $ | 10,000 | ||||||||||||||||
Each of the named executive officers also is entitled to continuation of health care coverage for up to 24 months at the same contribution rate as existed prior to the change in control. The cost to Kroger cannot be calculated, as Kroger self insures the health care benefit and the cost is based on the health care services utilized by the participant and eligible dependents.
Under KEPP benefits will be reduced, to the extent necessary, so that payments to an executive officer will in no event exceed 2.99 times the officer’s average W-2 earnings over the preceding five years.
Kroger’s change in control benefits under KEPP and under equity compensation awards are discussed further in the Compensation Discussion and Analysis section under the “Retirement and Other Benefits” heading.
Compensation Policies as They Relate to Risk Management
Kroger’s compensation policies and practices for its employees are designed to attract and retain highly qualified and engaged employees, and to minimize risks that would have a material adverse effect on Kroger. One of these policies, the executive compensation recoupment policy, is more particularly described in the Compensation Discussion and Analysis. Kroger does not believe that its compensation policies and practices create risks that are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on Kroger.service.
4051
Beneficial Ownership of Common Stock
AsThe following table sets forth the common shares beneficially owned as of February 15, 2013,April 1, 2016 by Kroger’s directors, the named executive officers,NEOs, and the directors and executive officers as a group, beneficially ownedgroup. The percentage of ownership is based on 964,367,417 of Kroger common shares outstanding on April 1, 2016. Shares reported as follows:beneficially owned include shares held indirectly through Kroger’s defined contribution plans and other shares held indirectly, as well as shares subject to stock options exercisable on or before May 31, 2016. Except as otherwise noted, each beneficial owner listed in the table has sole voting and investment power with regard to the common shares beneficially owned by such owner.
| Amount and Nature | |||||
| of | |||||
| Name | Beneficial Ownership | ||||
| Reuben V. Anderson | 98,620 | (1) | |||
| Kathleen S. Barclay | 82,287 | (2) | |||
| Robert D. Beyer | 140,767 | (1) | |||
| David B. Dillon | 2,263,954 | (2)(3)(4) | |||
| Paul W. Heldman | 516,645 | (2)(3)(5) | |||
| Susan J. Kropf | 43,250 | (6) | |||
| John T. LaMacchia | 111,496 | (1) | |||
| David B. Lewis | 74,752 | (1) | |||
| W. Rodney McMullen | 1,240,157 | (2)(3) | |||
| Jorge P. Montoya | 36,815 | (6) | |||
| Clyde R. Moore | 87,450 | (1) | |||
| Susan M. Phillips | 74,340 | (7) | |||
| Steven R. Rogel | 87,983 | (1) | |||
| James A. Runde | 51,750 | (8) | |||
| Ronald L. Sargent | 50,750 | (8) | |||
| J. Michael Schlotman | 284,526 | (2)(3) | |||
| Bobby S. Shackouls | 63,250 | (9) | |||
| Directors and Executive Officers as a group (including those named above) | 7,250,108 | (2)(3) | |||
| Name | Amount and Nature of Beneficial Ownership(1) (a) | Options | ||||||
| Nora A. Aufreiter(2) | 7,513 | — | ||||||
| Robert D. Beyer(2) | 295,682 | 77,200 | ||||||
| Michael J. Donnelly | 467,879 | 249,296 | ||||||
| Anne Gates | 2,386 | — | ||||||
| Christopher T. Hjelm | 379,250 | 141,152 | ||||||
| Susan J. Kropf | 137,460 | 67,200 | ||||||
| David B. Lewis(2) | 158,255 | 67,200 | ||||||
| W. Rodney McMullen | 3,292,520 | 1,041,184 | ||||||
| Jorge P. Montoya(3) | 101,362 | 67,200 | ||||||
| Clyde R. Moore | 145,860 | 57,200 | ||||||
| Frederick J. Morganthall II | 183,101 | — | ||||||
| Susan M. Phillips | 176,923 | 67,200 | ||||||
| James A. Runde | 154,460 | 77,200 | ||||||
| Ronald L. Sargent(2) | 152,630 | 77,200 | ||||||
| J. Michael Schlotman | 606,675 | 248,304 | ||||||
| Bobby S. Shackouls(2)(4) | 73,180 | — | ||||||
| Directors and executive officers as a group (29 persons, | ||||||||
| including those named above) | 8,187,350 | 2,998,844 | ||||||
| (1) | ||
| (2) | This amount includes incentive share awards that were deferred under the deferred compensation plan for independent directors in the following amounts: Ms. Aufreiter, 4,357; Mr. Beyer, 6,833; Mr. Lewis, 11,190; Mr. Sargent, 11,190; Mr. Shackouls, 11,190. | |
| (3) | ||
| This amount includes | ||
| This amount includes | ||
No director or officer owned as much as 1% of the common shares of Kroger. The directors and executive officers as a group beneficially owned 1% of the common shares of Kroger.
4152
No director or officer ownedThe following table sets forth information regarding the beneficial owners of more than five percent of Kroger common shares pledged as security.
As of February 15, 2013, the following reported beneficial ownership of Kroger common sharesApril 1, 2016 based on reports on Schedule 13G filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission or other reliable information as follows:SEC.
| Amount and | |||||||||||
| Nature of | Percentage | ||||||||||
| Name | Address of Beneficial Owner | Ownership | of Class | ||||||||
| BlackRock, Inc. | 40 East 52ndStreet | 30,824,789 | 5.95% | ||||||||
| New York, NY 10022 | |||||||||||
| The Kroger Co. Savings Plan | 1014 Vine Street | 28,433,496 | (1) | 5.5% | |||||||
| Cincinnati, OH 45202 | |||||||||||
| Name | Address of Beneficial Owner | Amount and Nature of Ownership | Percentage of Class | |||
| BlackRock, Inc.(1) | 55 East 52ndStreet | 66,134,371 | 6.80% | |||
| New York, NY 10055 | ||||||
| Vanguard Group Inc.(2) | 100 Vanguard Blvd | 54,699,370 | 5.61% | |||
| Malvern, PA 19355 |
| (1) | Reflects beneficial ownership by | |
| (2) | Reflects beneficial ownership by Vanguard Group Inc. as of December 31, 2015, as reported on Amendment No. 1 to Schedule 13G filed with the SEC on February 10, 2016, and reports sole voting power with respect to 1,804,169 common shares, shared voting power with respect to 94,000 common shares, sole dispositive power of 52,789,803 common shares, and shared dispositive power of 1,909,567 common shares. | |
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
Section 16(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 requires our officers and directors, and persons who own more than 10% of a registered class of our equity securities, to file reports of ownership and changes in ownership with the Securities and Exchange Commission.SEC. Those officers, directors and shareholders are required by SEC regulation to furnish us with copies of all Section 16(a) forms they file.
Based solely on our review of the copies of formsForms 3 and 4 received by Kroger, and any written representations from certain reporting persons that no Forms 5 were required for those persons, we believe that during fiscal year 20122015 all filing requirements applicable to our executive officers, directors and 10% beneficial owners were timely satisfied, with the following exception. In January 2013, Mr.August 2015, Michael L. Ellis, filed an amendedwho retired as President and Chief Operating Officer of the Company in July 2015, was 2 days late in the filing of a Form 34 to report ownershipa stock purchase in the amount of 750 additional shares that were inadvertently omitted from his original Form 3 and subsequent Form 4 filing.500 shares.
Related Person Transactions
Pursuant to ourStatement of Policy with Respect to Related Person Transactions and the rules of the SEC, Kroger
The Board has the following related person transactions, which were approved by Kroger’s Audit Committee, to disclose:
Director independence is discussed above under the heading “Information Concerning the Board of Directors.” Kroger’swritten policy on related person transactions is as follows:
42
Statement of Policywith Respect toRelated Person Transactions
A. Introduction
It is the policy of Kroger’s Board of Directorsrequiring that any Related Person Transaction may be consummated or may continue only if the Audit Committee approves or ratifies the transaction in accordance with the guidelines set forth in this policy. The Board of Directors has determined that the Audit Committee of the Board is best suited to review and approve Related Person Transactions.
For the purposes of this policy, a “Related Person” is:
For the purposes of this policy, aA “Related Person Transaction” is a transaction, arrangement or relationship (or any series of similar transactions, arrangements or relationships) since the beginning of Kroger’s last fiscal yearone (a) involving Kroger, (b) in which Kroger (including anyone of its subsidiaries) was, isour directors, nominees for director, executive officers, or will be a participant and the amount involved exceeds $120,000, and in which any Related Person had, hasgreater than five percent shareholders, or willtheir immediate family members, have a direct or indirect material interest (other than solely as a result of being a director or a less than 10 percent beneficial owner of another entity).
Notwithstanding the foregoing, the Audit Committee has reviewed the following types of transactionsinterest; and has determined that each type of transaction is deemed to be pre-approved, even if(c) the amount involved exceeds $120,000.$120,000 in a fiscal year.
43
B.The Audit Committee Approval
In the event management becomes aware of anywill approve only those Related Person Transactions that are in, or not deemed pre-approved under paragraph Ainconsistent with, the best interests of this policy, those transactions will be presented to the Committee for approval at the next regular Committee meeting, or where it is not practicable or desirable to wait until the next regular Committee meeting, to the Chair of the Committee (who will possess delegated authority to act between Committee meetings) subject to ratificationKroger and its shareholders, as determined by the Audit Committee atin good faith in accordance with its next regular meeting. If advancebusiness judgment. No director may participate in any review, approval or ratification of any transaction if he or she, or an immediate family member, has a Related Person Transaction is not feasible, thendirect or indirect material interest in the Related Person Transaction will be presented to the Committee for ratification at the next regular Committee meeting, or where it is not practicable or desirable to wait until the next regular Committee meeting, to the Chair of the Committee for ratification, subject to further ratification by the Committee at its next regular meeting.transaction.
In connection with each regular Committee meeting, a summary of each new Related Person Transaction deemed pre-approved pursuant to paragraphs A(1) and A(2) above will be provided to the Committee for its review.
IfWhere a Related Person Transaction will be ongoing, the Audit Committee may establish guidelines for management to follow in its ongoing dealings with the Related Person. Thereafter,related person and the Audit Committee on at least an annual basis, will review and assess ongoing relationshipsthe relationship on an annual basis to ensure it complies with the Related Person to see that they are in compliance with the Committee’ssuch guidelines and that the Related Person Transaction remains appropriate.
The Committee (or the Chair) will approve only those Related Person Transactions that are in, or are not inconsistent with, the best interests of Kroger and its shareholders, as the Committee (or the Chair) determines in good faith in accordance with its business judgment.
No director will participate in any discussion or approval of a Related Person Transaction for which he or she, or an immediate family member (as defined above), is a Related Person except that the director will provide all material information about the Related Person Transaction to the Committee.
C. Disclosure
Kroger will disclose all Related Person Transactions in Kroger’s applicable filings as required by the Securities Act of 1933, the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and related rules.
4453
Audit Committee ReportItem No. 3 Ratification of the Appointment of Kroger’s Independent Auditor
You are being asked to ratify the appointment of Kroger’s independent auditor, PricewaterhouseCoopers LLC. The Board of Directors recommends that you vote FOR the ratification of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP as our independent registered public accounting firm.
The primary function of the Audit Committee is to represent and assist the Board of Directors in fulfilling its oversight responsibilities regarding the Company’s financial reporting and accounting practices including the integrity of the Company’s financial statements; the Company’s compliance with legal and regulatory requirements; the independent public accountants’ qualifications and independence; the performance of the Company’s internal audit function and independent public accountants; and the preparation of this report that SEC rules require be included in the Company’s annual proxy statement.Audit Committee Report. The Audit Committee performs this work pursuant to a written charter approved by the Board of Directors. The Audit Committee charter most recently was revised during fiscal 2012 and is available on the Company’s website at ir.kroger.com.ir.kroger.com under Corporate Governance – Committee Composition. The Audit Committee has implemented procedures to assist it during the course of each fiscal year in devoting the attention that is necessary and appropriate to each of the matters assigned to it under the Committee’s charter. The Audit Committee held five meetings during fiscal year 2012. The Audit Committee meets separately with the Company’s internal auditor and PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, the Company’s independent public accountants, without management present, to discuss the results of their audits, their evaluations of the Company’s internal controls over financial reporting, and the overall quality of the Company’s financial reporting. The Audit Committee also meets separately with the Company’s Chief Financial Officer and General Counsel when needed. Following these separate discussions, the Audit Committee meets in executive session.
Management of the Company is responsible for the preparation and presentation of the Company’s financial statements, the Company’s accounting and financial reporting principles and internal controls, and procedures that are designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding compliance with accounting standards and applicable laws and regulations. The independent public accountants are responsible for auditing the Company’s financial statements and expressing opinions as to the financial statements’ conformity with generally accepted accounting principles and the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
In the performance of its oversight function, the Audit Committee has reviewed and discussed with management and PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP the audited financial statements for the year ended February 2, 2013, management’s assessment of the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of February 2, 2013, and PricewaterhouseCoopers’ evaluation of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of that date. The Audit Committee has also discussed with the independent public accountants the matters that the independent public accountants must communicate to the Audit Committee under applicable requirements of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board.
With respect to the Company’s independent public accountants, the Audit Committee, among other things, discussed with PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP matters relating to its independence and has received the written disclosures and the letter from the independent public accountants required by applicable requirements of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board regarding the independent public accountants’ communications with the Audit Committee concerning independence. The Audit Committee has reviewed and approved in advance all services provided to the Company by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP. The Audit Committee conducted a review of services provided by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP which included an evaluation by management and members of the Audit Committee.
Based upon the review and discussions described in this report, the Audit Committee recommended to the Board of Directors that the audited consolidated financial statements be included in the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended February 2, 2013, as filed with the SEC.
This report is submitted by the Audit Committee.
Ronald L. Sargent, ChairSusan J. KropfSusan M. PhillipsBobby S. Shackouls2015.
45
Advisory Vote on Executive Compensation(Item No. 2)
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, enacted in July 2010, requires that we give our shareholders the right to vote to approve, on a nonbinding, advisory basis, the compensation of our named executive officers as disclosed earlier in this proxy statement in accordance with the SEC’s rules.
As discussed earlier in ourCompensation Discussion and Analysis, our compensation philosophy is to:
Furthermore, as previously disclosed, an increased percentage of total potential compensation is performance-based as opposed to time-based as half of the compensation previously awarded to the named executive officers as restricted stock (and earned based on the passage of time) is now only earned to the extent that performance goals are achieved. In addition, annual and long-term cash bonuses are performance-based and earned only to the extent that performance goals are achieved. In tying a large portion of executive compensation to achievement of short-term and long-term strategic and operational goals, we seek to closely align the interests of our named executive officers with the interests of our shareholders.
The vote on this resolution is not intended to address any specific element of compensation. Rather, the vote relates to the compensation of our named executive officers as described in this proxy statement. The vote is advisory. This means that the vote is not binding on Kroger. The Compensation Committee of our Board of Directors is responsible for establishing executive compensation. In so doing that Committee will consider, along with all other relevant factors, the results of this vote.
The affirmative vote of a majority of the shares present and represented in person or by proxy is required to approve this proposal. Broker non-votes and abstentions will have no effect on the outcome of this vote.
We ask our shareholders to vote on the following resolution:
“RESOLVED, that the compensation paid to the company’s named executive officers, as disclosed pursuant to Item 402 of Regulation S-K, including Compensation Discussion and Analysis, compensation tables, and narrative discussion, is hereby APPROVED.”
The Board of Directors Recommends a VoteFor This Proposal.
Selection of Auditors
Independent Auditor(Item No. 3)
The Audit Committee of the Board of Directors is directly responsible for the appointment, compensation, retention, and retentionoversight of Kroger’s independent auditor, as required by law and by applicable NYSE rules. On March 13, 2013,9, 2016, the Audit Committee appointed PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP as Kroger’s independent auditor for the fiscal year ending February 1, 2014. January 28, 2017.
In determining whether to reappoint the independent auditor, our Audit Committee:
| ● | Reviews PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP’s independence and performance; |
| ● | Reviews, in advance, all non-audit services provided by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, specificallywith regard to the effect on the firm’s independence; |
| ● | Conducts an annual assessment of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP’s performance, including aninternal survey of their service quality by members of management and the Audit Committee; |
| ● | Conducts regular executive sessions with PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP; |
| ● | Conducts regular executive sessions with the Vice President of Internal Audit; |
| ● | Considers PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP’s familiarity with our operations, businesses, accountingpolicies and practices and internal control over financial reporting; |
| ● | Reviews candidates for the lead engagement partner in conjunction with the mandated rotation ofthe public accountants’ lead engagement partner; |
| ● | Reviews recent Public Company Accounting Oversight Board reports on PricewaterhouseCoopersLLP and its peer firms; and |
| ● | Obtains and reviews a report from PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP describing all relationshipsbetween the independent auditor and Kroger at least annually to assess the independence of theinternal auditor. |
As a result, the members of the Audit Committee believe that the continued retention ofPricewaterhouseCoopers LLP to serve as our independent registered public accounting firm is in the best interests of our company and its shareholders.
While shareholder ratification of the selection of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP as Kroger’sour independent auditor is not required by Kroger’s Regulations or otherwise, the Board of Directors is submitting the selection of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP to shareholders for ratification, as it has in past years, as a good corporate governance practice. If the shareholders fail to ratify the selection, the Audit Committee
54
may, but is not required to, reconsider whether to retain that firm. Even if the selection is ratified, the Audit Committee in its discretion may direct the appointment of a different auditor at any time during the year if it determines that such a change would be in the best interests of Krogerour company and itsour shareholders.
A representative of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP is expected to be present at the meeting to respond to appropriate questions and to make a statement if he or she desires to do so.
The Board of Directors Recommends a VoteFor This Proposal.
46Audit and Non-Audit Fees
Disclosure of Auditor Fees
The following describestable presents the aggregate fees billed to Krogerfor professional services performed by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP related to the fiscal years ended February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012:
| Fiscal Year 2012 | Fiscal Year 2011 | |||||||||
| Audit Fees | $ | 4,439,110 | $ | 4,163,571 | ||||||
| Audit-Related Fees | 45,993 | — | ||||||||
| Tax Fees | — | 75,819 | ||||||||
| All Other Fees | — | — | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 4,485,103 | $ | 4,239,390 | ||||||
Audit Feesfor the years ended February 2, 2013annual audit and January 28, 2012, respectively, were for professional services rendered for the auditsquarterly reviews of Kroger’sour consolidated financial statements the issuance of comfort letters to underwriters, consents,for fiscal 2015 and assistance with the review of documents filed with the SEC.
Audit-Related Fees. Audit related services2014, and for the year ended February 2, 2013 were for assuranceaudit-related, tax and related services pertaining to accounting consultation in connection with attest services that are not required by statute or regulation, and consultations concerning financial accounting and reporting standards. These services are considered approved under the Company’s existing Audit and Non-Audit Service Pre-Approval Policy. We did not engage PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP for any audit-related services for the year ended January 28, 2012.
Tax Fees for the year ended January 28, 2012 were for an analysis of sales tax. We did not engage PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP for any tax services for the year ended February 2, 2013.
All Other Fees. We did not engage PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP forall other services for the years ended February 2, 2013performed in 2015 and January 28, 2012.2014.
| Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||
| January 30, 2016 | January 31, 2015 | |||||||||
| Audit Fees(1) | $ | 5,659,193 | $ | 5,250,203 | ||||||
| Audit-Related Fees(2) | — | 441,704 | ||||||||
| Tax Fees(3) | — | 360,498 | ||||||||
| All Other Fees(4) | — | 85,000 | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 5,659,193 | $ | 6,137,405 | ||||||
| (1) | Includes annual audit and quarterly reviews of Kroger’s consolidated financial statements, the issuance of comfort letters to underwriters, consents, and assistance with review of documents filed with the SEC. | |
| (2) | Includes assurance and related services pertaining to accounting consultation in connection with attest services that are not required by statute or regulations, and consultation concerning financial accounting and reporting standards. These fees also included services related to acquisition related due diligence. | |
| (3) | Includes state tax compliance, tax audit support and debt restructuring. | |
| (4) | Includes fees for fiscal 2014 for advisory services pertaining to retiree healthcare benefits. | |
The Audit Committee requires that it approve in advance all audit and non-audit work performed by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP. On March 13, 2013,9, 2016, the Audit Committee approved services to be performed by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP for the remainder of fiscal year 20132015 that are related to the audit of Kroger or involve the audit itself. In 2007, the Audit Committee adopted an audit and non-audit service pre-approval policy. Pursuant to the terms of that policy, the Committee will annually pre-approve certain defined services that are expected to be provided by the independent auditors. If it becomes appropriate during the year to engage the independent accountant for additional services, the Audit Committee must first approve the specific services before the independent accountant may perform the additional work.
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP has advised the Audit Committee that neither the firm, nor any member of the firm, has any financial interest, direct or indirect, in any capacity in Kroger or its subsidiaries.
The Board of Directors Recommends a VoteFor This Proposal.
Shareholder Proposal55
Audit Committee Report
Management of the Company is responsible for the preparation and presentation of the Company’s financial statements, the Company’s accounting and financial reporting principles and internal controls, and procedures that are designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding compliance with accounting standards and applicable laws and regulations. The independent public accountants are responsible for auditing the Company’s financial statements and expressing opinions as to the financial statements’ conformity with generally accepted accounting principles and the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
In performing its functions, the Audit Committee:
| ● | Met separately with the Company’s internal auditor and PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP with andwithout management present to discuss the results of the audits, their evaluation and management’sassessment of the effectiveness of Kroger’s internal controls over financial reporting and the overallquality of the Company’s financial reporting; |
| ● | Met separately with the Company’s Chief Financial Officer or the Company’s General Counselwhen needed; |
| ● | Met regularly in executive sessions; |
| ● | Reviewed and discussed with management the audited financial statements included in ourAnnual Report; |
| ● | Discussed with PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP the matters required to be discussed under theapplicable requirements of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board; |
| ● | Received the written disclosures and the letter from PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP required by theapplicable requirements of the Public Accounting Oversight Board regarding the independent publicaccountant’s communication with the Audit Committee concerning independence and discussedwith them matters related to their independence; and |
Based upon the review and discussions described in this report, the Audit Committee recommended to the Board of Directors that the audited consolidated financial statements be included in the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 30, 2016, as filed with the SEC.
This report is submitted by the Audit Committee.
Ronald L. Sargent, Chair
Anne Gates
Susan J. Kropf
Susan M. Phillips
Bobby S. Shackouls
56
Item No. 4)4 Shareholder Proposal
We have been notified by fournine shareholders, the names and shareholdings of which will be furnished promptly to any shareholder upon written or oral request to Kroger’s Secretary at Kroger’sour executive offices, that they intend to propose the following resolution at the annual meeting:
2013 –The Kroger Company
Human Rights Risk Assessment - 2016
“RESOLVED, that shareholders of The Kroger Co. (“Kroger”) urge the Board of Directors to report to shareholders, at reasonable cost and omitting proprietary information, on Kroger’s process for identifying and analyzing potential and actual human rights risks of Kroger’s operations and supply chain (referred to herein as a “human rights risk assessment”) addressing the following:
| ● | Human rights principles used to frame the assessment |
| ● | Frequency of assessment |
| ● | Methodology used to track and measure performance |
| ● | Nature and extent of consultation with relevant stakeholders in connection with the assessment |
| ● | How the results of the assessment are incorporated into company policies and decision making. |
The report should be made available to shareholders on Kroger’s website no later than October 31, 2016.
WHEREASSupporting Statement,
As long-term shareholders, we favor policies and practices that protect and enhance the value of our investments. There is increasing recognition that company risks related to human rights violations, such as litigation, reputational damage, and project delays and disruptions, can adversely affect shareholder value.
Kroger, like many other companies, has adopted a supplier code of conduct (See The Kroger Company purchases significant amountsStandard Vendor Agreement) but has yet to publish a company-wide Human Rights Policy, addressing human rights issues and a separate human rights code that applies to its suppliers. Adoption of fruitsthese principles would be an important first step in effectively managing human rights risks. Companies must then assess risks to shareholder value of human rights practices in their operations and vegetables, from both domestic and international sources, andsupply chains to translate principles into protective practices.
The importance of human rights risk assessment is one of the largest supermarket chainsreflected in the United States,Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights (the “Ruggie Principles”) approved by the UN Human Rights Council in 2011. The Ruggie Principles urge that “business enterprises should carry out human rights due diligence... assessing actual and potential human rights impacts, integrating and acting upon the findings, tracking responses, and communicating how impacts are addressed.” (http://www.business-humanrights.org/media/documents/ruggie/ruggie-guiding-principles-21-mar-2011.pdf)
WHEREAS, the United States DepartmentKroger’s business exposes it to significant human rights risks. As of Justice has successfully prosecuted several casesyear-end 2014, Kroger operations, including supermarkets, convenience and jewelry stores, are located in over 40 states. While over 90% of modern-day slavery in the U.S. agricultural industry since 1996, involving over 1,000 workers, (see, for example, US v. Ramos; US v. Lee; US v. Flores; US v. Cuello; US v. Tecum) and thereKroger’s business is increasing public awareness and media coverage of the abuses that many agricultural workers face, and
47
WHEREAS, neither our company’s Supplierfood its vendor Code of Conduct or its 2012 Sustainability Report addresses human rights, a major corporate responsibility issue, and
WHEREAS, according to the Polaris Project, one of the leading organizations in the global fight against human trafficking and modern-day slavery, victims of labor trafficking have been found among the nation’s migrant and seasonal farmworkers, including men, women, families, or children as young as 5 or 6 years old who harvest crops and raise animals in fields, packing plants, orchards, and nurseries, and
WHEREAS, Kroger’s current Code of Conduct for suppliers is based heavily on compliance with the law, (Kroger 2012 Sustainability Report, page 42 “Vendor Standards”) http://sustainability.kroger.com/2012KrogerSustainabilityReport.pdf and U.S. agricultural workers are excluded from many labor laws that apply to other U.S. workers (for example, National Labor Relations Actworkers. The company’s supply chain is complex and global and violations of 1935, 29 U.S.C. § 151 at seq.; portionshuman rights in Kroger’s supply chain can lead to negative publicity, public protests, and a loss of the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938, 29 U.S.C. § 201, 213), andconsumer confidence that can have a negative impact on shareholder value.
We urge shareholders to vote for this proposal.”
WHEREAS57, although the company website stipulates that Kroger and its affiliates are subject to the provisions of the California Transparency in Supply Chains Act of 2010, compliance with this law is not verified by frequent third-party, unannounced audits,
THEREFORE BE IT RESOLVED that the shareholders urge the Board of Directors to publish a report assessing the human rights risks, including human trafficking and forced labor (modern day slavery), throughout its supply chain. The report should evaluate all policies and procedures in place to manage identified risks relating to the labor practices of suppliers, including labor brokers. In addition, the report should include the findings from any audits undertaken and the steps taken to resolve any identified issues.
The Board of Directors Recommends a VoteAgainst This Proposal for the Following Reasons:
KrogerLike the proponents, the Board also recognizes the importance of ensuring basic human rights are recognized bythat those seeking to do business with us. As such, Kroger hasus respect basic human rights. However, the Board opposes this proposal because we are already working to ensure an ethical supply chain for the products sold in placeour stores and we have a comprehensive code of conduct that is applicable to those that furnish goods or services to us, as well as their contractors. That code of conduct has been published and is available on our website at ir.kroger.com. Our existing code of conduct requires compliance with all applicable labor laws, regulations, and orders, including the Fair Labor Standards Act. In addition, the code of conduct:
Kroger’s code of conduct does more than simply reporting on human rights risks in its supply chain; it prohibits those that do business with us from engaging in the type of conduct of concernviolations. Furthermore, we regularly consider our policies and practices and we have recently taken several important steps to the proponents. Those that violate our code will not be permitted to do business with us until they comply with our code. As such, we do not believe that human rights violations indrive into our supply chain posegreater responsibility and accountability:
| ● | In 2015, after consultation with a number of stakeholders, we updated our Vendor Code of Conduct(the “Code of Conduct”), which is available at www.thekrogerco.com. The new Code of Conductmakes it clear that our suppliers and their suppliers are expected to live up to our standards as setforth in the Code of Conduct. To the extent they do not live up to such standards, we will not dobusiness with them. |
| ● | In 2015, we created a social responsibility center of excellence (the “Center of Excellence”) toschedule, review and monitor social responsibility audits, assess risks such as those describedabove and develop a reporting structure that informs our business decisions. The Center ofExcellence is also tasked with recommending ways to continually improve social accountability inour supply chain. |
| ● | In 2015, our annual sustainability report included a more in-depth report on our social responsibilityactivities, which is available at sustainability.kroger.com. |
| ● | Since 2012, we have more than doubled the number of social responsibility audits we haveconducted and we expect this program to continue to grow. |
| ○ | This past year, our work revealed several facility failures. Many of these facilities have significantly improved through corrective action plans, but we are no longer doing business with a few. |
| ● | In 2016, we made the Kroger Social Responsibility Audit Checklist (the “Audit Checklist”) availableonline. The Audit Checklist is required for Kroger suppliers that our social responsibility teamidentifies as higher risk due to variables such as country, product and/or industry. |
| ○ | In commodities and/or regions that are higher risk, like farmed shrimp in Thailand, we not only request supplier audits but also work with third party environmental and social certification programs to further eliminate risk in the supply chain. |
| ● | In 2016, Kroger will also conduct a third party review of commodities in our supply chain to furtherassess both environmental and social risks. |
We expect our program to continue to evolve and develop based on input from suppliers, customers, government, non-governmental organizations and developments within the industry. We believe that these efforts represent significant and positive steps forward for our Company’s social responsibility program.
Kroger is already actively implementing, monitoring, and continually improving our policies and practices, addressing a substantial risk,number of the areas discussed by the proponent. We believe that the requestedpreparation of an additional report would serve little benefitnot be an efficient use of our shareholders’ resources. We urge you to shareholders, and preparation of a report would divert resources that otherwise could be more appropriately used in the best interests of shareholders.voteAGAINST this proposal.
48
Shareholder Proposal(Item No. 5)5 Shareholder Proposal
We have been notified by aone shareholder, the name and shareholdings of which will be furnished promptly to any shareholder upon written or oral request to Kroger’s Secretary at Kroger’sour executive offices, that it intends to propose the following resolution at the annual meeting:
58
Independent Board ChairShareholder Proposal
Recyclability of Packaging
“WHEREAS: RESOLVED: The shareholdersA portion of Kroger (the “Company”) urgehouse brand product packaging is unrecyclable, including plastics, which are a growing component of marine litter. Authorities say that marine litter kills and injures marine life, spreads toxics, and poses a potential threat to human health.
Plastic is the Boardfastest growing form of Directorspackaging; U.S. flexible plastic sales are estimated at $26 billion. Dried fruit, frozen meat, cheese, and dog food are some of the Kroger house brand items packaged in unrecyclable plastic pouches. Private label items account for a quarter of all sales - nearly $20 billion annually. Using unrecyclable packaging when recyclable alternatives are available wastes valuable resources. William McDonough, a leading green design advisor, calls pouch packaging a “monstrous hybrid” designed to adoptend up either in a policy thatlandfill or incinerator.
Recyclability of household packaging is a growing area of focus as consumers become more environmentally conscious, yet recycling rates stagnate. Only 14% of plastic packaging is recycled, according to the Board’s chairman be an independent director. The policy should be implemented so as not to violate any contractual obligationU.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Billions of pouches and should specify: (a) how to select a new independent chairman if a current chairman ceasessimilar plastic laminates, representing significant embedded value, lie buried in landfills. Unrecyclable packaging is more likely to be littered and swept into waterways. A recent assessment of marine debris by a panel of the Global Environment Facility concluded that one cause of debris entering oceans is “design and marketing of products internationally without appropriate regard to their environmental fate or ability to be recycled...”
In the marine environment, plastics break down into indigestible particles that marine life mistake for food. Studies by the EPA suggest a synergistic effect between plastic debris and persistent, bio-accumulative, toxic chemicals. Plastics absorb toxics such as polychlorinated biphenyls and dioxins from water or sediment and transfer them to the marine food web and potentially to human diets. One study of fish from the North Pacific found one or more plastic chemicals in all fish tested, independent during the time between annual meetings of shareholders;location and (b) that compliance with the policy is excusedspecies.
California spends nearly $500 million annually preventing trash, much of it packaging, from polluting beaches, rivers and oceanfront. Making all packaging recyclable, if no independent director is available and willing to serve as chairman.
SUPPORTING STATEMENT: Itpossible, is the responsibilityfirst step needed to reduce the threat posed by ocean debris.
Companies who aspire to corporate sustainability yet use these risky materials need to explain why they use unrecyclable packaging. Other companies who manufacture and sell food and household goods are moving towards recyclability. Procter & Gamble and Colgate-Palmolive agreed to make most of the Boardtheir packaging recyclable by 2020. Keurig Green Mountain will make K-cup coffee pods recyclable; and McDonald’s and Dunkin Donuts shifted away from foam plastic cups, which cannot be readily recycled.
RESOLVED: Shareowners of Directors to protect shareholders’ long-term interests by providing independent oversight of management. By setting agendas, priorities and procedures,Kroger request that the position of Chairman is critical in shaping the work of the Board.
In our opinion, a board of directors is less likelyissue a report, at reasonable cost, omitting confidential information, assessing the environmental impacts of continuing to provide rigorous independent oversight of management the Chairman is the CEO, as is the case with our Company. CEO David B. Dillon has served as both Chairman and CEO since 2004.use unrecyclable brand packaging.
Supporting Statement: WeProponents believe that having a board chairman who is independentthe report should include an assessment of the Companyreputational, financial and its management isoperational risks associated with continuing to use unrecyclable brand packaging and, if possible, goals and a governance practice that will promote greater management accountabilitytimeline to shareholders and lead to a more objective evaluation of management.phase out unrecyclable packaging.”
According to the Millstein Center for Corporate Governance and Performance (Yale School of Management), “The independent chair curbs conflicts of interest, promotes oversight of risk, manages the relationship between the board and CEO, serves as a conduit for regular communication with shareowners, and is a logical next step in the development of an independent board.” (Chairing the Board: The Case for Independent Leadership in Corporate North America, 2009)
An NACD Blue Ribbon Commission on Directors’ Professionalism recommended several years ago that an independent director should be charged with “organizing the board’s evaluation of the CEO and provide ongoing feedback; chairing executive sessions of the board; setting the agenda and leading the board in anticipating and responding to crises.” A blue-ribbon report from The Conference Board echoed that sentiment a few years later.
A number of institutional investors believe that a strong, objective board leader can best provide the necessary oversight of management. Thus, the California Public Employees’ Retirement System’s Global Principles of Accountable Corporate Governance recommends that a company’s board should generally be chaired by an independent director, as does the Council of Institutional investors.
We thus believe that an independent director serving as chairman can help ensure the functioning of an effective board. We urge you to voteFOR this resolution.
The Board of Directors Recommends Aa VoteAgainst This Proposal for the Following Reasons:
Kroger’s Board is structured to provideKroger shares the best governance on behalf of shareholders. That structure also eliminates allproponent’s concerns regarding plastic recyclability and recognizes the important role we play as a good steward of the concerns raisedenvironment.
We continue to improve the recyclability of our Corporate Brand products, while still preserving their safety and quality. More specifically, we follow a balanced, multi-pronged approach to optimizing packaging design that considers factors such as food safety, shelf life, availability, quality, material type, function, recyclability and cost, among others.
We are increasingly labeling recyclable Corporate Brand products per the Federal Trade Commission’s Green Guides, prompting our customers to “PLEASE RECYCLE.” One example is through our redesign of Kroger brand milks, creams and orange juices that come in the proponent’s supporting statement.
Kroger’s Board is comprised of an overwhelming majority, 87%, of independent directors. Each of these directors is elected annually by the shareholders. And although not addressed in the proposal, Kroger’s Board is led by a strong independent Lead Director who serves the same functionsquart, pint and provides safeguards against mismanagement that the proposal seeks. In particular, Kroger’s Lead Director serves in a variety of roles, including reviewing and approving all Board meeting agendas, meeting materials and schedules to ensure that the appropriate topics are reviewed and that sufficient time is allocated to each; serving as a liaison between
4959
the chairmanhalf-pint packages. The packaging for these products is comprised of a bottle made from #1 polyethylene terephthalate (PETE), one of the Board, management,most widely recycled plastics available, and a shrink sleeve. While the shrink sleeve is also made from #1 PETE, these shrink sleeves may interfere with the ability of the bottles to be segregated and recycled when a recycling facility uses optical scanning technology. As a result, in order to increase the number of Corporate Brand #1 PETE bottles that can be properly recycled, we have added a tear perforation and the non-management directors; presidingconsumer message, “REMOVE LABEL TO RECYCLE BOTTLE,” to the shrink labels.
We recognize that creating lasting sustainable consumption patterns requires a comprehensive approach and so we also work with various industry experts and forums to advocate for expanded recycling infrastructure to support both multiple forms of plastic packaging and diversion from landfills.
Additionally, our banner brand bread bags are made from low-density polyethylene (LDPE). This type of plastic can be a contaminant in many single stream recycling programs. To help our customers recycle their LDPE bread bags we have added customer communication on the bag that reads, “Please recycle at your local, Kroger Family of Stores drop-off location.” These drop-off recycling bins are part of our plastic bag recycling program and are typically located in the executive sessionsfront vestibule of independent directors (held afterour stores. Along with bread bags, customers can also recycle clean and dry plastic bags, bottled water case wraps, bathroom tissue and diaper plastic overwraps, dry cleaning bags, and newspaper bags. This program is currently undergoing rebranding and expansion to encourage customers to recycle even more in 2016 and beyond.
For each Board meeting) and at all other meetings of the Boardpast several years we have published online our annual Sustainability Report that highlights our sustainability initiatives and waste reduction efforts in greater detail, available at which the chairman is not present; calling an executive session of the independent directors at any time; and serving as the Board’s representative for any consultation and direct communication, following a request, with major shareholders. These roles aresustainability.kroger.com. In that report, we set forth a rigorous and tangible goal to strive to have zero waste in the Board’sGuideline’s on Issues of Corporate Governance, published on our website at ir.kroger.com.
The Board routinely reviews Kroger’s leadership structure. This review includes a discussion of Kroger’s performance, the impact that the leadership has on that performance,retail locations. Through this initiative, and the structure that best serves the interests of shareholders.
Contrary to the assertions in the proponent’s supporting statement, there is no established consensus that separating the roles of the chairman and the CEO is a best practice or that such a separation enhances returns for shareholders. The authors of a 2004 Wharton School of Business article entitled “Splitting Up the Roles of CEO and Chairman: Reform or Red Herring?” (http://knowledge.wharton.upenn.edu/article.cfm?articleid=987) concluded that there is no evidence that separating the positions of chairman and CEO improves corporate performance. In “Corporate Governance Update: Analyzing Aspects of Board Composition,” David A Katz and Laura A. McIntosh, New York Law Journal, January 26, 2012, the authors concluded that from a board effectiveness perspective, there is no need to separate the roles of chairman and CEO so long as there is an effective lead director in place. In addition, the majority of U.S. companies have not implemented the structure recommended by the proposal.
While there may be circumstances in which shareholders of corporations would be best served by having an independent Board chair, those circumstances simply do not currently exist at Kroger. There have been times in Kroger’s past in which the positions of chairman of the Board and CEO have been separated, but current circumstances do not warrant a separation. The Boardothers, we will continue to review Kroger’s leadership structuresupport efforts to ensure that the structure best addresses Kroger’s evolvingreduce waste, find optimized solutions and dynamic business. For the foregoing reasons, the Board recommends aadvocate for expanded recycling infrastructure as we believe these efforts are significant and meaningful. We urge you to support these efforts and voteAGAINST this proposal.
Shareholder Proposal(Item No. 6)6 Shareholder Proposal
We have been notified by two shareholders, the names and shareholdings of which will be furnished promptly to any shareholder upon written or oral request to Kroger’s Secretary at our executive offices, that they intend to propose the following resolution at the annual meeting:
Shareholder Proposal
Renewable Energy
“Whereas:
To mitigate the worst impacts of climate change, the United Nations has stated that global warming must not increase more than 2 degrees Celsius beyond pre-industrial levels, which implies U.S. carbon dioxide emission reductions of 80% from 1990 levels by 2050. (IPCC 2013). At the 2015 United Nations Conference of Parties in Paris, 195 parties agreed on a pathway to achieve a 2 degree limit.
At $108 billion in sales, Kroger is the 6th largest global retailer, and is 20th on Fortune’s 2015 Fortune 500 list (Kroger 10k; Deloitte, 2015; Fortune). Kroger’s globally significant carbon emissions - which exceed 29 nations’ respective carbon emissions from energy - are not being adequately addressed. (Kroger, “Energy/Carbon” website; IEA, Energy Atlas). Kroger lacks climate targets, and where many companies are reducing carbon, Kroger’s 2014 Scope 1 emissions increased from the previous year. Despite its significant carbon footprint, Kroger has installed renewable energy at only 8 of its 3,806 stores, plants, and distribution centers, approximately 0.2% of its locations. (Kroger “Energy/Carbon” website, Factbook).
In contrast, Whole Foods Market offsets its entire power use with renewable energy credits, and Walmart is at 24% renewable power. (Whole Foods, “Green Mission”; Walmart, “Walmart’s Approach to Renewable Energy”). Indeed, Whole Foods Market, Walmart, Whole Foods Market, and other food companies including Coca-Cola Enterprises, Mars, Nestle, and Starbucks have committed to working towards 100% renewable energy. (RE100).
60
Investing in carbon reduction can benefit Kroger’s shareholder value. Carbon reduction activities can be lucrative, yielding returns over 30%. (“Lower emissions, higher ROI”, Carbon Disclosure Project, 2014). Research indicates that corporate management of climate impacts can lead to improved financial performance, including enhanced return on equity, stronger dividends, lower earnings volatility, and minimized regulatory risk. (“S&P 500 Leaders Report”, Carbon Disclosure Project, 2014)
According to Eric Schmidt, Executive Chairman of Google (another RE100 signatory): “Much of corporate America is buying renewable energy [...] not just to be sustainable, because it makes business sense, helping companies diversify their power supply, hedge against fuel risks, and support innovation in an increasingly cost-competitive way.” (“Google’s commitment to sustainability”, Google Green Blog, 2014).
Resolved:
Shareholders request that Kroger produce a report, by year end 2016, assessing the climate benefits and feasibility of adopting enterprise-wide, quantitative, time bound targets for increasing Kroger’s renewable energy sourcing. The report should be produced at reasonable cost and exclude proprietary information.
Supporting:Shareholders request that the report include an analysis of options and scenarios for achieving renewable energy targets, for example by using on-site distributed energy, off-site generation, power purchases, and renewable energy credits, or other opportunities management would like to consider, at its discretion.”
The Board of Directors Recommends a VoteAgainst This Proposal for the Following Reasons:
Kroger shares the proponents’ concerns regarding renewable energy sourcing. We are committed to environmental sustainability and we strive to reduce our impact on the environment by using natural resources responsibly and minimizing waste in all of our operations.
Our aggressive work in energy management resulted in a reduction of overall energy consumption in our stores saving more than 2.5 billion kWh since 2000. This is the carbon equivalent of taking 362,922 cars off the road for one year.
We are actively working to do more in both the short- and long-term. For example, our Turkey Hill Dairy has two wind energy turbines with 3.2 megawatt capacity. Since 2011, these turbines have supplied up to 25% of the dairy’s annual electricity needs, which is enough power to produce six million gallons of ice cream and 15 million gallons of iced tea. In addition, ten Kroger stores have approximately 3,092kW of solar energy capacity that in 2015 produced approximately 3.94 million kWh.
The Kroger Recovery System, located in Compton, CA at the Ralphs/Food 4 Less distribution center has been in operation since late 2012. It utilizes anaerobic digestion, a naturally occurring process, to transform food waste into renewable biogas. This system annually processes approximately 45,000 tons of food waste. This biogas is then turned into power for onsite operations. The system provided approximately 3.5 million kWh of renewable energy for the 650,000 square foot Ralphs/Food 4 Less distribution center. The system reduces area truck trips by more than 500,000 miles each year and reduces waste costs. These efforts are estimated to reduce carbon emissions by 90,000 tons per year.
For each of the past several years, we have published online our annual Sustainability Report that highlights our sustainability initiatives and waste reduction efforts in greater detail. We will continue to support efforts to increase our renewable energy sourcing as we believe these efforts are significant and meaningful. You can view our Sustainability Report atsustainability.kroger.com where we address a number of the requests made by the proponent including quantitative enterprise-wide renewable energy production metrics, and supply-chain management through our logistics initiative.
We remain committed to environmental sustainability and renewable energy sourcing and we will continue to publish reports to our shareholders tracking our initiatives. We urge you to support the furthering of our current programs and vote AGAINST this proposal.
61
Item No. 7 Shareholder Proposal
We have been notified by one shareholder, the name and shareholdings of which will be furnished promptly to any shareholder upon written or oral request to Kroger’s Secretary at Kroger’s executive offices, that it intends to propose the following resolution at the annual meeting:
WHEREAS product packaging is a significant consumer of natural resources and energy, and a major source of waste and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. More than half of U.S. product packaging is discarded in landfills or burned rather than recycled. Only 12% of plastic packaging is recycled.
Paper and packaging comprise 44% of U.S. landfill waste. Nestle Waters North America says plastic bottles are the largest contributor to it carbon footprint; Coca-Cola Co. reports packaging is the largest part of the carbon footprint of several products. A recent analysis of U.S. Environmental Protection Agency data estimates that the energy needed to produce and dispose of products and packaging accounts for 44% of total U.S. GHG emissions. Decaying paper packaging in landfills forms methane, whose greenhouse warming potential is 72 times more potent than CO2. Metal, paper and plastic packaging have large embodied energy and emissions profiles because of the high costs of processing raw materials.
For generations taxpayers have subsidized solid waste disposal and recycling in the U.S. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a corporate and public policy that shifts accountability for collection and recycling from taxpayers and governments to producers. Coca-Cola and Nestle Waters have endorsed such “Make It Take It” policies for financing the recycling of packaging if other producers also pay their fair share. When all producers pay fees based on the amount of packaging used, no company should have to pay disproportionate cost. Unilever has set goals to increase recovery of its used packaging 15% by 2020.
In many other countries, consumer brands that put packaging on the market are already financially responsible for its recycling. More than have of Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development members have some form of producer-financed packaging systems in place. EPR programs in Denmark, Belgium, Netherlands and Germany recover far higher rates of packaging than the U.S.
50
Producers control design and marketing decisions, and are so best positioned to choose the most recyclable packaging materials and reduce overall environmental impact of product packaging. EPR mandates can create new economic markets for used packaging. Increased recycling of packaging can yield strong environmental benefits, lead to more efficient use of materials, reduced extraction of natural resources, fewer GHG and toxic emissions, and less post-consumer packaging flowing into oceans where it imperils marine life.
BE IT RESOLVED THAT Shareowners of The Kroger Co. request that the board of directors issue a report at reasonable cost, omitting confidential information, assessing the feasibility of adopting a policy of Extended Producer Responsibility for house brand post-consumer product packaging as a means of increasing rates of packaging recycling, and reducing carbon emissions and air and water pollution resulting from the company’s business practices.
Supporting Statement: Proponents believe policy options reviewed in the report should include taking responsibility for house brand post-consumer package recycling, endorsing EPR mandates as appropriate and participating in development of producer financed and managed EPR systems.
The Board of Directors Recommends a VoteAgainst This Proposal for the Following Reasons:
Kroger shares the proponent’s concerns regarding waste reduction and recognizes the important role it plays as a good steward of the environment. We have numerous sustainability initiatives in place to preserve our natural resources and to conserve energy. For instance, the company recycled more than 32 million pounds of plastic waste, from bags and plastic film, in 2012. The company also recycles more than a billion pounds of cardboard each year. Most importantly, we’ve pioneered the Perishable Donations Partnership, which enables the donation of more than 48 million pounds of safe, wholesome food to Feeding America food banks to fight hunger in local communities. By implementing innovative methods of donating these food items, Kroger is reducing the amount of waste being sent to landfills. For each of the past several years we have published on-lineThe Kroger Co. Public Responsibilities Report and our annualSustainability Reportthat highlight the company’s sustainability initiatives and waste reduction efforts in greater detail.
This proposal requests that Kroger take additional steps to report on the feasibility of adopting a policy of “Extended Producer Responsibility,” or EPR. The resolution provides no guidance regarding proponent’s view of the requirements of a company-adopted EPR policy.
Kroger supports efforts to reduce waste in the supply chain, as described above and in our various sustainability reports. It would be inappropriate, however, to support a policy that is not clearly defined. We believe our support for waste reduction efforts in our supply chain are significant and meaningful.
Kroger is familiar with various EPR proposals in states and laws in other countries that require retailers and manufacturers to pay substantial taxes and fees related to waste disposal. The proposals vary in detail and implementation, and while we do assess new laws and regulations for their feasibility, cost and requirements, to do so for each individual EPR proposal at the federal, state, and international level would require significant resources that could be allocated more wisely in the best interests of shareholders.
Kroger often is asked to take a position on legislation or regulatory proposals. While occasionally we will communicate to federal, state and local officials our positions on specific policy issues, we believe it is premature to offer an official position statement on EPR legislative and regulatory proposals without first carefully examining the specifics of each individual law or regulation and how it would affect our customers and our business.
This proposal is virtually identical to one submitted to a vote at last year’s annual meeting and was soundly defeated by shareholders.
51
Shareholder Proposal(Item No. 7)
We have been notified by a shareholder, the name and shareholdings of which will be furnished promptly to any shareholder upon written or oral request to Kroger’s Secretary at Kroger’s executive offices, that it intends to propose the following resolution at the annual meeting:
Whereas:Shareholder Proposal
Share Repurchase vs. Dividend The social and environmental impact of palm oil production create important challenges for companies trying to ensure more sustainable and lower risk supply chain practices. Because our Company has not yet committed to procure certified sustainable palm oil for its products, we believe it opens itself to risks to its reputation as well as risks to the long-term security of its palm oil supply.
The largest suppliers of palm oil for the United States are Indonesia, Malaysia and Papua New Guinea.
In the Philippines, it is estimated that almost 25% of palm labor production comes from child labor (http://ctuhr.org/labor-groups-says-24-workers-in-palm-oil-plantations-are-children-calls-on-the-public-to-combat-child labor/). The U.S. Department of Labor reported that child and/or forced labor contributed to palm oil production in Indonesia and Malaysia. (http://www.dol.gov/liab/programs/ocft/PDF/2010TVPRA.pdf). Many of these children are not part of family farms. Such labor practices may violate international codes of human rights.
According to theUnion of Concerned Scientists“Resolved:, palm oil plantations “are a disproportionately large source of global warming emissions because they are often established on land converted from swamp forests. When these wetlands are drained, their carbon-rich peaty soils decay, releasing large amounts of both carbon dioxide and methane. Thus the expansion of plantations onto peat soils is an important source of the emissions that cause global warming.” (Ucsusa.org, June 2011).
Due in part to deforestation, Indonesia has been the 3rd largest emitter of greenhouse gases (GHGs) globally (World Bank). The conversion of peatlands accounts for roughly half of Indonesia’s GHG emissions buy only 1% of its gross domestic product (Mongabay, January 19, 2010).
Palm oil plantations that are not sustainably managed have devastated habitats of endangered species, such as the orangutan. Failure to manage reputational risk connected to palm oil in supply chains has been disruptive for a number of major companies including Nestle, Mattel, and others who made palm oil contracts in Indonesia that resulted in negative publicity (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sinar_Mas_Group).
To address the social and environmental concerns associated with palm oil production and to promote sustainable palm oil products, the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil was formed in 2004. Leading companies have committed to source only certified sustainable palm oil by 2015 or sooner, including: H.J. Heinz, SC Johnson, Wal-Mart, General Mills, McDonalds, Mars, Nestle and Unilever. Our company has not made such a commitment and has not adequately addressed the risks described above.
Resolved: Shareholders requestof The Kroger Co. ask the board of directors to adopt and implementissue a comprehensive sustainable palm oil policy.general payout policy that gives preference to share repurchases (relative to cash dividends) as a method to return capital to shareholders. If a general payout policy currently exists, we ask that it be amended appropriately.
Supporting statement: Supporting Statement:Share repurchases as a method to return capital to shareholders have distinct advantages relative to dividends. Share repurchases should be preferred for the following reasons: We
| 1) | Financial flexibility. Four professors from Duke University and Cornell University studied executives’ decisions to pay dividends or make repurchases by surveying hundreds of executives of public companies. They found that “maintaining the dividend level is on par with investment decisions, while repurchases are made out of the residual cash flow after investment spending.”1Further, in follow up interviews as part of the study, executives “state[d] that they would pass up some positive net present value (NPV) investment projects before cutting dividends.” The creation of long-term value is of paramount importance; I believe that repurchases have the distinct advantage that they do not create an incentive to forgo long-term value enhancing projects in order to preserve a historic dividend level. | ||
| 2) | Tax efficiency. Share repurchases have been described in the Wall Street Journal2as “akin to dividends, but without the tax bite for shareholders.” The distribution of a dividend may automatically trigger a tax liability for some shareholders. The repurchase of shares does not necessarily trigger that automatic tax liability and therefore gives a shareholder the flexibility to choose when the tax liability is incurred. Shareholders who desire cash flow can choose to sell shares and pay taxes as appropriate. (This proposal does not constitute tax advice.) | ||
| 3) | Market acceptance: Some may believe that slowing the growth rate or reducing the level of dividends would result in a negative stock market reaction. However, a study published in the Journal of Finance finds that the market response to cutting dividends by companies that were also share repurchasers was not statistically distinguishable from zero.3I believe this study provides evidence that there is market acceptance that repurchases are valid substitutes for dividends. | ||
Some may worry that share repurchases could be used to prop up metrics that factor into the compensation of executives. I believe that any such a policyconcern should include: 1) a target date for sourcing 100% Certified Sustainable Palm Oil or for purchasing GreenPalm certificates covering 100% of sourced palm oil; 2) plans for independent verification of suppliers’ compliancenot interfere with the policy; 3) supportchoice of optimal payout mechanism because compensation packages can be designed such that metrics are adjusted to account for share repurchases.
| 1 | http://www. sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304405XO5000528 | ||
| 2 | http://www.wsj.com/articles/companies-stock-buybacks-help-buoy-the-market-1410823441 | ||
| 3 | http://www.afajof.org/details/journalArticle/2893861/Dividends-Share-Repurchases-and-the- Substitution-Hypothesis.html | ||
5262
The Board of Directors Recommends a VoteAgainst This Proposal for the Following Reasons:
Kroger shares many ofbelieves that the proponent’s concerns regardingpolicy advocated by the social and environmental impacts of palm oil production. Thisshareholder proposal is a developing issue for manynot in the best interests of our suppliers,shareholders as it reduces long-term flexibility in the allocation of capital. In a rapidly evolving capital market, this flexibility is an essential element in the careful management of shareholder capital, which the Board thoughtfully oversees and reviews on a regular basis.
Our long-term financial strategy continues to be to use cash flow from operations, in a balanced manner, to repurchase shares, fund dividends, and increase capital investments, all while maintaining our current investment grade debt rating. Our balanced approach gives us the flexibility to pursue long-term growth strategies while returning capital to our shareholders.
Kroger is proud of our strong history of capital return to shareholders. We have made significant commitments over time to return capital to shareholders both through repurchases of our common shares and payment of cash dividends. We repurchased $703 million of Kroger common shares in 2015, as well as $1.1 billion in 2014, $338 million in 2013 and $1.2 billion in 2012. Additionally, we paid dividends totaling $385 million in 2015, $338 million in 2014, $319 million in 2013 and $267 million in 2012. We are also committed to working with themgrowing long-term shareholder value through significant capital investments. Excluding acquisitions, we invested $3.38 billion, $2.89 billion, $2.46 billion and $2.06 billion in capital projects in 2015, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Many of our shareholders view both dividends and share repurchases as an important component of Kroger’s investment profile, especially in light of our balanced capital return strategy that contributes to explore optionsa healthy TSR (total shareholder return), which outperforms both our peers and the S&P 500 over time.
When contemplating capital returns, the Board engages in a thorough analysis and oversight process. Before the Board approves any share repurchase program or declares a cash dividend, it takes into account a wide range of factors, including Kroger’s short and long-term growth strategies, liquidity needs and capital requirements, cash flows, net earnings, debt obligations, and leverage ratios. The Board also considers how the then-current capital market conditions affect Kroger’s policies and strategies. There is no one-size-fits-all policy or strategy in returning capital to improve sustainability inshareholders that would satisfy each market condition over the palm oil production supply chain.course of time. Balanced capital allocation decisions, overseen by an effective Board, remain the most effective and flexible strategy to continuously deliver healthy value to shareholders over the long-term.
This proposal requests that Kroger has recently announcedadopt a Palm Oil Policy via our corporate website and news release. Thegeneral policy includes an endorsement of the Roundtable for Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO). In accordance with Kroger’s policy, we will purchase only 100% Certified Sustainable Palm Oil by the end of 2015 through active RSPO members. The company will also disclose progress in our annual sustainability report at www.sustainability.kroger.com.
Kroger believes the resolution as written would require significantly more resources and is redundant given our recently announced Palm Oil Policy.
For these reasons, we recommend that gives preference to share repurchases relative to cash dividends. We urge you to voteAGAINST this proposal.
5363
——————Shareholder Proposals and Director Nominations – 2017 Annual Meeting
SHAREHOLDER PROPOSALS – 2014 ANNUAL MEETING. Shareholder proposals intended for inclusion in ourthe proxy material relating to Kroger’s annual meeting of shareholders in June 20142017 should be addressed to theKroger’s Secretary of Kroger and must be received at our executive offices not later than January 14, 2014.12, 2017. These proposals must comply with Rule 14a-8 and the SEC’s proxy rules established by the SEC. rules.
In addition, Kroger’s Regulations contain an advance notice of shareholder business and director nominations requirement, which generally prescribes the procedures that a shareholder of Kroger must follow if the shareholder intends, at an annual meeting, to nominate a person for election to Kroger’s Board of Directors or to propose other business to be considered by shareholders. These procedures include, among other things, that the shareholder give timely notice to Kroger’s Secretary of the nomination or other proposed business, that the notice contain specified information, and that the shareholder comply with certain other requirements. In order to be timely, this notice must be delivered in writing to Kroger’s Secretary, at our principal executive offices, not later 45 calendar days prior to the date on which our proxy solicited bystatement for the prior year’s annual meeting of shareholders was mailed to shareholders. If a shareholder’s nomination or proposal is not in compliance with the procedures set forth in the Regulations, we may disregard such nomination or proposal. Accordingly, if a shareholder intends, at the 2017 annual meeting, to nominate a person for election to the Board of Directors or to propose other business, the shareholder must deliver a notice of such nomination or proposal to Kroger’s Secretary not later March 28, 2017, and comply with the requirements of the Regulations. If a shareholder submits a proposal outside of Rule 14a-8 for the 20142017 annual meeting of shareholders willand such proposal is not delivered within the time frame specified in the Regulations, Kroger’s proxy may confer discretionary authority on persons being appointed as proxies on behalf of Kroger to vote on any shareholder proposal presented at the meeting unless we are provided with notice of the proposal on or before March 28, 2014. Please note, however, that Kroger’s Regulations require a minimum of 45 days’such proposal. Shareholder proposals, director nominations and advance notice tonotices should be addressed in writing to: Secretary, The Kroger in order for a matter to be brought before shareholders at the annual meeting. As a result, any attempt to present a proposal without notifying Kroger on or before March 28, 2014, will be ruled out of order and will not be permitted.Co., 1014 Vine Street, Cincinnati, Ohio 45202-1100.
——————2015 Annual Report
Attached to this Proxy Statement is Kroger’s 2012our 2015 Annual Report which includes a brief description of Kroger’sour business, including the general scope and nature thereof during 2012,fiscal year 2015, together with the audited financial information contained in our 2012 report to the SEC2015 Annual Report on Form 10-K.10-K filed with the SEC.A copy of that report is available to shareholders on request without charge by writing to: Scott M. Henderson,Todd A. Foley, Treasurer, The Kroger Co., 1014 Vine Street, Cincinnati, Ohio 45202-1100 or by calling 1-513-762-1220513-762-1220. Our SEC filings are available to the public fromon the SEC’s web sitewebsite at www.sec.gov.
Householding of Proxy Materials
We have adopted a procedure approved by the SEC called “householding.” Under this procedure, shareholders of record who have the same address and last name will receive only one copy of the Notice of Availability of Proxy Materials (or proxy materials in the case of shareholders who receive paper copies of such materials) unless one or more of these shareholders notifies us that they wish to continue receiving individual copies. This procedure will reduce our printing costs and postage fees. Householding will not in any way affect dividend check mailings.
If you are eligible for householding, but you and other shareholders of record with whom you share an address currently receive multiple copies of our Notice of Availability of Proxy Materials (or proxy materials in the case of shareholders who receive paper copies of such materials), or if you hold in more than one account, and in either case you wish to receive only a single copy for your household or if you prefer to receive separate copies of our documents in the future, please contact your bank or broker, or contact Kroger’s Secretary at 1014 Vine Street, Cincinnati, Ohio 45202-1100 or via telephone at 513-762-4000.
The management knows of no other matters that are to be presented at the meeting, but, if any should be presented, the Proxy Committee expects to vote thereon according to its best judgment.
By order of the Board of Directors, | |
|
5464
——————_____________
2015 ANNUAL REPORT
_____________
2012 Annual Report
——————
Financial Report 2012FINANCIAL REPORT 2015
Management’s Responsibility for Financial ReportingMANAGEMENT’S RESPONSIBILITY FOR FINANCIAL REPORTING
The management of The Kroger Co. has the responsibility for preparing the accompanying financial statements and for their integrity and objectivity. The statements were prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles applied on a consistent basis and are not misstated due to material error or fraud. The financial statements include amounts that are based on management’s best estimates and judgments. Management also prepared the other information in the report and is responsible for its accuracy and consistency with the financial statements.
The Company’sKroger’s financial statements have been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, whose selection has been approvedratified by the shareholders. Management has made available to PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP all of the Company’sKroger’s financial records and related data, as well as the minutes of the shareholders’ and directors’ meetings. Furthermore, management believes that all representations made to PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP during its audit were valid and appropriate.
Management also recognizes its responsibility for fostering a strong ethical climate so that the Company’sKroger’s affairs are conducted according to the highest standards of personal and corporate conduct. This responsibility is characterized and reflected inThe Kroger Co. Policy on Business Ethics, which is publicized throughout the CompanyKroger and available on the Company’sKroger’s website at ir.kroger.com.The Kroger Co. Policy on Business Ethics addresses, among other things, the necessity of ensuring open communication within the Company;Kroger; potential conflicts of interests; compliance with all domestic and foreign laws, including those related to financial disclosure; and the confidentiality of proprietary information. The CompanyKroger maintains a systematic program to assess compliance with these policies.
Management’ s Report on Internal Control Over Financial ReportingMANAGEMENT’S REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
The management of the CompanyManagement is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting for the Company. With the participation of the Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer, our management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework and criteria established inInternal Control – Integrated Framework (2013), issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Our management excluded Roundy’s, Inc. from its assessment of internal control over financial reporting because it was acquired in a purchase business combination on December 18, 2015. Roundy’s, Inc. is a wholly-owned subsidiary whose total assets and total revenues represent 2% and less than 1%, respectively, of the related consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the year ended January 30, 2016. Based on this evaluation, our management has concluded that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of February 2, 2013.January 30, 2016.
| J. Michael Schlotman |
Chairman of the Board and |
|
Chief Executive Officer | Chief Financial Officer |
A-1
Selected Financial DataSELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
| Fiscal Years Ended | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| February 2, | January 28, | January 29, | January 30, | January 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | January 30, | January 31, | February 1, 2014 (52 weeks)(1) | February 2, 2013 (53 weeks) | January 28, 2012 (52 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions, except per share amounts) | (In millions, except per share amounts) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales | $ 96,751 | $ 90,374 | $ 82,049 | $ 76,609 | $ 76,063 | $ | 109,830 | $ | 108,465 | $ | 98,375 | $ | 96,619 | $ | 90,269 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings including noncontrolling | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| interests | 1,508 | 596 | 1,133 | 57 | 1,250 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings including | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| noncontrolling interests | 2,049 | 1,747 | 1,531 | 1,508 | 596 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The Kroger Co. | 1,497 | 602 | 1,116 | 70 | 1,249 | 2,039 | 1,728 | 1,519 | 1,497 | 602 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The Kroger Co. per diluted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| common share | 2.77 | 1.01 | 1.74 | 0.11 | 1.89 | 2.06 | 1.72 | 1.45 | 1.39 | 0.51 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total assets | 24,652 | 23,476 | 23,505 | 23,126 | 23,290 | 33,897 | 30,497 | 29,281 | 24,634 | 23,454 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term liabilities, including obligations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| under capital leases and financing | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| obligations | 9,381 | 10,405 | 10,137 | 10,473 | 10,311 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total shareowners’ equity – | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term liabilities, including | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| obligations under capital leases | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| and financing obligations | 14,123 | 13,663 | 13,181 | 9,359 | 10,405 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total shareholders’ equity – | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The Kroger Co. | 4,207 | 3,981 | 5,296 | 4,852 | 5,225 | 6,811 | 5,412 | 5,384 | 4,207 | 3,981 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends per common share | 0.495 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.365 | 0.345 | 0.395 | 0.340 | 0.308 | 0.248 | 0.215 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Harris Teeter Supermarkets, Inc. (“Harris Teeter”) is included in our ending Consolidated Balance Sheets for 2015, 2014 and 2013 and in our Consolidated Statements of Operations for 2015 and 2014. Due to the timing of the merger closing late in fiscal year 2013, its results of operations were not material to our consolidated results of operations for 2013. |
Common Share Price RangeCOMMON SHARE PRICE RANGE
| 2012 | 2011 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Quarter | High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | |||||||||||||
| 1st | $24.78 | $21.76 | $25.48 | $21.29 | $ | 38.87 | $ | 34.05 | $ | 23.95 | $ | 17.57 | |||||||||
| 2nd | $23.22 | $20.98 | $25.85 | $21.52 | $ | 38.65 | $ | 37.09 | $ | 25.75 | $ | 23.25 | |||||||||
| 3rd | $25.44 | $21.57 | $23.78 | $21.14 | $ | 38.73 | $ | 27.32 | $ | 29.08 | $ | 24.99 | |||||||||
| 4th | $28.00 | $24.19 | $24.83 | $21.68 | $ | 42.75 | $ | 36.00 | $ | 35.03 | $ | 28.64 | |||||||||
Main trading market: New York Stock Exchange (Symbol KR) Number of shareholders of record at year-end 2012: 34,157 Number of shareholders of record at March 29, 2013: 33,996 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Main trading market: New York Stock Exchange (Symbol KR) Number of shareholders of record at fiscal year-end 2015: 29,102 Number of shareholders of record at March 23, 2016: 28,959 | Main trading market: New York Stock Exchange (Symbol KR) Number of shareholders of record at fiscal year-end 2015: 29,102 Number of shareholders of record at March 23, 2016: 28,959 | ||||||||||||||||||||
During 2011, the Company2015, we paid two quarterly cash dividends of $0.0925 per share and two quarterly cash dividends of $0.105 per share. During 2014, we paid three quarterly cash dividends of $0.105$0.0825 per share and one quarterly cash dividend of $0.115. During 2012, the Company paid three quarterly dividends of $0.115 and one quarterly dividend of $0.15. On March 1, 2013, the Company paid a quarterly dividend of $0.15$0.0925 per share. On March 14, 2013, the Company1, 2016, we paid a quarterly cash dividend of $0.105 per share. On March 10, 2016, we announced that itsour Board of Directors hashave declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.15$0.105 per share, payable on June 1, 2013,2016, to shareholders of record at the close of business on May 15, 2013.13, 2016. We currently expect to continue to pay comparable cash dividends on a quarterly basis depending on our earnings and other factors.
A-2
Performance GraphPERFORMANCE GRAPH
Set forth below is a line graph comparing the five-year cumulative total shareholder return on Kroger’sour common shares, based on the market price of the common shares and assuming reinvestment of dividends, with the cumulative total return of companies in the Standard & Poor’s 500 Stock Index and a peer group composed of food and drug companies.
COMPARISON OF CUMULATIVE FIVE-YEAR TOTAL RETURN*
Among The Kroger Co., the S&P 500, and Peer Group**
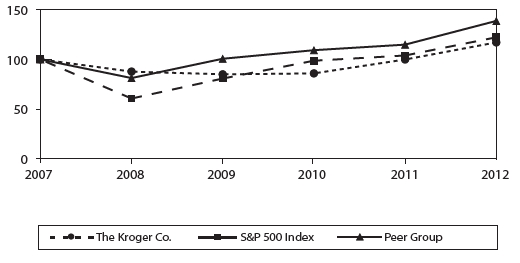
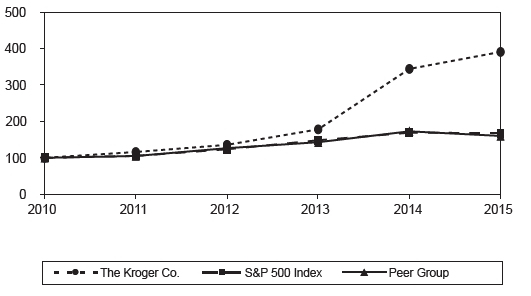
| Base | INDEXED RETURNS | Base | INDEXED RETURNS | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | Years Ending | Period | Years Ending | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Company Name/Index | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||
| The Kroger Co. | 100 | 87.70 | 84.94 | 85.89 | 99.86 | 117.04 | 100 | 116.26 | 136.28 | 179.49 | 348.32 | 395.78 | ||||||||||||
| S&P 500 Index | 100 | 60.63 | 80.72 | 98.63 | 103.89 | 122.17 | 100 | 105.33 | 123.87 | 149.02 | 170.22 | 169.08 | ||||||||||||
| Peer Group | 100 | 81.21 | 100.61 | 109.22 | 114.80 | 138.65 | 100 | 105.11 | 126.94 | 143.63 | 173.96 | 161.13 | ||||||||||||
* Total assumes $100 invested on February 2, 2008,January 30, 2011, in The Kroger Co., S&P 500 Index, and the Peer Group, with reinvestment of dividends. ** The Peer Group consists of Costco Wholesale Corp., CVS Caremark Corp, EtablissmentsEtablissements Delhaize Freres Et Cie Le Lion (Groupe Delhaize), Great Atlantic & Pacific Tea Company, Inc. (included through March 13, 2012 when it became private after emerging from bankruptcy), Koninklijke Ahold NV, Safeway, Inc. (included through January 29, 2015 when it was acquired by AB Acquisition LLC), Supervalu Inc., Target Corp., Tesco plc, Wal-Mart Stores Inc., Walgreens Boots Alliance Inc. (formerly, Walgreen Co.), Whole Foods Market Inc. and Winn-Dixie Stores, Inc. (included through March 9, 2012 when it became a wholly- ownedwholly-owned subsidiary of Bi-Lo Holding)Holdings). Data supplied by Standard & Poor’s.
The foregoing Performance Graph will not be deemed incorporated by reference into any other filing, absent an express reference thereto.
A-3
Issuer Purchases of Equity SecuritiesISSUER PURCHASESOF EQUITY SECURITIES
| Total Number of | Maximum Dollar | |||||||||||
| Shares | Value of Shares | |||||||||||
| Purchased as | that May Yet Be | |||||||||||
| Part of Publicly | Purchased Under | |||||||||||
| Total Number | Average | Announced | the Plans or | |||||||||
| of Shares | Price Paid | Plans or | Programs (3) | |||||||||
| Period (1) | Purchased | Per Share | Programs (2) | (in millions) | ||||||||
| First period - four weeks | ||||||||||||
| November 4, 2012 to December 1, 2012 | 950,000 | $24.80 | 950,000 | $483 | ||||||||
| Second period - four weeks | ||||||||||||
| December 2, 2012 to December 29, 2012 | 608,832 | $26.43 | 608,832 | $475 | ||||||||
| Third period – five weeks | ||||||||||||
| December 30, 2012 to February 2, 2013 | 690,343 | $25.95 | 690,343 | $466 | ||||||||
| Total | 2,249,175 | $25.59 | 2,249,175 | $466 | ||||||||
| Period(1) | Total Number of Shares Purchased(2) | Average Price Paid Per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs(3) | Maximum Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs(4) (in millions) | |||||||||||
| First period - four weeks | |||||||||||||||
| November 8, 2015 to December 5, 2015 | 94,717 | $ | 37.89 | 74,819 | $500 | ||||||||||
| Second period - four weeks | |||||||||||||||
| December 6, 2015 to January 2, 2016 | 906,648 | $ | 41.47 | 831,783 | $500 | ||||||||||
| Third period – four weeks | |||||||||||||||
| January 3, 2016 to January 30, 2016 | 213,721 | $ | 39.73 | 169,598 | $500 | ||||||||||
| Total | 1,215,086 | $ | 40.88 | 1,076,200 | $500 | ||||||||||
| (1) | The reported periods conform to our fiscal calendar composed of thirteen 28-day periods. The fourth quarter of | |
| (2) | ||
| (3) | Represents shares repurchased under the 1999 Repurchase Program. | |
| (4) | The amounts shown in this column reflect | |
BusinessBUSINESS
The Kroger Co. (the “Company” or “Kroger”) was founded in 1883 and incorporated in 1902. As of February 2, 2013, the Company wasJanuary 30, 2016, we are one of the largest retailers in the world based on annual sales. The CompanyWe also manufacturesmanufacture and processesprocess some of the food for sale in itsour supermarkets. The Company’sOur principal executive offices are located at 1014 Vine Street, Cincinnati, Ohio 45202, and itsour telephone number is (513) 762-4000. The Company maintainsWe maintain a web site (www.thekrogerco.com) that includes additional information about the Company. The Company makesWe make available through itsour web site, free of charge, itsour annual reports on Form 10-K, itsour quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, itsour current reports on Form 8-K and itsour interactive data files, including amendments. These forms are available as soon as reasonably practicable after the Company haswe have filed them with, or furnished them electronically to, the SEC.
The Company’sA-4
Our revenues are predominately earned and cash is generated as consumer products are sold to customers in its stores. The Company earnsour stores and fuel centers. We earn income predominantly by selling products at price levels that produce revenues in excess of itsthe costs to make these products available to itsour customers. Such costs include procurement and distribution costs, facility occupancy and operational costs, and overhead expenses. The Company’sOur fiscal year ends on the Saturday closest to January 31. All references to 2015, 2014 and 2013 are to the fiscal years ended January 30, 2016, January 31, 2015 and February 1, 2014, respectively, unless specifically indicated otherwise.
EmployeesEMPLOYEES
As of February 2, 2013, the CompanyJanuary 30, 2016, Kroger employed approximately 343,000431,000 full- and part-time employees. A majority of the Company’sour employees are covered by collective bargaining agreements negotiated with local unions affiliated with one of several different international unions. There are approximately 300350 such agreements, usually with terms of three to five years.
A-4STORES
During 2013, the Company will negotiate major labor contracts covering store employees in Indianapolis, Houston, Dallas, Cincinnati and Seattle, among others. These negotiations will be challenging, as the Company seeks competitive cost structures in each market while meeting our associates’ needs for good wages and affordable health care. In these negotiations, we will also need to address the underfunding of our multi-employer pension plans.
Stores
As of February 2, 2013, the CompanyJanuary 30, 2016, Kroger operated, either directly or through its subsidiaries, 2,424 supermarkets and multi-department2,778 retail food stores 1,169under a variety of local banner names, 1,387 of which had fuel centers. Approximately 45%42% of these supermarkets were operated in Company-owned facilities, including some Company-owned buildings on leased land. The Company’sOur current strategy emphasizes self-development and ownership of store real estate. The Company’sOur stores operate under severala variety of banners that have strong local ties and brand recognition. Supermarkets are generally operated under one of the following formats: combination food and drug stores (“combo stores”); multi-department stores; marketplace stores; or price impact warehouses.
The combo stores arestore is the primary food store format. They typically draw customers from a 2 – 2½ mile radius. The Company believesWe believe this format is successful because the stores are large enough to offer the specialty departments that customerscustomers’ desire for one-stop shopping, including natural food and organic sections, pharmacies, general merchandise, pet centers and high-quality perishables such as fresh seafood and organic produce.
Multi-department stores are significantly larger in size than combo stores. In addition to the departments offered at a typical combo store, multi-department stores sell a wide selection of general merchandise items such as apparel, home fashion and furnishings, outdoor living, electronics, automotive products, toys and fine jewelry.
Marketplace stores are smaller in size than multi-department stores. They offer full-service grocery, pharmacy and pharmacyhealth and beauty care departments as well as an expanded perishable offering and general merchandise area that includes outdoor living products, electronics,apparel, home goods and toys.
Price impact warehouse stores offer a “no-frills, low cost” warehouse format and feature everyday low prices plus promotions for a wide selection of grocery and health and beauty care items. Quality meat, dairy, baked goods and fresh produce items provide a competitive advantage. The average size of a price impact warehouse store is similar to that of a combo store.
In addition to the supermarkets, as of February 2, 2013, the CompanyJanuary 30, 2016, we operated, through subsidiaries, 786784 convenience stores, and 328323 fine jewelry stores.stores and an online retailer. All 121 of our fine jewelry stores located in malls are operated in leased locations. In addition, 8178 convenience stores were operated by franchisees through franchise agreements. Approximately 53%54% of the convenience stores operated by subsidiaries were operated in Company-owned facilities. The convenience stores offer a limited assortment of staple food items and general merchandise and, in most cases, sell gasoline.
SegmentsSEGMENTS
The Company operatesWe operate retail food and drug stores, multi-department stores, jewelry stores, and convenience stores throughout the United States. The Company’sOur retail operations, which represent over 99% of the Company’sour consolidated sales and EBITDA, are itsearnings before interest, taxes and depreciation and amortization (“EBITDA”), is our only reportable segment. The Company’sOur retail operating divisions have been aggregated into one reportable segment due to the operating divisions having similar economic characteristics with similar long-term financial performance. In addition, the Company’sour operating divisions offer to its customers similar products, have
A-5
similar distribution methods, operate in similar regulatory environments, purchase the majority of the Company’s merchandise for retail sale from similar (and in many cases identical) vendors on a coordinated basis from a centralized location, serve similar types of customers, and are allocated capital from a centralized location. The Company’sOur operating divisions reflect the manner in which the business is managed and how the Company’sour Chief Executive Officer, and Chief Operating Officer, who actacts as the Company’sour chief operating decision makers, assessmaker, assesses performance internally. All of the Company’sour operations are domestic. Revenues, profitprofits and losses and total assets are shown in the Company’sour Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in Item 8beginning on page A-29 below.
A-5MERCHANDISING AND MANUFACTURING
Merchandising and Manufacturing
Corporate brand products play an important role in the Company’sour merchandising strategy. Our supermarkets, on average, stock approximately 12,000over 14,000 private label items. The Company’sOur corporate brand products are primarily produced and sold in three “tiers.” Private SelectionSelection® is the premium quality brand designed to be a unique item in a category or to meet or beat the “gourmet” or “upscale” brands. The “banner brand” (Kroger, Ralphs,(Kroger®, Ralphs®, Fred Meyer®, King Soopers,Soopers®, etc.), which represents the majority of the Company’sour private label items, is designed to satisfy customers with quality products. Before Krogerwe will carry a banner brand“banner brand” product we must be satisfied that the product quality meets our customers’ expectations in taste and efficacy, and we guarantee it. Kroger Value isP$$T…®, Check This Out… and Heritage Farm™ are the three value brand,brands, designed to deliver good quality at a very affordable price. In addition, the Company recently introduced two corporate brand lines,we continue to grow our other brands, including Simple Truth® and Simple Truth Organic®. Both Simple Truth and Simple Truth Organic. Both brandsOrganic are free fromFree From 101 artificial preservatives and ingredients that customers have told us they do not want in their food, and the Simple Truth Organic products are USDA certified organic.
Approximately 40% of the corporate brand units sold in our supermarkets are produced in the Company’s manufacturingour food production plants; the remaining corporate brand items are produced to the Company’sour strict specifications by outside manufacturers. The Company performsWe perform a “make or buy” analysis on corporate brand products and decisions are based upon a comparison of market-based transfer prices versus open market purchases. As of February 2, 2013, the CompanyJanuary 30, 2016, we operated 37 manufacturing38 food production plants. These plants consisted of 17 dairies, nineten deli or bakery plants, five grocery product plants, two beverage plants, two meat plants and two cheese plants.
SEASONALITY
The majority of our revenues are generally not seasonal in nature. However, revenues tend to be higher during the major holidays throughout the year.
EXECUTIVE OFFICERS OF THE REGISTRANT
The disclosure regarding executive officers is set forth in Item 10 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for fiscal year 2015 under the heading “Executive Officers of the Company,” and is incorporated herein by reference.
COMPETITIVE ENVIRONMENT
For the disclosure related to our competitive environment, see Item 1A of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for fiscal year 2015 under the heading “Competitive Environment.”
A-6
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Our BusinessOUR BUSINESS
The KrogerCo. was founded in 1883 and incorporated in 1902. ItKroger is one of the nation’s largest retailers, as measured by revenue, operating 2,4242,778 supermarket and multi-department stores under two dozen banners including Kroger, City Market, Dillons, Jay C, Food 4 Less, Fred Meyer, Fry’s, King Soopers, QFC, Ralphsa variety of local banner names in 35 states and Smith’s.the District of Columbia. Of these stores, 1,1691,387 have fuel centers. We also operate 786784 convenience stores, either directly or through franchisees, and 328323 fine jewelry stores.stores and an online retailer.
Kroger operates 37 manufacturingWe operate 38 food production plants, primarily bakeries and dairies, which supply approximately 40% of the corporate brand units sold in our retail outlets.supermarkets.
Our revenues are earned and cash is generated as consumer products are sold to customers in our stores. We earn income predominately by selling products at price levels that produce revenues in excess of the costs we incur to make these products available to our customers. Such costs include procurement and distribution costs, facility occupancy and operational costs, and overhead expenses. Our retail operations, which represent over 99% of Kroger’sour consolidated sales and EBITDA, areis our only reportable segment.
Our 2012 PerformanceOn December 18, 2015, we closed our merger with Roundy’s by purchasing 100% of the Roundy’s outstanding common stock for $3.60 per share and assuming Roundy’s outstanding debt, for a purchase price of $866 million. Roundy’s is included in our ending Consolidated Balance Sheets for 2015 and in our Consolidated Statements of Operations for the last six weeks of 2015. Certain year-over-year comparisons will be affected as a result. See Note 2 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information related to our merger with Roundy’s.
On August 18, 2014, we closed our merger with Vitacost.com by purchasing 100% of the Vitacost. com outstanding common stock for $8.00 per share or $287 million. Vitacost.com is included in our ending Consolidated Balance Sheets and Consolidated Statements of Operations for 2014 and 2015. See Note 2 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information related to our merger with Vitacost.com.
On January 28, 2014, we closed our merger with Harris Teeter by purchasing 100% of the Harris Teeter outstanding common stock for approximately $2.4 billion. Harris Teeter is included in our ending Consolidated Balance Sheets for 2014 and 2015 and in our Consolidated Statements of Operations for 2014 and 2015. Due to the timing of the merger closing late in fiscal year 2013, its results of operations were not material to our consolidated results of operations for 2013. Certain year-over-year comparisons will be affected as a result. See Note 2 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information related to our merger with Harris Teeter.
OUR 2015 PERFORMANCE
We achieved outstanding results in 2012.2015. Our business strategy continues to resonate with a full range of customers and our results reflect the balance we seek to achieve across our business including positive identical supermarket sales growth, increases in loyal household count, and good cost control, as well as growth in net earnings and net earnings per diluted share. Our 20122015 net earnings were $1.5$2.0 billion or $2.77$2.06 per diluted share, compared to $602 million,$1.7 billion, or $1.01$1.72 per diluted share for 2014. All share and per share amounts presented are reflective of the same period of 2011. For 2012, this includes estimatedtwo-for-one stock split that began trading at the split adjusted price on July 14, 2015.
Our net earnings of $91for 2015 include a $110 million pre-tax ($58 million after-tax) or $0.11 per diluted share dueexpense to a 53rd week in fiscal year 2012 (the “extra week”). In addition, net earnings benefited by $115 million pre-tax ($74 million after-tax) or $0.14 per diluted share from a settlement with Visaoperating, general, and MasterCard and from a reduction in our obligationadministrative (“OG&A”) for certain contributions to fund the United Food and Commercial Workers International Union (“UFCW”) consolidatedConsolidated Pension Plan (“2015 UFCW Contributions”) made during the third and fourth quarters of 2015. In addition, our net earnings for 2015 include a lower last-in, first-out (“LIFO”) charge compared to 2014. Net earnings for 2014 include a net $39 million after-tax charge for an $87 million ($56 million after-tax) charge to OG&A due to the commitments and withdrawal liabilities arising from restructuring of certain multi-employer obligations (“2014 Multi-Employer Pension Plan Obligation”) to help stabilize associates’ future pension fund createdbenefits, offset partially by the benefits from certain tax items of $17 million (“2014 Adjusted
A-7
Items”). In addition, our net earnings for 2014 include unusually high fuel margins, partially offset by a LIFO charge that was significantly higher than 2013 and $140 million in January 2012. Excluding the Visa and MasterCard settlement,contributions charged to OG&A expenses for the UFCW consolidated pensionConsolidated Pension Plan ($55 million) and The Kroger Co. Foundation ($85 million) (“2014 Contributions”). The 2015 and 2014 contributions to the UFCW Consolidated Pension Plan was to further fund adjustmentthe plan. The $85 million contribution, in 2014, to The Kroger Co. Foundation will enable it to continue to support causes such as hunger relief, breast cancer awareness, the military and their families and local community organizations. Fuel margin per gallon was $0.19 in 2014, compared to $0.14 in 2013. Our net earnings for 2013 include a net benefit of $23 million, which includes benefits from certain tax items of $40 million, offset partially by costs of $11 million in interest and $16 million in OG&A expenses ($17 million after-tax) related to our merger with Harris Teeter (“2013 Adjusted Items”).
Our 2015 net earnings were $2.0 billion or $2.06 per diluted share, compared to $1.7 billion, or $1.72 per diluted share for 2014. Net earnings for 2015 totaled $2.0 billion, or $2.06 per diluted share, compared to net earnings in 2014 of $1.8 billion, or $1.76 per diluted share, excluding the extra week in 2012, our2014 Adjusted Items. We believe adjusted net earnings were $1.4 billion or $2.52 per diluted share. Our 2011 results included a charge related to the consolidation of four multi-employer pension plans to the UFCW consolidated pension plan totaling $953 million, pre-tax ($591 million after-tax). Excluding the 2011 adjusted item, our 2011 adjusted net earnings were $1.2 billion or $2.00 per diluted share. After accounting for these adjusted items, our 2012and adjusted net earnings per diluted share present a more accurate year-over-year comparison of our financial results because the 2014 Adjusted Items were not the result of our normal operations. Our net earnings per diluted share for 2015 represent a 26%17% increase, incompared to 2014 adjusted net earnings per diluted share. Please refer to the “Net Earnings” section of MD&A for more information related to the increase in net earnings for 2012, compared to 2011.information.
Our identical supermarket sales increased by 3.5%5.0%, excluding fuel, in 2012.2015, compared to 2014. We have achieved 3749 consecutive quarters of positive identical supermarket sales growth, excluding fuel. As we continue to outpace many of our competitors on identical supermarket sales growth, we continue to gain market share. We focus on identical supermarket sales growth, excluding fuel, becauseas it is a key performance target for our business model emphasizes this primary component.long-term growth strategy.
Increasing market share is an important part of our long-term strategy as it best reflects how our products and services resonate with customers. Market share growth allows us to spread the fixed costs in our business over a wider revenue base. Our fundamental operating philosophy is to maintain and increase market share by offering customers good prices and superior products and service. Based on Nielsen Homescan Data,POS+ data, our estimatedoverall market share increasedof the products we sell in totalmarkets in which we operate increased by approximately 2040 basis points in 2012 across our 19 marketing areas outlined by the Nielsen report.2015. This informationdata also indicates that our market share increased in 10 of the marketing areas17 markets and declined in nine. Wal-Mart supercenters are a primary competitor in 17 of these 19 marketing areas. In these 17 marketing areas, our market share increased in nine and declined in eight. Nielsen Homescan Data is generated by customers who self-report their grocery purchases to Nielsen, regardless of retail channel or grocery outlet.one. These market share results reflect our long-term strategy of market share growth.
A-7RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Results of Operations
The following discussion summarizes our operating results for 20122015 compared to 20112014 and for 20112014 compared to 2010.2013. Comparability is affected by income and expense items that fluctuated significantly between and among the periods, our merger with Roundy’s in late 2015 and an extra weekour merger with Harris Teeter in 2012.
Net Earnings
Net earnings totaled $1.5 billion in 2012, $602 million in 2011late 2013. All share and $1.1 billion in 2010. The net earnings for 2012 include benefits from net earnings of approximately $58 million, after-tax, for the extra week, a $74 million, after-tax, settlement with Visa and MasterCard and a reduction in our obligation to fund the UFCW consolidated pension fund created in January 2012 (“2012 adjusted items”). The net earnings for 2011 include a UFCW consolidated pension plan charge totaling $591 million, after-tax (“2011 adjusted item”). The net earnings for 2010 include a non-cash goodwill impairment charge totaling $12 million, after-tax, related to a small number of stores (“2010 adjusted item”). Excluding these benefits and charges for adjusted items in 2012, 2011 and 2010, adjusted net earnings were $1.4 billion in 2012, $1.2 billion in 2011 and $1.1 billion in 2010. 2012 adjusted net earnings improved, compared to 2011, due to an increase in first-in, first-out (“FIFO”) non-fuel operating profit, increased net earnings from our fuel operations and a last-in, first-out (“LIFO”) charge of $55 million (pre-tax), compared to a LIFO charge of $216 million (pre-tax) in 2011, partially offset by increased interest expense and income tax expense. 2011 adjusted net earnings improved, compared to 2010, due to an increase in FIFO non-fuel operating profit, lower interest expense, favorable resolutions for certain tax issues and higher retail fuel margins, partially offset by a LIFO charge of $216 million (pre-tax), compared to a LIFO charge of $57 million (pre-tax) in 2010.
2012 net earnings per diluted share totaled $2.77, and adjusted net earnings per diluted share in 2012 totaled $2.52, which excludes the 2012 adjusted items. 2011 net earnings per diluted share totaled $1.01, and adjusted net earnings per diluted share in 2011 totaled $2.00, which excludes the 2011 adjusted item. 2010 net earnings per diluted share totaled $1.74, and adjusted net earnings per diluted share in 2010 totaled $1.76, which excludes the 2010 adjusted item. Adjusted net earnings per diluted share in 2012, compared to 2011, increased primarily due to fewer shares outstanding as a resultamounts presented below are reflective of the repurchase of Kroger common shares, increased FIFO non-fuel operating profit, increased net earnings from our fuel operations and a decrease intwo-for-one stock split that began trading at the LIFO charge to $55 million (pre-tax), compared to a LIFO charge of $216 million (pre-tax) in 2011, partially offset by increased interest expense and income tax expense. Adjusted net earnings per diluted share in 2011, compared to 2010, increased primarily due to increased retail fuel margins, the repurchase of Kroger common shares, increased FIFO non-fuel operating profit, and the favorable resolution of certain tax issues, offset by a LIFO charge of $216 million (pre-tax), compared to a LIFO charge of $57 million (pre-tax) in 2010.split adjusted price on July 14, 2015.
Management believes adjusted net earnings (and adjusted net earnings per diluted share) are useful metrics to investors and analysts because they more accurately reflect our day-to-day business operations than do the amounts referenced above ingenerally accepted accounting principle (“GAAP”) measures of net earnings and net earnings per diluted share are not directly related to our day-to-day business.share. Adjusted net earnings (and adjusted net earnings per diluted share) are non-generally accepted accounting principle (“non-GAAP”) financial measures and should not be considered alternatives to net earnings (and net earnings per diluted share) or any other generally accepted accounting principle (“GAAP”)GAAP measure of performance. Adjusted net earnings (and adjusted net earnings per diluted share) should not be reviewedviewed in isolation or considered substitutes for our financial results as reported in accordance with GAAP. Management uses adjusted net earnings (and adjusted net earnings per diluted share) in evaluating our results of operations as it believes these measures are more meaningful indicators of ongoing operating performance since, as adjusted, those earnings relate more directly to our day-to-day operations. Management also uses adjusted net earnings (and adjusted net earnings per diluted share) as a performance metric for management incentive programs, and to measure our progress against internal budgets and targets. In addition, management takes into account adjusted net earnings when calculating management incentive programs.
A-8
Net Earnings
Net earnings totaled $2.0 billion in 2015, $1.7 billion in 2014 and $1.5 billion in 2013. Net earnings improved in 2015, compared to net earnings in 2014, due to an increase in operating profit, partially offset by an increase in income tax expense. Operating profit increased in 2015, compared to 2014, primarily due to an increase in first-in, first-out (“FIFO”) non-fuel operating profit, lower charges for total contributions to The Kroger Co. Foundation, UFCW Consolidated Pension Plan, the charge related to the 2014 Multi-Employer Pension Plan Obligation and a lower LIFO charge which was $28 million (pre-tax), compared to a LIFO charge of $147 million (pre-tax) in 2014, partially offset by a decrease in fuel operating profit and continued investments in lower prices for our customers. The decrease in fuel operating profit was primarily due to a decrease in fuel margin per gallon to $0.17 in 2015, compared to $0.19 in 2014, partially offset by an increase in fuel gallons sold. Continued investments in lower prices for our customers includes our pharmacy department, which experienced high levels of inflation that were not fully passed on to the customer in 2015. Net earnings improved in 2014, compared to net earnings in 2013, due to an increase in operating profit, partially offset by increases in interest and income tax expense. Operating profit increased in 2014, compared to 2013, primarily due to an increase in FIFO non-fuel operating profit, excluding Harris Teeter, the effect of our merger with Harris Teeter and an increase in fuel operating profit, partially offset by continued investments in lower prices for our customers, the 2014 Contributions, the charge related to the 2014 Multi-Employer Pension Plan Obligation and a higher LIFO charge which was $147 million (pre-tax), compared to a LIFO charge of $52 million (pre-tax) in 2013.
The net earnings for 2015 do not include any non-GAAP adjustments. The net earnings for 2014 include a net charge of $39 million, after tax, related to the 2014 Adjusted Items. The net earnings for 2013 include a net benefit of $23 million, after tax, related to the 2013 Adjusted Items. Excluding these benefits and charges for Adjusted Items for 2014 and 2013, adjusted net earnings were $2.0 billion in 2015, $1.8 billion in 2014 and $1.5 billion in 2013. 2015 net earnings improved, compared to adjusted net earnings in 2014, due to an increase in FIFO non-fuel operating profit, lower charges for total contributions to The Kroger Co. Foundation and UFCW Consolidated Pension Plan and a lower LIFO charge which was $28 million (pre-tax), compared to a LIFO charge of $147 million (pre-tax) in 2014, partially offset by continued investments in lower prices for our customers, a decrease in fuel operating profit and an increase in income tax expense. Continued investments in lower prices for our customers includes our pharmacy department, which experienced high levels of inflation that were not fully passed on to the customer in 2015. 2014 adjusted net earnings improved, compared to adjusted net earnings in 2013, due to an increase in FIFO non-fuel operating profit, excluding Harris Teeter, the effect of our merger with Harris Teeter and an increase in fuel operating profit, partially offset by continued investments in lower prices for our customers, the 2014 Contributions, increases in interest and income tax expense and a higher LIFO charge which was $147 million (pre-tax), compared to a LIFO charge of $52 million (pre-tax) in 2013.
Net earnings per diluted share totaled $2.06 in 2015, $1.72 in 2014 and $1.45 in 2013. Net earnings per diluted share in 2015, compared to 2014, increased primarily due to fewer shares outstanding as a result of the repurchase of Kroger common shares and an increase in net earnings. Net earnings per diluted share in 2014, compared to 2013, increased primarily due to fewer shares outstanding as a result of the repurchase of Kroger common shares and an increase in net earnings.
There were no adjustment items in 2015, but excluding the 2014 and 2013 Adjusted Items, adjusted net earnings per diluted share totaled $1.76 in 2014 and $1.43 in 2013. Net earnings per diluted share in 2015, compared to adjusted net earnings per diluted share in 2014, increased primarily due to fewer shares outstanding as a result of the repurchase of Kroger common shares and an increase in adjusted net earnings. Adjusted net earnings per diluted share in 2014, compared to adjusted net earnings per diluted share in 2013, increased primarily due to fewer shares outstanding as a result of the repurchase of Kroger common shares and an increase in adjusted net earnings.
A-9
The following table provides a reconciliation of net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. to net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. excluding Adjusted Items for 2014 and 2013 and a reconciliation of net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per diluted common share to the net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per diluted common share excluding Adjusted Items for 2014 and 2013. In 2015, we did not have any adjustment items that affect net earnings or net earnings per diluted share.
Net Earnings per Diluted Share excluding the Adjusted Items
(in millions, except per share amounts)
| 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. | $ | 2,039 | $ | 1,728 | $ | 1,519 | ||||
| 2014 Adjusted Items | — | 39 | — | |||||||
| 2013 Adjusted Items | — | — | (23 | ) | ||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. excluding the | ||||||||||
| adjustment items above | $ | 2,039 | $ | 1,767 | $ | 1,496 | ||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per diluted common share | $ | 2.06 | $ | 1.72 | $ | 1.45 | ||||
| 2014 Adjusted Items(1) | — | 0.04 | — | |||||||
| 2013 Adjusted Items(1) | — | — | (0.02 | ) | ||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per diluted common share | ||||||||||
| excluding the adjustment items above | $ | 2.06 | $ | 1.76 | $ | 1.43 | ||||
| Average numbers of common shares used in diluted calculation | 980 | 993 | 1,040 | |||||||
| (1) | The amounts presented represent the net earnings per diluted common share effect of each adjusted item. |
Sales
Total Sales(in millions)
| Total Sales | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | Percentage | Percentage | Percentage | Percentage | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | Adjusted (2) | Increase (3) | 2011 | Increase (4) | 2010 | 2015 | Increase(2) | 2014 | Increase(3) | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total supermarket sales | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| without fuel | $ | 75,311 | $ | 73,865 | 3.9% | $ | 71,109 | 5.0 | % | $ | 67,742 | $ | 91,310 | 5.8 | % | $ | 86,281 | 12.5 | % | $ | 76,666 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fuel sales | 18,896 | 18,413 | 8.9% | 16,901 | 39.9 | % | 12,081 | 14,804 | (21.5 | % | ) | 18,850 | (0.6 | %) | 18,962 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other sales (1) | 2,544 | 2,515 | 6.4% | 2,364 | 6.2 | % | 2,226 | 3,716 | 11.5 | % | 3,334 | 21.4 | % | 2,747 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total sales | $ | 96,751 | $ | 94,793 | 4.9% | $ | 90,374 | 10.1 | % | $ | 82,049 | $ | 109,830 | 1.3 | % | $ | 108,465 | 10.3 | % | $ | 98,375 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Other sales primarily relate to sales at convenience stores, excluding fuel; jewelry stores; | |
| (2) | ||
| (3) | This column represents the sales percentage | |
TheTotal sales increased in 2015, compared to 2014, by 1.3%. This increase in 2012 adjusted2015 total sales, compared to 2011 total sales,2014, was primarily due to ouran increase in identical supermarket sales, increase, excluding fuel, of 3.5% and5.0%. Total sales also increased due to the inclusion of Roundy’s sales, due to our merger, for the period of December 18, 2015 to January 30, 2016. Identical supermarket sales, excluding fuel, for 2015, compared to 2014, increased primarily due to an increase in fuel salesthe number of 8.9%. Thehouseholds shopping with us, an increase in total supermarket sales without fuel for 2012, adjusted for the extra week, compared to 2011, was due to our identical supermarket sales increase, excluding fuel of 3.5%.visits per household, changes in product mix and product cost inflation. Total fuel sales increaseddecreased in 2012, adjusted for the extra week,2015, compared to 2011,2014, primarily due to a 26.7% decrease in the average retail fuel price, partially offset by an increase in fuel gallons sold of 7.8%7.1%.
Total sales increased in 2014, compared to 2013, by 10.3%. This increase in 2014 total sales, compared to 2013, was primarily due to our merger with Harris Teeter, which closed on January 28, 2014, and an increase in the average retail fuel price of 1.7%. The increase in the average retail fuel price was caused by an increase in the product cost of fuel. Identical supermarket sales, excluding fuel, increased primarily due to inflation, increased transaction count and an increase in the average sale per shopping trip, also primarily due to inflation.
The increase in total sales for 2011 compared to 2010 was primarily the result of our identical supermarket sales increase, excluding fuel, of 4.9% and an increase in fuel sales of 39.9%. Total fuel sales increased over the same period due to a 26.3% increase in average retail fuel prices and a 10.8% increase in fuel gallons sold. The increase in the average retail fuel price was caused by an increase in the product cost of fuel. The increase in total supermarket sales without fuel for 2011 compared to 2010 was primarily the result of increases in identical supermarket sales, excluding fuel, of 4.9%5.2%. Identical supermarket
A-10
sales, excluding fuel for 2014, compared to 2013, increased primarily due to inflation, increased transaction count and an increase in the average salenumber of households shopping with us, an increase in visits per shopping trip, alsohousehold and product cost inflation. Total fuel sales decreased in 2014, compared to 2013, primarily due to inflation.a 6.8% decrease in the average retail fuel price, partially offset by an increase in fuel gallons sold of 6.6%.
We define a supermarket as identical when it has been in operation without expansion or relocation for five full quarters. Although identical supermarket sales is a relatively standard term, numerous methods exist for calculating identical supermarket sales growth. As a result, the method used by our management to calculate identical supermarket sales may differ from methods other companies use to calculate identical supermarket sales. We urge you to understand the methods used by other companies to calculate identical supermarket sales before comparing our identical supermarket sales to those of other such companies. Fuel discounts received at our fuel centers and earned based on in-store purchases are included in all of the supermarket identical sales results calculations illustrated below and reduce our identical supermarket sales results. Differences between total supermarket sales and identical supermarket sales primarily relate to changes in supermarket square footage. Identical supermarket sales include sales from all departments at identical Fred Meyer multi-department stores.stores and include Roundy’s sales for the last six weeks of fiscal 2015 for stores that are identical as if they were part of the Company in the prior year. We calculate annualized identical supermarket sales by adding together four quarters of identical supermarket sales. Our identical supermarket sales results are summarized in the table below, based on the 53-week period of 2012, compared to the previous year results adjusted to a comparable 53 week period.below.
A-9
Identical Supermarket Sales
(dollars in millions)
| 2012 | 2011 (1) | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||
| Including supermarket fuel centers | $ | 86,801 | $ | 83,072 | $ | 98,916 | $ | 97,813 | ||||||||
| Excluding supermarket fuel centers | $ | 72,562 | $ | 70,087 | $ | 87,553 | $ | 83,349 | ||||||||
| Including supermarket fuel centers | 4.5 | % | 9.2 | % | 1.1 | % | 4.2 | % | ||||||||
| Excluding supermarket fuel centers | 3.5 | % | 4.9 | % | 5.0 | % | 5.2 | % | ||||||||
Gross Margin and FIFO Gross Margin
We calculate gross margin as sales less merchandise costs, including advertising, warehousing, and transportation expenses. Merchandise costs exclude depreciation and rent expenses. Our gross margin rates, as a percentage of sales, were 20.56%22.16% in 2012, 20.89%2015, 21.16% in 20112014 and 22.24%20.57% in 2010.2013. The decreaseincrease in 2012,2015, compared to 2011,2014, resulted primarily from increaseda decrease in retail fuel sales and reductions in transportation costs and a decrease in our LIFO charge, as a percentage of sales, partially offset by continued investments in lower prices for our customers and increased shrink costs, as a percentage of sales. The increase in 2014, compared to 2013, resulted primarily from the effect of our merger with Harris Teeter, an increase in fuel gross margin rate and warehousinga reduction in warehouse and transportation costs, as a percentage of sales, partially offset partially by a decreasecontinued investments in thelower prices for our customers and an increase in our LIFO charge, as a percentage of sales. The decreasemerger with Harris Teeter, which closed late in 2011,fiscal year 2013, had a positive effect on our gross margin rate in 2014 since Harris Teeter has a higher gross margin rate as compared to 2010,total Company without Harris Teeter. The increase in fuel gross margin rate for 2014, compared to 2013, resulted primarily from increased fuel sales, continued investments in lower prices for our customers, higher transportation costs and an increase in the LIFO charge, offset partially by improvementsfuel margin per gallon sold of $0.19 in shrink, advertising and warehousing costs2014, compared to $0.14 in 2013. Our retail fuel operations lower our gross margin rate, as a percentage of sales. Retail fuel sales, lower our gross margin rate due to the very low gross margin on retail fuel sales as compared to non-fuel sales. A lower growth rate in retail fuel sales, as compared to the growth rate for the total Company, increases the gross margin rates, as a percentage of sales, when compared to the prior year.
We calculate FIFO gross margin as sales minusless merchandise costs, including advertising, warehousing, and transportation expenses, but excluding the LIFO charge. Merchandise costs exclude depreciation and rent expenses. Our LIFO charge was $55$28 million in 2012, $2162015, $147 million in 20112014 and $57$52 million in 2010.2013. FIFO gross margin is a non-GAAP financial measure and should not be considered as an alternative to gross margin or any other GAAP measure of performance. FIFO gross margin should not be reviewed in isolation or considered as a substitute for our financial results as reported in accordance
A-11
with GAAP. FIFO gross margin is an important measure used by management to evaluate merchandising and operational effectiveness. Management believes FIFO gross margin is a useful metric to investors and analysts because it measures our day-to-day merchandising and operational effectiveness.
Our FIFO gross margin rates, as a percentage of sales, were 22.18% in 2015, 21.30% in 2014 and 20.62% in 2012, 21.13% in 2011 and 22.31% in 2010. Retail2013. Our retail fuel salesoperations lower our FIFO gross margin rate, as a percentage of sales, due to the very low FIFO gross margin rate on retail fuel sales as compared to non-fuel sales. Excluding the effect of retail fuel operations, our FIFO gross margin rate decreased 41four basis points in 2012,2015, as a percentage of sales, compared to 2011. This2014. The decrease in 2012,FIFO gross margin rates, excluding retail fuel, in 2015, compared to 2011,2014, resulted primarily from continued investments in lower prices for our customers and increased shrink and warehousingcosts, partially offset by a reduction in transportation costs, as a percentage of sales. Excluding the effect of retail fuel, operations, our FIFO gross margin rate decreased 33three basis points in 2011,2014, as a percentage of sales, compared to 2010. This2013. The decrease in 2011,FIFO gross margin rates, excluding retail fuel, in 2014, compared to 2010, was2013, resulted primarily due tofrom continued investments in lower prices for our customers, offset partially by the effect of inflationour merger with Harris Teeter and highera reduction of warehouse and transportation expenses, partially offset by improvements in shrink, advertising, and warehousing expenses,costs, as a percentage of sales.
LIFO Charge
The LIFO charge was $55$28 million in 2012, $2162015, $147 million in 20112014 and $57$52 million in 2010. Like many food retailers,2013. In 2015, we experienced lower levels of product cost inflation, in 2012, compared to 2011.2014, which resulted in a lower LIFO charge. In 2012,2015, our LIFO charge primarily resulted from annualized product cost inflation related to pharmacy, and was partially offset by annualized product cost deflation related to meat and dairy. In 2014, we experienced higher product cost inflation, compared to 2013, which resulted in a higher LIFO charge. In 2014, our LIFO charge primarily resulted from annualized product cost inflation related to pharmacy, grocery, deli, meat and seafood. In 2013, our LIFO charge resulted primarily from an annualized product cost inflation related to grocery, natural foods, meat, deli and bakery, general merchandise and pharmacy, partially offset by deflation in seafood and manufactured product. In 2011, we experienced higher levels of product cost inflation, compared to 2010. In 2011, our LIFO charge primarily resulted from an annualized product cost inflation related to grocery, meat and seafood,pharmacy.
A-10
deli and bakery, and pharmacy. In 2010, our LIFO charge primarily resulted from annualized product cost inflation related to meat, pharmacy and Company-manufactured products, partially offset by deflation in grocery products.
Operating, General and Administrative Expenses
Operating, general and administrative (“OG&A”)&A expenses consist primarily of employee-related costs such as wages, health care benefits and retirement plan costs, utilities and credit card fees. Rent expense, depreciation and amortization expense and interest expense are not included in OG&A.
OG&A expenses, as a percentage of sales, were 15.35%16.34% in 2012, 16.98%2015, 15.82% in 2011,2014 and 16.85%15.45% in 2010. Excluding the 2012 and 2011 adjusted items,2013. The increase in OG&A expenses, as a percentage of sales, were 15.47% in 2012 and 15.92%2015, compared to 2014, resulted primarily from a decrease in 2011. The growth in our retail fuel sales, reducesincreases in EMV chargebacks, company sponsored pension, healthcare and incentive plan costs, as a percentage of sales, partially offset by increased supermarket sales, the 2014 Multi-Employer Pension Plan Obligation, lower charges for total contributions to The Kroger Foundation and UFCW Consolidated Pension Plan, productivity improvements and effective cost controls at the store level. The increase in OG&A expenses, as a percentage of sales, in 2014, compared to 2013, resulted primarily from the 2014 Contributions, the 2014 Multi-Employer Pension Plan Obligation, the effect of fuel, the effect of our merger with Harris Teeter and increases in credit card fees and incentive plan costs, as a percentage of sales, partially offset by increased supermarket sales growth, productivity improvements and effective cost controls at the store level. Retail fuel sales lower our OG&A rate due to the very low OG&A rate, as a percentage of sales, of retail fuel sales compared to non-fuel sales. The merger with Harris Teeter, which closed late in fiscal year 2013, increased our OG&A rate, as a percentage of sales, since Harris Teeter has a higher OG&A rate as compared to the total Company without Harris Teeter.
Our retail fuel operations reduce our overall OG&A rate, as a percentage of sales, due to the very low OG&A rate on retail fuel sales as compared to non-fuel sales. OG&A expenses, as a percentage of sales excluding fuel, the 2015 UFCW Contributions, the 2014 Contributions and the 2012 adjusted items,2014 Multi-Employer Pension Plan Obligation, decreased 399 basis points, in 2012, compared to 2011. This2014. The decrease in our adjusted OG&A rate in 2015, compared to 2014, resulted primarily from increased identical supermarket sales, growth, productivity improvements and effective cost controls at the store level, the benefit receivedpartially offset by increases in lower operating expenses from the consolidation
A-12
EMV chargebacks, company sponsored pension, healthcare and incentive plan costs, as a percentage of four UFCW multi-employer pension plans in the prior year and decreased incentive compensation, offset partially by increased healthcare costs.sales. OG&A expenses, as a percentage of sales excluding fuel, the 2014 Contributions and the 2011 adjusted item,2014 Multi-Employer Pension Plan Obligation, decreased 2519 basis points in 2011,2014, compared to 2010.2013, adjusted for the 2013 Adjusted Items. The 2011 decrease in our adjusted OG&A rate in 2014, compared to 2010,2013, resulted primarily from increased identical supermarket sales growth, productivity improvements and strongeffective cost controls at the store level, offset partially by increasedthe effect of our merger with Harris Teeter and increases in credit and debit card fees and incentive compensation and health care costs.plan costs, as a percentage of sales.
Rent Expense
Rent expense was $628$723 million in 2012, as2015, compared to $619$707 million in 20112014 and $623$613 million in 2010.2013. Rent expense, as a percentage of sales, was 0.66% in 2015, compared to 0.65% in 2012, as2014 and 0.62% in 2013. Rent expense increased in 2015, compared to 0.68% in 2011 and 0.76% in 2010. Rent expense, as a percentage2014, due to the effect of sales excluding fuel, was 0.78% in 2012, as compared to 0.82% in 2011 and 0.87% in 2010. These continual decreases in rent expense, as a percentage of sales both including and excluding fuel, reflectsour merger with Roundy’s, partially offset by our continued emphasis on owning rather than leasing, whenever possible. Rent expense, as a percentage of sales, in 2015 was consistent with 2014 due to the effect of our merger with Roundy’s, partially offset by our continued emphasis to own rather than lease, whenever possible, and the benefit of increased supermarket sales. The increase in rent expense, as a percentage of sales, in 2014, compared to 2013, is due to the effect of our merger with Harris Teeter, partially offset by our continued emphasis to own rather than lease, whenever possible, and the benefit of increased sales. The merger with Harris Teeter, which closed late in fiscal year 2013, increased rent expense, as a percentage of sales, since Harris Teeter has a higher rent expense rate compared to the total Company without Harris Teeter.
Depreciation and Amortization Expense
Depreciation and amortization expense was $2.1 billion, compared to $1.9 billion in 2014 and $1.7 billion in 2012 and $1.6 billion in both 2011 and 2010.2013. Depreciation and amortization expense, as a percentage of sales, was 1.71%1.90% in 2012, 1.81%2015, 1.80% in 20112014 and 1.95%1.73% in 2010. Excluding the extra week2013. The increase in 2012, depreciation and amortization expense as a percentagefor 2015, compared to 2014, was the result of sales, was 1.74% in 2012. Depreciationadditional depreciation due to our merger with Roundy’s and amortization expense, as a percentageon capital investments, including mergers and lease buyouts, of sales$3.4 billion, excluding fuel, was 1.99% in 2012, 2.10% in 2011 and 2.17% in 2010. Excluding the extra week in 2012, depreciation and amortization expense, as a percentage of sales excluding fuel, was 2.03%. These continual decreasesRoundy’s. The increase in depreciation and amortization expense, as a percentage of sales, bothfrom 2015, compared to 2014, is primarily due to the additional depreciation resulting from our increased capital investments, including mergers and excluding fuellease buyouts in 2015, compared to 2014. The increase in depreciation and amortization expense for 2014, compared to 2013, in total dollars, was due to the extra week, areeffect of our merger with Harris Teeter and our increased spending in capital investments, including mergers and lease buyouts, of $3.1 billion in 2014. The increase in depreciation and amortization expense, as a percentage of sales, from 2014, compared to 2013, is primarily due to the resulteffect of increasingour merger with Harris Teeter and our increased spending in capital investments, partially offset by increased supermarket sales. The merger with Harris Teeter, which closed late in fiscal year 2013, increased our depreciation and amortization expense, as a percentage of sales, since Harris Teeter has a higher depreciation expense rate as compared to the total Company without Harris Teeter.
Operating Profit and Adjusted FIFO Operating Profit
Operating profit was $2.8$3.6 billion in 2012, $1.32015, $3.1 billion in 20112014 and $2.2 billion in 2010. Excluding the extra week, operating profit was $2.7 billion in 2012.2013. Operating profit, as a percentage of sales, was 2.86%3.26% in 2012, 1.41%2015, 2.89% in 20112014 and 2.66%2.77% in 2010.2013. Operating profit, as a percentage of sales, excludingincreased 37 basis points in 2015, compared to 2014, primarily from increased supermarket sales, a LIFO charge that was significantly lower in 2015, lower charges for total contributions to The Kroger Co. Foundation and UFCW Consolidated Pension Plan, the extra week, was 2.81%. Operating2014 Multi-Employer Pension Obligation, productivity improvements, effective cost controls at the store level, and reductions in transportation costs, as a percentage of sales, partially offset by the effect of our merger with Roundy’s, continued investments in lower prices for our customers, a decrease in operating profit excludingfrom our fuel operations, an increase in depreciation and amortization expense and increases in EMV chargebacks, company sponsored pension, healthcare, incentive plan and shrink costs, as a percentage of sales. The decrease in operating profit from our fuel operations for 2015, compared to 2014, resulted primarily from a decrease in the 2012, 2011 and 2010 adjusted items, was $2.6 billionaverage margin per gallon of fuel sold, partially offset by an increase in 2012 and $2.2 billion in both 2011 and 2010.
A-13
fuel gallons sold. Operating profit, as a percentage of sales, excludingincreased 12 basis points in 2014, compared to 2013, primarily from the 2012, 2011effect of our merger with Harris Teeter, an increase in fuel gross margin rate and 2010 adjusted items, was 2.74%a reduction in 2012, 2.47% in 2011warehouse and 2.68% in 2010. Operating profit, excluding the extra weektransportation costs, rent and the 2012 adjusted items, was $2.5 billion in 2012. Operating profit,depreciation and amortization expenses, as a percentage of sales, excluding the extra week and the 2012 adjusted items, was 2.69% in 2012.
A-11
Operating profit, as a percentage of sales excluding the 2012 and 2011 adjusted items and the extra week, increased 22 basis points in 2012, compared to 2011, primarily due to improvements in operating, general and administrative expenses, rent, depreciation and the LIFO charge,partially offset partially by continued investments in lower prices for our customers and increased shrink and warehousing costs. Operating profit, as a percentage of sales excluding the 2011 and 2010 adjusted items, decreased 21 basis points in 2011, compared to 2010, primarily due to an increase in the LIFO charge, continued investments in lower prices for our customers and higher transportation costs, offset partially by improvements in operating, general and administrative expenses, rent, depreciation, advertising, shrink and warehousing costs.as a percentage of sales.
We calculate FIFO operating profit as operating profit excluding the LIFO charge. FIFO operating profit is a non-GAAP financial measure and should not be considered as an alternative to operating profit or any other GAAP measure of performance. FIFO operating profit should not be reviewed in isolation or considered as a substitute for our financial results as reported in accordance with GAAP. FIFO operating profit is an important measure used by management to evaluate operational effectiveness. Management believes FIFO operating profit is a useful metric to investors and analysts because it measures our day-to-day merchandising and operational effectiveness. Since fuel discounts are earned based on in-store purchases, fuel operating profit does not include fuel discounts, which are allocated to our in-store supermarket location departments. We also derive operating, general and administrative expenses,OG&A, rent and depreciation and amortization expenses through the use of estimated allocations in the calculation of fuel operating profit.
FIFO operating profit was $3.6 billion in 2015, $3.3 billion in 2014 and $2.8 billion in 2012, $1.5 billion in 2011 and $2.2 billion in 2010. Excluding the extra week, FIFO operating profit was $2.7 billion in 2012.2013. FIFO operating profit, as a percentage of sales, was 2.91%3.28% in 2012, 1.65%2015, 3.03% in 20112014 and 2.73%2.82% in 2010.2013. FIFO operating profit, excluding the 2015 UFCW Contributions, the 2014 Contributions, the 2014 Multi-Employer Pension Plan Obligation and 2013 Adjusted Items, was $3.7 billion in 2015, $3.5 billion in 2014 and $2.8 billion in 2013. FIFO operating profit, as a percentage of sales excluding the extra week,2015 UFCW Contributions, the 2014 Contributions, the 2014 Multi-Employer Pension Plan Obligation and 2013 Adjusted Items, was 2.87%3.38% in 2012. FIFO operating profit, excluding the 2012, 20112015, 3.24% in 2014 and 2010 adjusted items, was $2.7 billion2.84% in 2012, $2.4 billion in 2011 and $2.3 billion in 2010. FIFO operating profit, excluding the extra week and the 2012 adjusted items, was $2.8 billion in 2012. FIFO operating profit, as a percentage of sales excluding the 2012, 2011 and 2010 adjusted items, was 2.79% in 2012, 2.71% in 2011 and 2.75% in 2010. FIFO operating profit, excluding the extra week and the 2012 adjusted items, was 2.75% in 2012.2013.
Retail fuel sales lower our overall FIFO operating profit rate due to the very low FIFO operating profit rate, as a percentage of sales, of retail fuel sales compared to non-fuel sales. FIFO operating profit, as a percentage of sales excluding fuel, was $2.6 billionthe 2015 UFCW Contributions, the 2014 Contributions and the 2014 Multi-Employer Pension Plan Obligation, increased 5 basis points in 2012, $1.3 billion2015, compared to 2014. The increase in 2011 and $2.1 billion in 2010. Excluding the extra week,our adjusted FIFO operating profit excluding fuel,rate in 2015, compared to 2014, was $2.5 billionprimarily due to increased supermarket sales, productivity improvements, effective cost controls at the store level and reductions in 2012.transportation costs, as a percentage of sales, partially offset by continued investments in lower prices for our customers, the effect of our merger with Roundy’s, an increase in depreciation and amortization expense and increases in EMV chargebacks, company sponsored pension, healthcare, incentive plan and shrink costs, as a percentage of sales. Excluding the effects of our merger with Roundy’s, FIFO operating profit increased 8 basis points in 2015, compared to 2014. FIFO operating profit, as a percentage of sales, excluding fuel, was 3.34%the 2014 Contributions and the 2014 Multi-Employer Pension Plan Obligation, increased 10 basis points in 2012, 1.77%2014, compared to 2013, adjusted for the 2013 Adjusted Items. The increase in 2011 and 3.00% in 2010. Excluding the extra week,our adjusted FIFO operating profit rate in 2014, compared to 2013, was primarily due to the effect of our merger with Harris Teeter and a reduction in warehouse and transportation costs, improvements in OG&A, rent and depreciation and amortization expense, as a percentage of sales, excluding fuel, was 3.28% in 2012. FIFO operating profit, excluding fuel and the 2012, 2011 and 2010 adjusted items, was $2.5 billion in 2012, $2.3 billion in 2011 and $2.1 billion in 2010. FIFO operating profit, as a percentage of sales excluding fuel and the 2012, 2011 and 2010 adjusted items, was 3.19% in 2012, 3.07% in 2011 and 3.02% in 2010. Excluding the extra week, FIFO operating profit, excluding fuel and the 2012 adjusted items was $2.4 billion in 2012. Excluding the extra week, FIFO operating profit, as a percentage of sales excluding fuel and the 2012 adjusted items, was 3.13% in 2012.
Excluding fuel, FIFO operating profit, as a percentage of sales excluding the 2012 and 2011 adjusted items and the extra week, increased six basis points in 2012, compared to 2011, primarily due to improvements in operating, general and administrative expenses, rent and depreciation,partially offset partially by continued investments in lower prices for our customerscustomers.
Interest Expense
Interest expense totaled $482 million in 2015, $488 million in 2014 and increased shrink and warehousing costs. Excluding fuel, FIFO operating profit, as a percentage of sales excluding the 2011 and 2010 adjusted items, increased five basis points$443 million in 2011,2013. The decrease in interest expense in 2015, compared to 2010,2014, resulted primarily due to improvementsthe timing of debt principal payments and debt issuances, partially offset by an increase in operating, general and administrative expenses, rent, depreciation, advertising, shrink and warehousing costs, offset partially by continued investments in lower prices for our customers and higher transportation costs.
A-12
The following table provides a reconciliation of operating profit to FIFO operating profit and FIFO operating profit, excluding fuel and the adjusted items, for 2012, 2011 and 2010 ($ in millions):
| 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | Adjusted | 2011 | 2010 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Percentage | 2012 | Percentage | Percentage | Percentage | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | of Sales | Adjusted (1) | of Sales | 2011 | of Sales | 2010 | of Sales | |||||||||||||||||
| Sales | $ | 96,751 | $ | 94,793 | $ | 90,374 | $ | 82,049 | ||||||||||||||||
| Fuel sales | 18,896 | 18,413 | 16,901 | 12,081 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales excluding fuel | $ | 77,855 | $ | 76,380 | $ | 73,473 | $ | 69,968 | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating profit | $ | 2,764 | 2.86% | $ | 2,664 | 2.81% | $ | 1,278 | 1.41% | $ | 2,182 | 2.66% | ||||||||||||
| LIFO charge | 55 | 0.06% | 55 | 0.06% | 216 | 0.24% | 57 | 0.07% | ||||||||||||||||
| FIFO operating profit | 2,819 | 2.91% | 2,719 | 2.87% | 1,494 | 1.65% | 2,239 | 2.73% | ||||||||||||||||
| Fuel operating profit | 218 | 1.15% | 215 | 1.17% | 192 | 1.14% | 143 | 1.18% | ||||||||||||||||
| FIFO operating profit | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| excluding fuel | 2,601 | 3.34% | 2,504 | 3.28% | 1,302 | 1.77% | 2,096 | 3.00% | ||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted items | (115 | ) | (115 | ) | 953 | 19 | ||||||||||||||||||
| FIFO operating profit | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| excluding fuel and the | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| adjusted items | $ | 2,486 | 3.19% | $ | 2,389 | 3.13% | $ | 2,255 | 3.07% | $ | 2,115 | 3.02% | ||||||||||||
Percentages may not sum due to rounding.
Interest Expense
Net interest expense totaled $462 million in 2012, $435 million in 2011 and $448 million in 2010. Excluding the extra week, net interest expense was $454 million in 2012.associated with our commercial paper program. The increase in net interest expense in 2012 excluding the extra week,2014, compared to 2011,2013, resulted primarily from a decrease in the benefit from interest rate swaps and an increase in net total debt, offset partially by a lower weighted average interest rate. The decrease in net interest expense in 2011, comparedprimarily due to 2010, resulted primarily from a lower weighted average interest ratefinancing the merger with Harris Teeter and an average lower debt balance for the year, offset partially by a decrease in the benefit from interest rate swaps.repurchases of our outstanding common shares.
Income Taxes
Our effective income tax rate was 34.5%33.8% in 2012, 29.3%2015, 34.1% in 20112014 and 34.7%32.9% in 2010.2013. The 20122015, 2014 and 2013 tax rate differed from the federal statutory rate primarily as a result of the utilization of tax credits, the favorable resolution of certain tax issuesDomestic Manufacturing Deduction and other changes, partially offset by the effect of state income taxes. The 2011 and 2010 effective tax rates differed from the federal statutory rate primarily as a result of the utilization of tax credits and favorable resolution of certain tax issues, partially offset by the effect of state income taxes. The 2011 effective tax rate was also lower than 2012 and 2010 due to the effect on pre-tax income of the UFCW consolidated pension plan charge of $953 million ($591 million after-tax). Excluding the UFCW consolidated pension plan charge, our effective rate in 2011 would have been 33.9%.
Common Share Repurchase ProgramA-14
COMMON SHARE REPURCHASE PROGRAMS
We maintain share repurchase programs that comply with Rule 10b5-1 of the Securities Exchange Act Rule 10b5-1of 1934 and allow for the orderly repurchase of our common shares, from time to time. We made open market purchases of Krogerour common shares totaling $1.2$500 million in 2015, $1.1 billion in 2012, $1.4 billion in 20112014 and $505$338 million in 20102013 under these repurchase programs. In addition to these repurchase programs, we also repurchase common shares to reduce dilution resulting from our employee stock option plans. This program is solely funded by proceeds from stock option exercises, and the tax benefit from these exercises. We repurchased approximately $96$203 million in 2012, $1272015, $155 million in 2011,2014 and $40$271 million in 20102013 of Krogerour common shares under the stock option program.
A-13
The shares reacquiredrepurchased in 20122015 were reacquiredacquired under fourtwo separate share repurchase programs. The first is a $1 billion repurchase program that was authorized by Kroger’s Board of Directors on September 15, 2011. The second is a $1 billion repurchase program that was authorized by Kroger’s Board of Directors on June 14, 2012, that replaced the first referenced program. The third is a $500 million repurchase program that was authorized by Kroger’sour Board of Directors on October 16, 2012, that replaced theJune 26, 2014. The second referenced program. The fourth is a program that uses the cash proceeds from the exercises of stock options by participants in Kroger’sour stock option and long-term incentive plans as well as the associated tax benefits. AsOn June 25, 2015, our Board of February 2, 2013, we had $466 million remaining on the October 16, 2012Directors approved a new $500 million share repurchase program to replace our prior authorization, which had been exhausted. As of January 30, 2016, we have not repurchased any shares utilizing the June 25, 2015 repurchase program. On March 10, 2016, our Board of Directors approved a new $500 million share repurchase program to supplement the 2015 Repurchase Program, which is expected to be exhausted by the end of the second quarter of 2016.
Capital InvestmentsCAPITAL INVESTMENTS
Capital investments, including changes in construction-in-progress payables and excluding acquisitionsmergers and the purchase of leased facilities, totaled $2.0$3.3 billion in 2012 and $1.92015, $2.8 billion in both 20112014 and 2010.$2.3 billion in 2013. Capital investments for mergers totaled $168 million in 2015, $252 million in 2014 and $2.3 billion in 2013. Payments for mergers of $168 million in 2015, $252 million in 2014 and $2.3 billion in 2013 relate to our mergers with Roundy’s, Vitacost.com and Harris Teeter, respectively. Refer to Note 2 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information on the mergers with Roundy’s, Vitacost.com and Harris Teeter. Capital investments for the purchase of leased facilities totaled $73$35 million in 2012, $602015, $135 million in 20112014 and $38$108 million for 2010.in 2013. The table below shows our supermarket storing activity and our total food store square footage:
Supermarket Storing Activity
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||||
| Beginning of year | 2,435 | 2,460 | 2,469 | 2,625 | 2,640 | 2,424 | |||||||||||
| Opened | 18 | 10 | 14 | 31 | 33 | 17 | |||||||||||
| Opened (relocation) | 7 | 12 | 6 | 12 | 13 | 7 | |||||||||||
| Acquired | — | 6 | 4 | 159 | — | 227 | |||||||||||
| Acquired (relocation) | — | 2 | — | ||||||||||||||
| Closed (operational) | (29 | ) | (41 | ) | (27 | ) | (37 | ) | (48 | ) | (28 | ) | |||||
| Closed (relocation) | (7 | ) | (14 | ) | (6 | ) | (12 | ) | (13 | ) | (7 | ) | |||||
| End of year | 2,424 | 2,435 | 2,460 | 2,778 | 2,625 | 2,640 | |||||||||||
| Total food store square footage (in millions) | 149 | 149 | 149 | 173 | 162 | 161 | |||||||||||
Return on Invested CapitalRETURN ON INVESTED CAPITAL
We calculate return on invested capital (“ROIC”) by dividing adjusted operating profit for the prior four quarters by the average invested capital. Adjusted operating profit is calculated by excluding certain items included in operating profit, and adding back our LIFO charge, depreciation and amortization and rent.rent to our U.S. GAAP operating profit of the prior four quarters. Average invested capital is calculated as the sum of (i) the average of our total assets, (ii) the average LIFO reserve, (iii) the average accumulated depreciation and amortization and (iv) a rent factor equal to total rent for the last four quarters multiplied by a factor of eight; minus (i) the average taxes receivable, (ii) the average trade accounts payable, (iii) the average accrued salaries and wages and (iv) the average other current liabilities.liabilities, excluding accrued income taxes. Averages are calculated for return on invested capitalROIC by adding the beginning balance of the first
A-15
quarter and the ending balance of the fourth quarter, of the last four quarters, and dividing by two. We use a factor of eight for our total rent as we believe this is a common factor used by our investors, analysts and analysts.rating agencies. ROIC is a non-GAAP financial measure of performance. ROIC should not be reviewed in isolation or considered as a substitute for our financial results as reported in accordance with GAAP. ROIC is an important measure used by management to evaluate our investment returns on capital. Management believes ROIC is a useful metric to investors and analysts because it measures how effectively we are deploying our assets. All items included in the calculation of ROIC are GAAP measures, excluding certain adjustments to operating income.
Although ROIC is a relatively standard financial term, numerous methods exist for calculating a company’s ROIC. As a result, the method used by our management to calculate ROIC may differ from methods other companies use to calculate their ROIC. We urge you to understand the methods used by other companies to calculate their ROIC before comparing our ROIC to that of such other companies.
A-14
The following table provides a calculation of ROIC for 20122015 and 2011 on a 52 week basis ($ in millions):2014. The 2015 calculation of ROIC excludes the financial position, results and merger costs for the Roundy’s transaction:
| February 2, | January 28, | January 30, | January 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | 2012 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Return on Invested Capital | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Numerator | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating profit on a 53 week basis in fiscal year 2012 | $ | 2,764 | $ | 1,278 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 53rdweek operating profit adjustment | (100 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Operating profit | $ | 3,576 | $ | 3,137 | ||||||||||||||||||
| LIFO charge | 55 | 216 | 28 | 147 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 1,652 | 1,638 | 2,089 | 1,948 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Rent on a 53 week basis in fiscal year 2012 | 628 | 619 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 53rdweek rent adjustment | (12 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 adjusted item | — | 953 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 adjusted items | (115 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rent | 723 | 707 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjustments for pension plan agreements | — | 87 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | (13 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted operating profit | $ | 4,872 | $ | 4,704 | $ | 6,403 | $ | 6,026 | ||||||||||||||
| Denominator | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average total assets | $ | 24,064 | $ | 23,491 | $ | 32,197 | $ | 29,860 | ||||||||||||||
| Average taxes receivable (1) | (22 | ) | (21 | ) | (206 | ) | (19 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Average LIFO reserve | 1,071 | 935 | 1,259 | 1,197 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Average accumulated depreciation and amortization | 14,051 | 13,088 | 17,441 | 16,057 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Average trade accounts payable | (4,427 | ) | (4,278 | ) | (5,390 | ) | (4,967 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Average accrued salaries and wages | (1,017 | ) | (972 | ) | (1,359 | ) | (1,221 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Average other current liabilities (2) | (2,313 | ) | (2,151 | ) | (3,054 | ) | (2,780 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Adjustment for Roundy’s merger | (714 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rent x 8 | 4,928 | 4,952 | 5,784 | 5,656 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Average invested capital | $ | 36,335 | $ | 35,044 | $ | 45,958 | $ | 43,783 | ||||||||||||||
| Return on Invested Capital | 13.4 | % | 13.4 | % | 13.93 | % | 13.76 | % | ||||||||||||||
| (1) | Taxes receivable were | |
| (2) | Other current liabilities included accrued income taxes of | |
Critical Accounting PoliciesA-16
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES
We have chosen accounting policies that we believe are appropriate to report accurately and fairly our operating results and financial position, and we apply those accounting policies in a consistent manner. Our significant accounting policies are summarized in Note 1 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses, and related disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities. We base our estimates on historical experience and other factors we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
We believe that the following accounting policies are the most critical in the preparation of our financial statements because they involve the most difficult, subjective or complex judgments about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain.
A-15
Self-Insurance Costs
We primarily are self-insured for costs related to workers’ compensation and general liability claims. The liabilities represent our best estimate, using generally accepted actuarial reserving methods, of the ultimate obligations for reported claims plus those incurred but not reported for all claims incurred through February 2, 2013.January 30, 2016. We establish case reserves for reported claims using case-basis evaluation of the underlying claim data and we update as information becomes known.
For both workers’ compensation and general liability claims, we have purchased stop-loss coverage to limit our exposure to any significant exposure on a per claim basis. We are insured for covered costs in excess of these per claim limits. We account for the liabilities for workers’ compensation claims on a present value basis utilizing a risk-adjusted discount rate. A 25 basis point decrease in our discount rate would increase our liability by approximately $2 million. General liability claims are not discounted.
The assumptions underlying the ultimate costs of existing claim losses are subject to a high degree of unpredictability, which can affect the liability recorded for such claims. For example, variability in inflation rates of health care costs inherent in these claims can affect the amounts realized. Similarly, changes in legal trends and interpretations, as well as a change in the nature and method of how claims are settled can affect ultimate costs. Our estimates of liabilities incurred do not anticipate significant changes in historical trends for these variables, and any changes could have a considerable effect on future claim costs and currently recorded liabilities.
Impairments of Long-Lived Assets
We monitor the carrying value of long-lived assets for potential impairment each quarter based on whether certain triggertriggering events have occurred. These events include current period losses combined with a history of losses or a projection of continuing losses or a significant decrease in the market value of an asset. When a triggertriggering event occurs, we perform an impairment calculation, comparing projected undiscounted cash flows, utilizing current cash flow information and expected growth rates related to specific stores, to the carrying value for those stores. If we identify impairment for long-lived assets to be held and used, we compare the assets’ current carrying value to the assets’ fair value. Fair value is determined based on market values or discounted future cash flows. We record impairment when the carrying value exceeds fair market value. With respect to owned property and equipment held for disposal, we adjust the value of the property and equipment to reflect recoverable values based on our previous efforts to dispose of similar assets and current economic conditions. We recognize impairment for the excess of the carrying value over the estimated fair market value, reduced by estimated direct costs of disposal. We recorded asset impairments in the normal course of business totaling $18$46 million in 2012,2015, $37 million in 20112014 and $25$39 million in 2010.2013. We record costs to reduce the carrying value of long-lived assets in the Consolidated Statements of Operations as “Operating, general and administrative” expense.
A-17
The factors that most significantly affect the impairment calculation are our estimates of future cash flows. Our cash flow projections look several years into the future and include assumptions on variables such as inflation, the economy and market competition. Application of alternative assumptions and definitions, such as reviewing long-lived assets for impairment at a different level, could produce significantly different results.
Goodwill
Our goodwill totaled $1.2$2.7 billion as of February 2, 2013.January 30, 2016. We review goodwill for impairment in the fourth quarter of each year, and also upon the occurrence of triggering events. We perform reviews of each of our operating divisions and variable interest entities (collectively, our reporting units) with“reporting units”) that have goodwill balances. Fair value is determined using a multiple of earnings, or discounted projected future cash flows, and we compare fair value to the carrying value of a reporting unit for purposes of identifying potential impairment. We base projected future cash flows on management’s knowledge of the current operating environment and expectations for the future. If we identify potential for impairment, we measure the fair value of a reporting unit against the fair value of its underlying assets and liabilities, excluding goodwill, to estimate an implied fair value of the division’sreporting unit’s goodwill. We recognize goodwill impairment for any excess of the carrying value of the division’sreporting unit’s goodwill over the implied fair value.
A-16In 2015, goodwill increased $420 million primarily due to our merger with Roundy’s. In 2014, goodwill increased $169 million primarily due to our merger with Vitacost.com. For additional information related to the allocation of the purchase price for Roundy’s and Vitacost.com, refer to Note 2 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
The annual evaluation of goodwill performed for our other reporting units during the fourth quarter of 20122015, 2014 and 20112013 did not result in impairment.
The annual evaluation of goodwill performed during the fourth quarter of 2010 resulted in an impairment charge of $18 million. Based on the results of our step one analysis in the fourth quarter of 2010, a supermarket reporting unit with a small number of stores indicated potential impairment. Due to estimated future expected cash flows being lower than in the past, our estimated fair value of the reporting unit decreased. We concluded that the carrying value of goodwill for this reporting unit exceeded its implied fair value, resulting in a pre-tax impairment charge of $18 million ($12 million after-tax). In 2009, we disclosed that a 10% reduction in fair value of this supermarket reporting unit would indicate a potential for impairment. Subsequent to the impairment, no goodwill remains at this reporting unit.
Based on current and future expected cash flows, we believe goodwill impairments are not reasonably possible.likely. A 10% reduction in fair value of our reporting units would not indicate a potential for impairment of our goodwill balance.
For additional information relating to our results of the goodwill impairment reviews performed during 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 20102013 see Note 23 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
The impairment review requires the extensive use of management judgment and financial estimates. Application of alternative estimates and assumptions, such as reviewing goodwill for impairment at a different level, could produce significantly different results. The cash flow projections embedded in our goodwill impairment reviews can be affected by several factors such as inflation, business valuations in the market, the economy and market competition.
Store Closing Costs
We provide for closed store liabilities on the basis of the present value of the estimated remaining non-cancellable lease payments after the closing date, net of estimated subtenant income. We estimate the net lease liabilities using a discount rate to calculate the present value of the remaining net rent payments on closed stores. We usually pay closed store lease liabilities over the lease terms associated with the closed stores, which generally have remaining terms ranging from one to 20 years. Adjustments to closed store liabilities primarily relate to changes in subtenant income and actual exit costs differing from original estimates. We make adjustments for changes in estimates in the period in which the change becomes known. We review store closing liabilities quarterly to ensure that any accrued amount that is not a sufficient estimate of future costs or that no longer is needed for its originally intended purpose, is adjusted to earnings in the proper period.
We estimate subtenant income, future cash flows and asset recovery values based on our experience and knowledge of the market in which the closed store is located, our previous efforts to dispose of similar assets and current economic conditions. The ultimate cost of the disposition of the leases and the related assets is affected by current real estate markets, inflation rates and general economic conditions.
A-18
We reduce owned stores held for disposal to their estimated net realizable value. We account for costs to reduce the carrying values of property, equipment and leasehold improvements in accordance with our policy on impairment of long-lived assets. We classify inventory write-downs in connection with store closings, if any, in “Merchandise costs.” We expense costs to transfer inventory and equipment from closed stores as they are incurred.
Post-Retirement Benefit Plans
We account for our defined benefit pension plans using the recognition and disclosure provisions of GAAP, which require the recognition of the funded status of retirement plans on the Consolidated Balance Sheet. We record, as a component of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (“AOCI”), actuarial gains or losses, prior service costs or credits and transition obligations that have not yet been recognized.
The determination of our obligation and expense for Company-sponsored pension plans and other post-retirement benefits is dependent upon our selection of assumptions used by actuaries in calculating those amounts. Those assumptions are described in Note 1315 to the Consolidated Financial Statements and include,
A-17
among others, the discount rate, the expected long-term rate of return on plan assets, average life expectancymortality and the rate of increases in compensation and health care costs. Actual results that differ from our assumptions are accumulated and amortized over future periods and, therefore, generally affect our recognized expense and recorded obligation in future periods. While we believe that our assumptions are appropriate, significant differences in our actual experience or significant changes in our assumptions, including the discount rate used and the expected return on plan assets, may materially affect our pension and other post-retirement obligations and our future expense. Note 1315 to the Consolidated Financial Statements discusses the effect of a 1% change in the assumed health care cost trend rate on other post-retirement benefit costs and the related liability.
The objective of our discount rate assumptions was intended to reflect the rates at which the pension benefits could be effectively settled. In making this determination, we take into account the timing and amount of benefits that would be available under the plans. Our policymethodology for selecting the discount rates as of year-end 2012 changed from the policy as of year-end 2011 and 2010. In 2012, our policy was to match the plan’s cash flows to that of a hypothetical bond portfolio whose cash flow from coupons and maturities match the plan’s projected benefit cash flows. The discount rates are the single rates that produce the same present value of cash flows. The selection of the 4.29%4.62% and 4.11%4.44% discount rates as of year-end 20122015 for pension and other benefits, respectively, represents the hypothetical bond portfolio using bonds with an AA or better rating constructed with the assistance of an outside consultant. In 2011We utilized a discount rate of 3.87% and 2010, our policy was to match the plan’s cash flows to that of a yield curve that provides the equivalent yields on zero-coupon corporate bonds for each maturity. Benefit cash flows due in a particular year can theoretically be “settled” by “investing” them in the zero-coupon bond that matures in the same year. The discount rates are the single rates that produce the same present value of cash flows. The selection of the 4.55% and 4.40% discount rates3.74% as of year-end 20112014 for pension and other benefits, respectively, represents the equivalent single rates constructed under a broad-market AA yield curve constructed with the assistance of an outside consultant.respectively. A 100 basis point increase in the discount rate would decrease the projected pension benefit obligation as of February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, by approximately $412.$438 million.
To determine the expected rate of return on pension plan assets held by Kroger for 2015, we considerconsidered current and forecasted plan asset allocations as well as historical and forecasted rates of return on various asset categories. For 2012 and 2011, weIn 2015, our assumed a pension plan investment return rate of 8.5%.was 7.44%, compared to 7.44% in 2014 and 8.50 in 2013. Our pension plan’splans’ average rate of return was 9.7%6.47% for the 10 calendar years ended December 31, 2012,2015, net of all investment management fees and expenses. The value of all investments in our Company-sponsored defined benefit pension plans during the calendar year ending December 31, 2012,2015, net of investment management fees and expenses, increased 15.0%decreased 0.80%. For the past 20 years, our average annual rate of return has been 9.9%. The average annual return for the S&P 500 over the same period of time has been 8.5%7.99%. Based on the above information and forward looking assumptions for investments made in a manner consistent with our target allocations, we believe an 8.5%a 7.44% rate of return assumption is reasonable.reasonable for 2015. See Note 1315 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information on the asset allocations of pension plan assets.
On January 31, 2015, we adopted new mortality tables, including industry-based tables for annuitants, reflecting more current mortality experience and assumptions for future generational mortality improvement in calculating our projected benefit obligations as of January 30, 2016 and January 31, 2015 and our 2015 pension expense. The tables assume an improvement in life expectancy and increased our benefit obligation and future expenses. We used the RP-2000 projected to 2021 mortality table in calculating our 2013 year end pension obligation and 2014 and 2013 pension expense.
A-19
Sensitivity to changes in the major assumptions used in the calculation of Kroger’s pension plan liabilities for the qualified plans is illustrated below (in millions).
| Projected | |||||||||
| Benefit | |||||||||
| Percentage | Obligation | Expense | |||||||
| Point | Decrease/ | Decrease/ | |||||||
| Change | |||||||||
| Discount Rate | +/- 1.0% | $ | ) | $ | |||||
| Expected Return on Assets | +/- 1.0% | — | $ | ||||||
WeIn 2015, we contributed $71$5 million in 2012, $52 million in 2011 and $141 million in 2010 to our Company-sponsored defined benefit pension plans. In February 2013, we contributed $100 million to the Company-sponsored defined benefit pension plans and do not expect to make any additional contributions to these plans in 2013.2016. In 2014, we did not contribute to our Company-sponsored defined benefit plans and do not expect to make any contributions to this plan in 2015. We expect contributions made duringdid not make a contribution in 2014 and contributed $100 million in 2013 will decreaseto our required contributions in future years.Company-sponsored defined benefit pension plans. Among other things, investment performance of plan assets, the interest rates required to be used to calculate the pension obligations, and future changes in legislation, will determine the amounts of contributions.
A-18
We contributed and expensed $140$196 million in 2012, $1302015, $177 million in 2011,2014 and $119$148 million in 20102013 to employee 401(k) retirement savings accounts. The increase in 2015, compared to 2014, is due to a higher employee savings rate. The increase in 2014, compared to 2013, is due to the effect of our merger with Harris Teeter. The 401(k) retirement savings account plans provide to eligible employees both matching contributions and automatic contributions from the Company based on participant contributions, plan compensation, and length of service.
Multi-Employer Pension Plans
We also contribute to various multi-employer pension plans, including the UFCW Consolidated Pension Plan, based on obligations arising from collective bargaining agreements. We are designated as the named fiduciary of the UFCW Consolidated Pension Plan and have sole investment authority over these assets. These multi-employer pension plans provide retirement benefits to participants based on their service to contributing employers. The benefits are paid from assets held in trust for that purpose. Trustees are appointed in equal number by employers and unions. The trustees typically are responsible for determining the level of benefits to be provided to participants as well as for such matters as the investment of the assets and the administration of the plans.
In the fourth quarter of 2011, we entered into a memorandum of understanding (“MOU”) with 14 locals of the UFCW that participated in four multi-employer pension funds. The MOU established a process that amended each of the collective bargaining agreements between Kroger and the UFCW locals under which we made contributions to these funds and consolidated the four multi-employer pension funds into one multi-employer pension fund.
Under the terms of the MOU, the locals of the UFCW agreed to a future pension benefit formula through 2021. We are designated as the named fiduciary of the new consolidated pension plan with sole investment authority over the assets. We committed to contribute sufficient funds to cover the actuarial cost of current accruals and to fund the pre-consolidation Unfunded Actuarial Accrued Liability (“UAAL”) that existed as of December 31, 2011, in a series of installments on or before March 31, 2018. At January 1, 2012, the UAAL was estimated to be $911 million (pre-tax). In accordance with GAAP, we expensed $911 million in 2011 related to the UAAL. The expense was based on a preliminary estimate of the contractual commitment. In 2012, we finalized the UAAL contractual commitment and recorded an adjustment that reduced our 2011 estimated commitment by $53 million (pre-tax). The final UAAL contractual commitment, at January 1, 2012, was $858 million (pre-tax). In the fourth quarter of 2011,2015, we contributed $650$190 million to the consolidated multi-employerUFCW Consolidated Pension Plan. We had previously accrued $60 million of the total contributions at January 31, 2015 and recorded expense for the remaining $130 million at the time of payment in 2015. In 2014, we incurred a charge of $56 million (after-tax) related to commitments and withdrawal liabilities associated with the restructuring of pension plan agreements, of which $600$15 million was allocatedcontributed to the UAAL and $50 million was allocatedUFCW Consolidated Pension Plan in 2014. As of January 30, 2016, we are not required to service and interest costs and expensed in 2011. In the fourth quarter of 2012, we contributed $258 millioncontribute to the consolidated multi-employer pension plan to fully fund our UAAL contractual commitment. Future contributions will be dependent, among other things, on the investment performance of assetsUFCW Consolidated Pension Plan in the plan. The funding commitments under the MOU replace the prior commitments under the four existing funds to pay an agreed upon amount per hour worked by eligible employees.2016.
We recognize expense in connection with these plans as contributions are funded or in the case of the UFCW consolidated pension plan, when commitments are made, in accordance with GAAP. We made cash contributions to these plans of $492$426 million in 2012, $9462015, $297 million in 20112014 and $262$228 million in 2010. The cash contributions for 2012 and 2011 include our $258 million contribution in 2012 and our $650 million contribution in 2011 to the UFCW consolidated pension plan in the fourth quarter of each year.2013.
Based on the most recent information available to us, we believe that the present value of actuarially accrued liabilities in most of thesethe multi-employer plans to which we contribute substantially exceeds the value of the assets held in trust to pay benefits. We have attempted to estimate the amount by which these liabilities exceed the assets, (i.e., the amount of underfunding), as of December 31, 2012.2015. Because Kroger iswe are only one of a number of employers contributing to these plans, we also have attempted to estimate the ratio of Kroger’sour contributions to the total of all contributions to these plans in a year as a way of assessing Kroger’sour “share” of the underfunding. Nonetheless, the underfunding is not a direct obligation or liability of Krogerours or of any employer except as noted above.employer. As of December 31, 2012,2015, we estimate that Kroger’sour share of the underfunding of multi-employer plans to which Kroger contributeswe contribute was $1.8approximately $2.9 billion, pre-tax, or $1.1
A-20
$1.8 billion, after-tax.after-tax, which includes Roundy’s share of underfunding of its multi-employer plans. This represents a decreasean increase in the estimated amount of underfunding of approximately $471 million,$1.1 billion, pre-tax, or $295approximately $680 million, after-tax, as of December 31, 2012,2015, compared to December 31, 2011.2014. The decreaseincrease in the amount of underfunding is attributable to our contribution to the UFCW consolidated pension plan in 2012 and the increasedlower than expected returns on
A-19
the assets held in the multi-employer plans during 2012.2015, changes in mortality rate assumptions and the merger of Roundy’s. Our estimate is based on the most current information available to us including actuarial evaluations and other data (that include the estimates of others), and such information may be outdated or otherwise unreliable.
We have made and disclosed this estimate not because, except as noted above, this underfunding is a direct liability of Kroger.ours. Rather, we believe the underfunding is likely to have important consequences. In 2012, excluding all payments to the UFCW consolidated pension plan and the pension plans that were consolidated into the UFCW consolidated pension plan, our contributions to these plans increased approximately 5% over the prior year and have grown at a compound annual rate of approximately 7% since 2007.In 2013,2016, we expect to contribute approximately $225$260 million to our multi-employer pension plans, subject to collective bargaining and capital market conditions. This amount reflects a contribution decrease, compared to 2012, due to the UFCW consolidated pension plan. Excluding all payments to the UFCW consolidated pension plan and the pension plans that were consolidated into the UFCW consolidated pension plan, based on current market conditions,weWe expect increases in expense as a result of increases in multi-employer pension plan contributions over the next few years.Finally,years. Finally, underfunding means that, in the event we were to exit certain markets or otherwise cease making contributions to these funds, we could trigger a substantial withdrawal liability. Any adjustment for withdrawal liability will be recorded when it is probable that a liability exists and can be reasonably estimated, in accordance with GAAP.
The amount of underfunding described above is an estimate and could change based on contract negotiations, returns on the assets held in the multi-employer plans and benefit payments. The amount could decline, and Kroger’sour future expense would be favorably affected, if the values of the assets held in the trust significantly increase or if further changes occur through collective bargaining, trustee action or favorable legislation. On the other hand, Kroger’sour share of the underfunding could increase and Kroger’sour future expense could be adversely affected if the asset values decline, if employers currently contributing to these funds cease participation or if changes occur through collective bargaining, trustee action or adverse legislation. We continue to evaluate our potential exposure to under-funded multi-employer pension plans. Although these liabilities are not a direct obligation or liability of ours, any commitments to fund certain multi-employer plans will be expensed when our commitment is probable and an estimate can be made.
See Note 1416 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information relating to our participation in these multi-employer pension plans.
Deferred Rent
We recognize rent holidays, including the time period during which we have access to the property for construction of buildings or improvements, as well as construction allowances and escalating rent provisions on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease. The deferred amount is included in Other Current Liabilities and Other Long-Term Liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Uncertain Tax Positions
We review the tax positions taken or expected to be taken on tax returns to determine whether and to what extent a benefit can be recognized in our consolidated financial statements.Consolidated Financial Statements. Refer to Note 45 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for the amount of unrecognized tax benefits and other related disclosures related to uncertain tax positions.
Various taxing authorities periodically audit our income tax returns. These audits include questions regarding our tax filing positions, including the timing and amount of deductions and the allocation of income to various tax jurisdictions. In evaluating the exposures connected with these various tax filing positions, including state and local taxes, we record allowances for probable exposures. A number of years may elapse before a particular matter, for which an allowance has been established, is audited and fully resolved. As of February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, the Internal Revenue Service had concluded its field examination of our 20082010 and 20092011 federal tax returns. We have filed an administrative appeal within the Internal Revenue Service protesting certain adjustments proposed by the Internal Revenue Service as a result of their field work.Tax years 2012 and 2013 remain under examination.
The assessment of our tax position relies on the judgment of management to estimate the exposures associated with our various filing positions.
A-20
Share-Based Compensation Expense
We account for stock options under the fair value recognition provisions of GAAP. Under this method, we recognize compensation expense for all share-based payments granted. We recognize share-based compensation expense, net of an estimated forfeiture rate, over the requisite service period of the award. In addition, we record expense for restricted stock awards in an amount equal to the fair market value of the underlying stock on the grant date of the award, over the period the award restrictions lapse.
A-21
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost (principally on a LIFO basis) or market. In total, approximately 96%95% of inventories in 20122015 and 97% of inventories in 20112014 were valued using the LIFO method. Cost for the balance of the inventories, including substantially all fuel inventories, was determined using the FIFO method. Replacement cost was higher than the carrying amount by $1.1 billion at February 2, 2013, and by $1.0$1.3 billion at January 28, 2012.30, 2016 and January 31, 2015. We follow the Link-Chain, Dollar-Value LIFO method for purposes of calculating our LIFO charge or credit.
We follow the item-cost method of accounting to determine inventory cost before the LIFO adjustment for substantially all store inventories at our supermarket divisions. This method involves counting each item in inventory, assigning costs to each of these items based on the actual purchase costs (net of vendor allowances and cash discounts) of each item and recording the cost of items sold. The item-cost method of accounting allows for more accurate reporting of periodic inventory balances and enables management to more precisely manage inventory when compared to the retail method of accounting.inventory. In addition, substantially all of our inventory consists of finished goods and is recorded at actual purchase costs (net of vendor allowances and cash discounts).
We evaluate inventory shortages throughout the year based on actual physical counts in our facilities. We record allowances for inventory shortages based on the results of recent physical counts to provide for estimated shortages from the last physical count to the financial statement date.
Vendor Allowances
We recognize all vendor allowances as a reduction in merchandise costs when the related product is sold. In most cases, vendor allowances are applied to the related product cost by item, and therefore reduce the carrying value of inventory by item. When it is not practicable to allocate vendor allowances to the product by item, we recognize vendor allowances as a reduction in merchandise costs based on inventory turns and as the product is sold. We recognized approximately $7.3 billion in 2015, $6.9 billion in 2014 and $6.2 billion in 2012, $5.9 billion in 2011, and $6.4 billion in 20102013 of vendor allowances as a reduction in merchandise costs. We recognized approximately 95%91% of all vendor allowances in the item cost with the remainder being based on inventory turns.
Recently Adopted Accounting StandardsRECENTLY ADOPTED ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
In June 2011,2015, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) amended its rules regardingAccounting Standards Codification 835, “Interest-Imputation of Interest.” The amendment simplifies the presentation of comprehensive income.debt issuance costs related to a recognized debt liability by requiring it be presented in the balance sheet as a direct deduction from the carrying amount of that debt liability, consistent with debt discounts. This amendment became effective beginning February 1, 2015, and was adopted retrospectively in accordance with the standard. The objectiveadoption of this amendment resulted in amounts previously reported in other assets to now be reported within long-term debt including obligations under capital leases and financing obligations in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. These amounts were not material to the prior year. The adoption of this amendment did not have an effect on our Consolidated Statements of Operations.
RECENTLY ISSUED ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
In May 2014, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers,” which provides guidance for revenue recognition. The standard’s core principle is that a company will recognize revenue when it transfers promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. Per ASU 2015-14, “Deferral of Effective Date,” this guidance will be effective for us in the first quarter of our fiscal year ending February 2, 2019. Early adoption is permitted as of the first quarter of our fiscal year ending February 3, 2018. We are currently in the process of evaluating the effect of adoption of this ASU on our Consolidated Financial Statements.
A-22
In April 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-04, “Retirement Benefits (Topic 715): Practical Expedient for the Measurement Date of an Employer’s Defined Benefit Obligation and Plan Assets.” This amendment permits an entity to measure defined benefit plan assets and obligations using the month end that is closest to the entity’s fiscal year end for all plans. This guidance will be effective for us in the fiscal year ending January 28, 2017. The implementation of this amendment will not have an effect on our Consolidated Statements of Operations, and will not have a significant effect on our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
In April 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-07, “Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosures for Investments in Certain Entities That Calculate Net Asset Value per Share (or Its Equivalent).” This amendment removes the requirement to categorize within the fair value hierarchy all investments for which fair value is measured using the net asset value per share. This guidance will be effective for us in the fiscal year ending January 28, 2017. The implementation of this amendment will have an effect on our Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements and will not have an effect on our Consolidated Statements of Operations or Consolidated Balance Sheets.
In September 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-16, “Business Combinations (Topic 805): Simplifying the Accounting for Measurement-Period Adjustments.” This amendment eliminates the requirement to retrospectively account for adjustments made to provisional amounts recognized in a business combination. This guidance will be effective for us in the fiscal year ending January 28, 2017. The implementation of this amendment is not expected to improvehave a significant effect on our Consolidated Financial Statements.
In November 2015, the comparability, consistencyFASB issued ASU 2015-17, “Income Taxes (Topic 740): Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes.” This amendment requires deferred tax liabilities and transparencyassets be classified as noncurrent in a classified statement of financial reporting and to increase the prominenceposition. This guidance will be effective for our fiscal year ending January 28, 2017. Early adoption is permitted. The implementation of items reported in other comprehensive income. Specifically, this amendment requires that all non-owner changes in shareholders’ equity be presented either in a single continuous statement of comprehensive income or in two separate but consecutive statements. The new rules became effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2011. In December 2011, the FASB deferred certain aspects of this standard beyond the December 15, 2011 effective date, specifically the provisions dealing with reclassification adjustments. We adopted these amended standards effective January 29, 2012 by presenting separatewill not have an effect on our Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income immediately following theOperations and will not have a significant effect on our Consolidated Statements of Operations.Balance Sheets.
In May 2011,February 2016, the FASB amendedissued ASU 2016-02, “Leases”, which provides guidance for the recognition of lease agreements. The standard’s core principle is that a company will now recognize most leases on its rules for disclosure requirements for common fair value measurement. These amendments,balance sheet as lease liabilities with corresponding right-of-use assets. This guidance will be effective for us in the interim and annual periods beginning on or after December 15, 2011 (earlyfirst quarter of fiscal year ending February 1, 2020. Early adoption was prohibited),is permitted. The adoption of this ASU will result in a common definitionsignificant increase to our Consolidated Balance Sheets for lease liabilities and right-of-use assets, and we are currently evaluating the other effects of fair value and common requirements for fair value measurement and disclosure between GAAP and Internationaladoption of this ASU on our Consolidated Financial Accounting Standards.Statements. We believe our current off-balance sheet leasing commitments are reflected in our investment grade debt rating.
A-21LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Consequently, the amendments change some fair value measurement principles and disclosure requirements. The implementation of the amended accounting guidance did not have a material effect on our consolidated financial position or results of operations.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
As discussed above under Recently Adopted Accounting Standards, in December 2011 the FASB deferred certain provisions of its 2011 rule amendments dealing with reclassification adjustments. In February 2013, the FASB amended its standards on comprehensive income by requiring disclosure in the footnotes of information about amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by component. Specifically, the amendment will require disclosure of the line items of net income in which the item was reclassified only if it is reclassified to net income in its entirety in the same reporting period. It will also require cross reference to other disclosures for amounts that are not reclassified in their entirety in the same reporting period. The new disclosures will be required for us prospectively only for annual periods beginning February 3, 2013 and interim periods within those annual periods.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Cash Flow Information
Net cash provided by operating activities
We generated $2.8$4.8 billion of cash from operations in 2012,2015, compared to $2.7$4.2 billion in 20112014 and $3.4$3.6 billion in 2010.2013. The cash provided by operating activities came from net earnings including non-controlling interests adjusted primarily for non-cash expenses of depreciation and amortization, stock compensation, expense for Company-sponsored pension plans, the LIFO charge and changes in working capital.
The increase in net cash provided by operating activities in 2012,2015, compared to 2011,2014, resulted primarily due to an increase in net earnings including non-controlling interests, offset by a declinean increase in long-term liabilitiesnon-cash items and changes in working capital. The declineincrease in long-term liabilitiesnon-cash items in 2012 is2015, as compared to 2014, was primarily due to the investment returns of ourincreases in depreciation and amortization expense and expense for Company-sponsored pension plans, during the year and our funding of the remaining UAAL commitment, partially offset by a lower discount rate on our Company-sponsored pension plans. LIFO charge.
A-23
The decreaseincrease in net cash provided by operating activities in 2011,2014, compared to 2010, was2013, resulted primarily due to the declinean increase in net earnings including non-controlling interests, duewhich include the results of Harris Teeter, an increase in non-cash items, a reduction in contributions to the UFCW consolidatedCompany-sponsored pension plan charge,plans and changes in working capital, offset by an increase in long-term liabilities.capital. The increase in long-term liabilitiesnon-cash items in 2011 was due to establishing a liability for our remaining estimated commitment for the UAAL in excess of the cash contribution and a lower discount rate on our Company-sponsored pension plans, offset by the investment returns of our Company-sponsored pension plans during the year. Changes in working capital also provided (used) cash from operating activities of ($332) million in 2012,2014, as compared to ($300) million in 2011 and $698 million in 2010. The decrease in cash provided by changes in working capital for 2012, compared to 2011,2013, was primarily due to an increase in inventories and prepaid expenses, offset partially by an increase in accrued expenses. Prepaid expenses increased in 2012, compared to 2011, due to Kroger prefunding $250 million of employee benefits at the end of 2012. The decrease in cash provided by changes in working capital for 2011, compared to 2010, was primarily due to an increase in inventories, offset partially by increases in trade accounts payabledepreciation and accrued expenses. These amounts are also net of cash contributions to our Company-sponsored defined benefit pension plans totaling $71 million in 2012, $52 million in 2011amortization expense and $141 million in 2010.
the LIFO charge. The amount of cash paid for income taxes increased in 2012,2014, compared to 2011,2013, primarily due to an increase in net earnings including non-controlling interests. The amount of cash paid
Cash provided (used) by operating activities for income taxes decreasedchanges in 2011,working capital was $96 million in 2015, compared to 2010,($49) million in 2014 and $63 million in 2013. The increase in cash provided by operating activities for changes in working capital in 2015, compared to 2014, was primarily due to an increase in cash provided by trade accounts payables and store deposits in transit, partially offset by a decrease in net earnings including non-controlling interestscash provided by income taxes receivable and from the bonus depreciation deductions allowedpayable. The increase in cash used by the 2010 Tax Relief Actoperating activities for property placed into servicechanges in 2011.working capital in 2014, compared to 2013, was primarily due to an increase in cash used for receivables and a decrease in cash provided by trade accounts payables, partially offset by an increase in cash provided by accrued expenses.
A-22
Net cash used by investing activities
Cash used by investing activities was $2.2$3.6 billion in 2012,2015, compared to $1.9$3.1 billion in 20112014 and $2.0$4.8 billion in 2010.2013. The amount of cash used by investing activities increased in 2012,2015, compared to 2011,2014, due to increased payments for capital investments, and acquisitions.partially offset by lower payments for mergers. The amount of cash used by investing activities decreased in 2011,2014, compared to 2010,2013, due to decreased payments for other investing activities,mergers, offset partiallyprimarily by increased payments for acquisitions.capital investments. Capital investments, including changes in construction-in-progress payables andpayments for lease buyouts, but excluding acquisitions,mergers, were $2.1$3.3 billion in 2012, $2.02015, $2.8 billion in 20112014 and $1.9$2.3 billion in 2010.2013. Merger payments were $168 million in 2015, $252 million in 2014 and $2.3 billion in 2013. Merger payments decreased in 2014, compared to 2013, primarily due to our merger with Harris Teeter in 2013. Refer to the Capital Investment“Capital Investments” section for an overview of our supermarket storing activity during the last three years.
Net cash usedprovided (used) by financing activities
Financing activities used $600 million(used) provided cash of cash($1.3) billion in 2012, compared to2015, ($1.2) billion in 2014 and $1.4 billion in 2011 and $1.0 billion in 2010. The decrease in the amount of cash used for financing activities in 2012, compared to 2011, was primarily related to increased proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt and net borrowings from our commercial paper program, offset partially by payments on long-term debt.2013. The increase in the amount of cash used for financing activities in 2011,2015, compared to 2010,2014, was primarily related to increased payments on long-term debt and commercial paper, partially offset by higher proceeds from issuances of long-term debt and decreased treasury stock purchases. The increase in the amount of cash used for financing activities in 2014, compared to 2013, was primarily related to decreased proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt and increased treasury stock purchases, offset partially offset by increaseddecreased payments on long-term debt. Proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt were $1.2 billion in 2015, $576 million in 2014 and $3.5 billion in 2013. Net (payments) borrowings underprovided from our commercial paper program.program were ($285) million in 2015, $25 million in 2014 and ($395) million in 2013. Please refer to the “Debt Management” section of MD&A for additional information. We repurchased $1.3 billion$703 million of Kroger common shares in 2012,2015, compared to $1.5$1.3 billion in 20112014 and $545$609 million in 2010.2013. We paid dividends totaling $267$385 million in 2012, $2572015, $338 million in 20112014 and $250$319 million in 2010.2013.
Debt Management
Total debt, including both the current and long-term portions of capital leaseslease and lease-financing obligations, increased $714$481 million to $8.9$12.1 billion as of year-end 2012,2015, compared to 2011.2014. The increase in 2012,2015, compared to 2011,2014, resulted primarily from increased borrowings of $1.3 billion of commercial paper supported by our credit facility and the issuance of (i) $500$300 million of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 3.4% and2.00%, (ii) $350$300 million of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 5.0%2.60%, offset partially by payments at maturity of (i) $491 million of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 6.75%, (ii) $346 million of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 6.2% and (iii) $500 million of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 5.5%. This3.50% and (iv) an increase was primarilyin capital lease obligations due to our $258merger with Roundy’s and various leased locations, partially offset by payments of $678 million UFCW consolidated pension plan contribution in the fourth quarteron long-term debt obligations assumed as part of 2012, prefunding $250our merger with Roundy’s and $500 million of employee benefit costspayments at maturity of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 3.90%. The increase in financing obligations was due to partially funding our merger with Roundy’s.
A-24
Total debt, including both the endcurrent and long-term portions of 2012, our common share repurchase activity duringcapital lease and lease-financing obligations increased $346 million to $11.7 billion as of year-end 2014, compared to 2013. The increase in 2014, compared to 2013, resulted primarily from (i) the year, the payment at maturityissuance of $500 million of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 5.5%2.95% and the purchase of a specialty pharmacy. Total debt increased $273 million to $8.2 billion as of year-end 2011, compared to year-end 2010. The(ii) an increase in 2011, compared to 2010, resulted from increased net borrowings of commercial paper of $370$25 million, and the issuancepartially offset by payments at maturity of $450$300 million of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 2.20%, offset by the payment at maturity of4.95%. The increase in financing obligations was due to partially funding our $478 million of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 6.80%.outstanding common share repurchases.
In 2013, we expect to refinance $1.5 billion of debt. We plan on refinancing our debt maturities in 2013 along with an additional issuance of approximately $500 million to replace the senior notes bearing an interest rate of 5.5% that matured in the fourth quarter of 2012. The debt that matured in the fourth quarter of 2012 was previously refinanced with commercial paper. We have entered into $850 million notional amount of forward starting interest rate swaps to effectively hedge the changes in future benchmark interest rates on a portion of our expected issuances of fixed rate debt.
Liquidity Needs
We estimate our liquidity needs over the next twelve-month period to be approximately $5range from $6.6 to $6.9 billion, which includes anticipated requirements for working capital, capital expenditures,investments, interest payments and scheduled principal payments of debt and commercial paper, offset by cash and temporary cash investments on hand at the end of 2012.2015. We generally operate with a working capital deficit due to our efficient use of cash in funding operations and because we have consistent access to the capital markets. Based on current operating trends, we believe that cash flows from operating activities and other sources of liquidity, including borrowings under our commercial paper program and bank credit facility, will be adequate to meet our liquidity needs for the next twelve months and for the foreseeable future beyond the next twelve months. We have approximately $1.6 billion$990 million of commercial paper and $1.0$1.3 billion of senior notes maturing in the next twelve months, which is included in the $5range of $6.6 to $6.9 billion in estimated liquidity needs. We expect to refinance this debt, in 2016, by issuing additional senior notes or commercial paper on favorable
A-23
terms based on our past experience. $2.0 billion of this debt matures in the first quarter of 2013. In the first quarter of 2013, we anticipate refinancing this $2.0 billion through cash flows from operating activities and by issuing $1.0 billion to $1.2 billion of additional senior notes. We also currently do not expectplan to repurchase ourcontinue repurchases of common shares atunder the levels we did in 2012. We used our commercial paper program toward the end of 2012 to fund our commonCompany’s share repurchases, a $250 million (pre-tax) pre-funding of employee benefit costs at the end of 2012, a $258 million UFCW consolidated pension plan contribution in the fourth quarter of 2012 and the payment at maturity of $500 of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 5.5%. We also expect our contributions to the UFCW consolidated pension plan to decrease in future periods. We may use our commercial paper program to fund debt maturities at the end of 2013 but do not currently expect to use the program permanently.repurchase programs. We believe we have adequate coverage of our debt covenants to continue to maintain our current debt ratings and to respond effectively to competitive conditions.
Factors Affecting Liquidity
We can currently borrow on a daily basis approximately $2$2.75 billion under our commercial paper (“CP”) program. At February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, we had $1.6 billion$990 million of CP borrowings outstanding. CP borrowings are backed by our credit facility, and reduce the amount we can borrow under the credit facility. If our short-term credit ratings fall, the ability to borrow under our current CP program could be adversely affected for a period of time and increase our interest cost on daily borrowings under our CP program. This could require us to borrow additional funds under the credit facility, under which we believe we have sufficient capacity. However, in the event of a ratings decline, we do not anticipate that our borrowing capacity under our CP program would be any lower than $500 million on a daily basis. Although our ability to borrow under the credit facility is not affected by our credit rating, the interest cost on borrowings under the credit facility could be affected by an increase in our Leverage Ratio. As of March 29, 2013,23, 2016, we had $1.1 billion of CP borrowings outstanding. The decreaseincrease as of March 29, 2013,23, 2016, compared to year-end 2012,2015, was due to applying cash from operations againstpartially funding our year-end CP outstanding borrowings.common share repurchases.
Our credit facility requires the maintenance of a Leverage Ratio and a Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio (our “financial covenants”). A failure to maintain our financial covenants would impair our ability to borrow under the credit facility. These financial covenants and ratios are described below:
| ● | Our Leverage Ratio (the ratio of Net Debt to Consolidated EBITDA, as defined in the credit facility) was 1.97 to 1 as of January 30, 2016. If this ratio were to exceed 3.50 to 1, we would be in default of our credit facility and our ability to borrow under the facility would be impaired. In addition, our Applicable Margin on borrowings is determined by our Leverage Ratio. |
| ● | Our Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio (the ratio of Consolidated EBITDA plus Consolidated Rental Expense to Consolidated Cash Interest Expense plus Consolidated Rental Expense, as defined in the credit facility) was 5.30 to 1 as of January 30, 2016. If this ratio fell below 1.70 to 1, we would be in default of our credit facility and our ability to borrow under the facility would be impaired. |
Consolidated EBITDA, as defined in our credit facility, includes an adjustment for unusual gains and losses including our UFCW consolidated pension plan liability adjustment in 2012. Our credit agreement is more fully described in Note 56 to the Consolidated Financial Statements. We were in compliance with our financial covenants at year-end 2012.2015.
A-24A-25
The tables below illustrate our significant contractual obligations and other commercial commitments, based on year of maturity or settlement, as of February 2, 2013January 30, 2016 (in millions of dollars):
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | Thereafter | Total | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | Thereafter | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligations(1) (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt (3) | $ | 2,700 | $ | 320 | $ | 517 | $ | 463 | $ | 607 | $ | 3,869 | $ | 8,476 | $ | 2,318 | $ | 735 | $ | 1,307 | $ | 774 | $ | 724 | $ | 5,538 | $ | 11,396 | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest on long-term debt (4) | 360 | 318 | 297 | 284 | 257 | 2,422 | 3,938 | 476 | 410 | 375 | 315 | 279 | 2,550 | 4,405 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital lease obligations | 51 | 47 | 42 | 39 | 38 | 232 | 449 | 103 | 72 | 62 | 57 | 52 | 527 | 873 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating lease obligations | 707 | 663 | 601 | 540 | 467 | 2,025 | 5,003 | 967 | 922 | 853 | 774 | 674 | 4,199 | 8,389 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Low-income housing obligations | 6 | 1 | — | — | — | — | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financed lease obligations | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 116 | 181 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 74 | 139 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Self-insurance liability (5) | 205 | 126 | 84 | 54 | 25 | 43 | 537 | 223 | 138 | 98 | 63 | 38 | 79 | 639 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction commitments | 230 | — | — | — | — | — | 230 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Purchase obligations | 500 | 76 | 45 | 34 | 28 | 68 | 751 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction commitments(6) | 418 | — | — | — | — | — | 418 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Purchase obligations(7) | 532 | 161 | 77 | 58 | 42 | 106 | 976 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 4,772 | $ | 1,564 | $ | 1,599 | $ | 1,427 | $ | 1,435 | $ | 8,775 | $ | 19,572 | $ | 5,050 | $ | 2,451 | $ | 2,786 | $ | 2,054 | $ | 1,822 | $ | 13,072 | $ | 27,235 | |||||||||||||||||
| Other Commercial Commitments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standby letters of credit | $ | 148 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 148 | $ | 244 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 244 | |||||||||||||||||
| Surety bonds | 294 | — | — | — | — | — | 294 | 332 | — | — | — | — | — | 332 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Guarantees | 6 | — | — | — | — | — | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 448 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 448 | $ | 576 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 576 | |||||||||||||||||
| (1) | The contractual obligations table excludes funding of pension and other postretirement benefit obligations, which totaled approximately | |
| (2) | The liability related to unrecognized tax benefits has been excluded from the contractual obligations table because a reasonable estimate of the timing of future tax settlements cannot be determined. | |
| (3) | As of | |
| (4) | Amounts include contractual interest payments using the interest rate as of | |
| (5) | The amounts included in the contractual obligations table for self-insurance liability related to workers’ compensation claims have been stated on a present value basis. | |
| (6) | Amounts include funds owed to third parties for projects currently under construction. These amounts are reflected in other current liabilities in our Consolidated Balance Sheets. | |
| (7) | Amounts include commitments, many of which are short-term in nature, to be utilized in the normal course of business, such as several contracts to purchase raw materials utilized in our food production plants and several contracts to purchase energy to be used in our stores and food production plants. Our obligations also include management fees for facilities operated by third parties and outside service contracts. Any upfront vendor allowances or incentives associated with outstanding purchase commitments are recorded as either current or long-term liabilities in our Consolidated Balance Sheets. | |
Our construction commitments include funds owed to third parties for projects currently under construction. These amounts are reflected in other current liabilities in our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Our purchase obligations include commitments to be utilized in the normal course of business, such as several contracts to purchase raw materials utilized in our manufacturing plants and several contracts to purchase energy to be used in our stores and manufacturing facilities. Our obligations also include management fees for facilities operated by third parties. Any upfront vendor allowances or incentives associated with outstanding purchase commitments are recorded as either current or long-term liabilities in our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
As of February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, we maintained a $2$2.75 billion (with the ability to increase by $500$750 million), unsecured revolving credit facility that, unless extended, terminates on January 25, 2017.June 30, 2019. Outstanding borrowings under the credit agreement and commercial paper borrowings, and some outstanding letters of credit, reduce funds available under the credit agreement. In addition to the credit agreement, we maintained two uncommitted money market lines totaling $75 million in the aggregate. The money market lines allow us to borrow from banks at mutually agreed upon rates, usually at rates below the rates offered under the credit agreement. As of
A-25
February 2, 2013, January 30, 2016, we had $1.6 billion$990 million of borrowings of commercial paper and no borrowings under our credit agreement and money market lines.agreement. The outstanding letters of credit that reduce funds available under our credit agreement totaled $13 million as of February 2, 2013.January 30, 2016.
A-26
In addition to the available credit mentioned above, as of February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, we had authorized for issuance $700$900 million of securities under a shelf registration statement filed with the SEC and effective on December 15, 2010. On January 18, 2013, the Board of Directors authorized for issuance additional securities in the amount of $1.8 billion over and above the $700 million of securities available for issuance as of February 2,13, 2013. Subsequent to year-end, we filed a Current Report on Form 8-K, on February 11, 2013, incorporating by reference additional exhibits to the shelf registration statement including the Board of Directors’ resolution.
We also maintain surety bonds related primarily to our self-insured workers’ compensation claims. These bonds are required by most states in which we are self-insured for workers’ compensation and are placed with predominately third-party insurance providers to insure payment of our obligations in the event we are unable to meet our claim payment obligations up to our self-insured retention levels. These bonds do not represent liabilities of Kroger,ours, as we already have reserves on our books for the claims costs. Market changes may make the surety bonds more costly and, in some instances, availability of these bonds may become more limited, which could affect our costs of, or access to, such bonds. Although we do not believe increased costs or decreased availability would significantly affect our ability to access these surety bonds, if this does become an issue, we would issue letters of credit, in states where allowed, against our credit facility to meet the state bonding requirements. This could increase our cost and decrease the funds available under our credit facility.
We have guaranteed half of the indebtedness of two real estate entities in which we have a 50% ownership interest. Our share of the responsibility for this indebtedness, should the entities be unable to meet their obligations, totals approximately $6 million. Based on the covenants underlying this indebtedness as of February 2, 2013, we believe that it is unlikely that we will be responsible for repayment of these obligations.
We also are contingently liable for leases that have been assigned to various third parties in connection with facility closings and dispositions. We could be required to satisfy obligations under the leases if any of the assignees are unable to fulfill their lease obligations. Due to the wide distribution of our assignments among third parties, and various other remedies available to us, we believe the likelihood that we will be required to assume a material amount of these obligations is remote. We have agreed to indemnify certain third-party logistics operators for certain expenses, including pension trust fund contribution obligations and withdrawal liabilities.
In addition to the above, we enter into various indemnification agreements and take on indemnification obligations in the ordinary course of business. Such arrangements include indemnities against third party claims arising out of agreements to provide services to Kroger;us; indemnities related to the sale of our securities; indemnities of directors, officers and employees in connection with the performance of their work; and indemnities of individuals serving as fiduciaries on benefit plans. While Kroger’sour aggregate indemnification obligation could result in a material liability, we are not aware of any current matter that could result in a material liability.
OutlookOUTLOOK
This discussion and analysis contains certain forward-looking statements about Kroger’sour future performance. These statements are based on management’s assumptions and beliefs in light of the information currently available.available to it. Such statements relate to, among other things: projected changes in net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co.; identical supermarket sales growth; expected product cost; expected pension plan contributions; our ability to generate operating cash flows; projected capital expenditures; square footage growth; opportunities to reduce costs; cash flow requirements; and our operating plan for the future; and are indicated by words such as “comfortable,” “committed,” “will,” “expect,” “goal,” “should,” “intend,” “target,” “believe,” “anticipate,” “plan,” and similar words or phrases. These forward-looking statements are subject to uncertainties and other factors that could cause actual results to differ materially.
A-26
Statements elsewhere in this report and below regarding our expectations, projections, beliefs, intentions or strategies are forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. While we believe that the statements are accurate, uncertainties about the general economy, our labor relations, our ability to execute our plans on a timely basis and other uncertainties described below could cause actual results to differ materially.
| ● | We expect net earnings to be $2.19 to $2.28 per diluted share, which is essentially in line with our long-term net earnings per diluted share growth rate of 8% - 11%. Where we fall within the range will be primarily driven by actual fuel margins, which we expect to be at or slightly below the five-year average, with continued volatility. We expect our core business in 2016 to grow in line with our long-term net earnings per diluted share growth rate of 8% – 11%. |
| ● | We expect identical supermarket sales growth, excluding fuel sales, of 2.5%-3.5% in 2016, reflecting the lower inflationary environment. |
| ● | We expect full-year FIFO operating margin in 2016, excluding fuel, to expand slightly compared to 2015 results. |
A-27
next few years, excluding acquisitions and purchases of leased facilities, to accomplish
| ● | We expect capital investments, excluding mergers, acquisitions and purchases of leased facilities, to be $4.1 to $4.4 billion. These capital investments include approximately 100 major projects covering new stores, expansions and relocations, including 10 Ruler locations; 200 to 220 major remodels; and other investments including minor remodels and technology and infrastructure to support our Customer 1st business strategy.
|
| ● | We expect total supermarket square footage for 2016 to grow approximately 3.0% - 3.5% before mergers, acquisitions and operational closings. |
| ● | We expect 2016 year-end ROIC to increase slightly compared to the 2015 result. |
| ● | We expect the 2016 effective tax rate to be approximately 35%, excluding the resolution of certain tax items. |
| ● | In 2016, we anticipate annualized product cost inflation of 1.0% to 2.0%, excluding fuel, and an annualized LIFO charge of approximately $50 million. We expect inflation to be lower during the earlier portion of 2016 and to gradually rise during the later portion of 2016. |
| ● | We expect 2016 Company-sponsored pension plans expense to be approximately $80 million. We do not expect to make a cash contribution in 2016. |
| ● | In 2016, we expect to contribute approximately $260 million to multi-employer pension funds. We continue to evaluate and address our potential exposure to under-funded multi-employer pension plans. Although these liabilities are not a direct obligation or liability of Kroger, any new agreements that would commit us to fund certain multi-employer plans will be expensed when our commitment is probable and an estimate can be made. |
| ● | In 2016, we will negotiate agreements with UFCW for store associates in Houston, Indianapolis, Little Rock, Nashville, Portland, Southern California and Fry’s in Arizona. Negotiations this year will be challenging as we must have competitive cost structures in each market while meeting our associates’ needs for solid wages and good quality, affordable health care and retirement benefits. |
Various uncertainties and other factors could cause usactual results to fail to achieve our goals.differ materially from those contained in the forward-looking statements. These include:
| ● | The extent to which our sources of liquidity are sufficient to meet our requirements may be affected by the state of the financial markets and the effect that such condition has on our ability to issue commercial paper at acceptable rates. Our ability to borrow under our committed lines of credit, including our bank credit facilities, could be impaired if one or more of our lenders under those lines is unwilling or unable to honor its contractual obligation to lend to us, or in the event that natural disasters or weather conditions interfere with the ability of our lenders to lend to us. Our ability to refinance maturing debt may be affected by the state of the financial markets. |
| ● | Our ability to achieve sales, earnings and cash flow goals may be affected by: labor negotiations or disputes; changes in the types and numbers of businesses that compete with us; pricing and promotional activities of existing and new competitors, including non-traditional competitors, and the aggressiveness of that competition; our response to these actions; the state of the economy, including interest rates, the inflationary and deflationary trends in certain commodities, and the unemployment rate; the effect that fuel costs have on consumer spending; volatility of fuel margins; changes in government-funded benefit programs; manufacturing commodity costs; diesel fuel costs related to our logistics operations; trends in consumer spending; the extent to which our customers exercise caution in their purchasing in response to economic conditions; the inconsistent pace of the economic recovery; changes in inflation or deflation in product and operating costs; stock repurchases; our ability to retain pharmacy sales from third party payors; consolidation in the healthcare industry, including pharmacy benefit managers; our ability to negotiate modifications to multi-employer pension plans; natural disasters or adverse weather conditions; the potential costs and risks associated with potential cyber-attacks or data security breaches; the success of our future growth plans; and the successful integration of Harris Teeter and Roundy’s. Our ability to achieve sales and earnings goals may also be affected by our ability to manage the factors identified above. Our ability to execute our financial strategy may be affected by our ability to generate cash flow. |
A-29A-28
| ● | During the first three quarters of each fiscal year, our LIFO charge and the recognition of LIFO expense is affected primarily by estimated year-end changes in product costs. Our fiscal year LIFO charge is affected primarily by changes in product costs at year-end. |
| ● | If actual results differ significantly from anticipated future results for certain reporting units including variable interest entities, an impairment loss for any excess of the carrying value of the reporting units’ goodwill over the implied fair value would have to be recognized. |
| ● | Our effective tax rate may differ from the expected rate due to changes in laws, the status of pending items with various taxing authorities, and the deductibility of certain expenses. |
| ● | Changes in our product mix may negatively affect certain financial indicators. For example, we continue to add supermarket fuel centers to our store base. Since fuel generates lower profit margins than our supermarket sales, we expect to see our FIFO gross margins decline as fuel sales increase. |
A-30
We cannot fully foresee the effects of changes in economic conditions on Kroger’s business. We have assumed economic and competitive situations will not change significantly in 2013.2016.
Other factors and assumptions not identified above could also cause actual results to differ materially from those set forth in the forward-looking information. Accordingly, actual events and results may vary significantly from those included in, contemplated or implied by forward-looking statements made by us or our representatives. We undertake no obligation to update the forward-looking information contained in this filing.
A-31A-29
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting FirmREPORTOF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the ShareownersShareholders and Board of Directors of
The Kroger Co.
In our opinion, the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, cash flows and changes in shareowners’shareholders’ equitypresent fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of The Kroger Co. and its subsidiariesat February 2, 2013January 30, 2016 and January 28, 2012,31, 2015, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended February 2, 2013 January 30, 2016in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, based on criteria established inInternal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting appearing on page A-1. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements and on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
As described in Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting, management has excluded Roundy’s, Inc. from its assessment of internal control over financial reporting as of January 30, 2016 because it was acquired by the Company in a purchase business combination on December 18, 2015. We have also excluded Roundy’s, Inc. from our audit of internal control over financial reporting. Roundy’s, Inc. is a wholly-owned subsidiary whose total assets and total revenues represent 2% and less than 1%, respectively, of the related consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the year ended January 30, 2016.
Cincinnati, OhioApril 2, 2013March 29, 2016
A-30
THE KROGER CO.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| (In millions, except par values) | January 30, 2016 | January 31, 2015 | ||||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||||||
| Current assets | ||||||||||||
| Cash and temporary cash investments | $ | 277 | $ | 268 | ||||||||
| Store deposits in-transit | 923 | 988 | ||||||||||
| Receivables | 1,734 | 1,266 | ||||||||||
| FIFO inventory | 7,440 | 6,933 | ||||||||||
| LIFO reserve | (1,272 | ) | (1,245 | ) | ||||||||
| Prepaid and other current assets | 790 | 701 | ||||||||||
| Total current assets | 9,892 | 8,911 | ||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 19,619 | 17,912 | ||||||||||
| Intangibles, net | 1,053 | 757 | ||||||||||
| Goodwill | 2,724 | 2,304 | ||||||||||
| Other assets | 609 | 613 | ||||||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 33,897 | $ | 30,497 | ||||||||
| LIABILITIES | ||||||||||||
| Current liabilities | ||||||||||||
| Current portion of long-term debt including obligations under capital leases and | ||||||||||||
| financing obligations | $ | 2,370 | $ | 1,874 | ||||||||
| Trade accounts payable | 5,728 | 5,052 | ||||||||||
| Accrued salaries and wages | 1,426 | 1,291 | ||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 221 | 287 | ||||||||||
| Other current liabilities | 3,226 | 2,888 | ||||||||||
| Total current liabilities | 12,971 | 11,392 | ||||||||||
| Long-term debt including obligations under capital leases and financing obligations | ||||||||||||
| Face-value of long-term debt including obligations under capital leases and | ||||||||||||
| financing obligations | 9,708 | 9,723 | ||||||||||
| Adjustment to reflect fair-value interest rate hedges | 1 | — | ||||||||||
| Long-term debt including obligations under capital leases and | ||||||||||||
| financing obligations | 9,709 | 9,723 | ||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 1,752 | 1,209 | ||||||||||
| Pension and postretirement benefit obligations | 1,380 | 1,463 | ||||||||||
| Other long-term liabilities | 1,287 | 1,268 | ||||||||||
| Total Liabilities | 27,099 | 25,055 | ||||||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (see Note 13) | ||||||||||||
| SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||||||
| Preferred shares, $100 par per share, 5 shares authorized and unissued | — | — | ||||||||||
| Common shares, $1 par per share, 2,000 shares authorized; | ||||||||||||
| 1,918 shares issued in 2015 and 2014 | 1,918 | 1,918 | ||||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 2,980 | 2,748 | ||||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (680 | ) | (812 | ) | ||||||||
| Accumulated earnings | 14,011 | 12,367 | ||||||||||
| Common stock in treasury, at cost, 951 shares in 2015 and 944 shares in 2014 | (11,409 | ) | (10,809 | ) | ||||||||
| Total Shareholders’ Equity - The Kroger Co. | 6,820 | 5,412 | ||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interests | (22 | ) | 30 | |||||||||
| Total Equity | 6,798 | 5,442 | ||||||||||
| Total Liabilities and Equity | $ | 33,897 | $ | 30,497 | ||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
A-31
THE KROGER CO.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTSOF OPERATIONS
Years Ended January 30, 2016, January 31, 2015 and February 1, 2014
| (In millions, except per share amounts) | 2015 (52 weeks) | 2014 (52 weeks) | 2013 (52 weeks) | ||||||||||||
| Sales | $ | 109,830 | $ | 108,465 | $ | 98,375 | |||||||||
| Merchandise costs, including advertising, warehousing, and | |||||||||||||||
| transportation, excluding items shown separately below | 85,496 | 85,512 | 78,138 | ||||||||||||
| Operating, general and administrative | 17,946 | 17,161 | 15,196 | ||||||||||||
| Rent | 723 | 707 | 613 | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,089 | 1,948 | 1,703 | ||||||||||||
| Operating Profit | 3,576 | 3,137 | 2,725 | ||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 482 | 488 | 443 | ||||||||||||
| Earnings before income tax expense | 3,094 | 2,649 | 2,282 | ||||||||||||
| Income tax expense | 1,045 | 902 | 751 | ||||||||||||
| Net earnings including noncontrolling interests | 2,049 | 1,747 | 1,531 | ||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interests | 10 | 19 | 12 | ||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. | $ | 2,039 | $ | 1,728 | $ | 1,519 | |||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per basic common share | $ | 2.09 | $ | 1.74 | $ | 1.47 | |||||||||
| Average number of common shares used in basic calculation | 966 | 981 | 1,028 | ||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per diluted common share | $ | 2.06 | $ | 1.72 | $ | 1.45 | |||||||||
| Average number of common shares used in diluted calculation | 980 | 993 | 1,040 | ||||||||||||
| Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.408 | $ | 0.350 | $ | 0.315 | |||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
A-32
THE KROGER CO.
Consolidated Balance SheetsCONSOLIDATED STATEMENTSOF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
| February 2, | January 28, | |||||||||
| (In millions, except par values) | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||||
| Current assets | ||||||||||
| Cash and temporary cash investments | $ | 238 | $ | 188 | ||||||
| Deposits in-transit | 955 | 786 | ||||||||
| Receivables | 1,051 | 949 | ||||||||
| FIFO inventory | 6,244 | 6,157 | ||||||||
| LIFO reserve | (1,098 | ) | (1,043 | ) | ||||||
| Prepaid and other current assets | 569 | 288 | ||||||||
| Total current assets | 7,959 | 7,325 | ||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 14,875 | 14,464 | ||||||||
| Goodwill | 1,234 | 1,138 | ||||||||
| Other assets | 584 | 549 | ||||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 24,652 | $ | 23,476 | ||||||
| LIABILITIES | ||||||||||
| Current liabilities | ||||||||||
| Current portion of long-term debt including obligations under capital leases | ||||||||||
| and financing obligations | $ | 2,734 | $ | 1,315 | ||||||
| Trade accounts payable | 4,524 | 4,329 | ||||||||
| Accrued salaries and wages | 977 | 1,056 | ||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 284 | 190 | ||||||||
| Other current liabilities | 2,538 | 2,215 | ||||||||
| Total current liabilities | 11,057 | 9,105 | ||||||||
| Long-term debt including obligations under capital leases and financing obligations | ||||||||||
| Face-value of long-term debt including obligations under capital leases and | ||||||||||
| financing obligations | 6,141 | 6,826 | ||||||||
| Adjustment related to fair-value of interest rate hedges | 4 | 24 | ||||||||
| Long-term debt including obligations under capital leases and financing obligations | 6,145 | 6,850 | ||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 800 | 647 | ||||||||
| Pension and postretirement benefit obligations | 1,291 | 1,393 | ||||||||
| Other long-term liabilities | 1,145 | 1,515 | ||||||||
| Total Liabilities | 20,438 | 19,510 | ||||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (see Note 11) | ||||||||||
| SHAREOWNERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||||
| Preferred shares, $100 par per share, 5 shares authorized and unissued | — | — | ||||||||
| Common shares, $1 par per share, 1,000 shares authorized; | ||||||||||
| 959 shares issued in 2012 and 2011 | 959 | 959 | ||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 3,451 | 3,427 | ||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (753 | ) | (844 | ) | ||||||
| Accumulated earnings | 9,787 | 8,571 | ||||||||
| Common stock in treasury, at cost, 445 shares in 2012 and 398 shares in 2011 | (9,237 | ) | (8,132 | ) | ||||||
| Total Shareowners’ Equity - The Kroger Co. | 4,207 | 3,981 | ||||||||
| Noncontrolling interests | 7 | (15 | ) | |||||||
| Total Equity | 4,214 | 3,966 | ||||||||
| Total Liabilities and Equity | $ | 24,652 | $ | 23,476 | ||||||
Years Ended January 30, 2016, January 31, 2015 and February 1, 2014
| (In millions) | 2015 (52 weeks) | 2014 (52 weeks) | 2013 (52 weeks) | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings including noncontrolling interests | $ | 2,049 | $ | 1,747 | $ | 1,531 | ||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized gain on available for sale securities, net of | ||||||||||||||||||
| income tax(1) | 3 | 5 | 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Change in pension and other postretirement defined benefit plans, | ||||||||||||||||||
| net of income tax(2) | 131 | (329 | ) | 295 | ||||||||||||||
| Unrealized losses on cash flow hedging activities, | ||||||||||||||||||
| net of income tax(3) | (3 | ) | (25 | ) | (12 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Amortization of unrealized gains and losses on cash flow hedging | ||||||||||||||||||
| activities, net of income tax(4) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Total other comprehensive income (loss) | 132 | (348 | ) | 289 | ||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income | 2,181 | 1,399 | 1,820 | |||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 10 | 19 | 12 | |||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income attributable to The Kroger Co. | $ | 2,171 | $ | 1,380 | $ | 1,808 | ||||||||||||
| (1) | Amount is net of tax of $2 in 2015 and $3 in 2014 and 2013. |
| (2) | Amount is net of tax of $77 in 2015, $(193) in 2014 and $173 in 2013. |
| (3) | Amount is net of tax of $(2) in 2015, $(14) in 2014 and $(8) in 2013. |
| (4) | Amount is net of tax of $1 in 2013. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
A-33
THE KROGER CO.
Consolidated Statements of OperationsCONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS oF CASH FLOWS
Years Ended January 30, 2016, January 31, 2015 and February 2, 2013, January 28, 2012 and January 29, 20111, 2014
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||||||||||
| (In millions, except per share amounts) | (53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||
| Sales | $ | 96,751 | $ | 90,374 | $ | 82,049 | |||||||
| Merchandise costs, including advertising, warehousing, and | |||||||||||||
| transportation, excluding items shown separately below | 76,858 | 71,494 | 63,803 | ||||||||||
| Operating, general and administrative | 14,849 | 15,345 | 13,823 | ||||||||||
| Rent | 628 | 619 | 623 | ||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 1,652 | 1,638 | 1,600 | ||||||||||
| Goodwill impairment charge | — | — | 18 | ||||||||||
| Operating Profit | 2,764 | 1,278 | 2,182 | ||||||||||
| Interest expense | 462 | 435 | 448 | ||||||||||
| Earnings before income tax expense | 2,302 | 843 | 1,734 | ||||||||||
| Income tax expense | 794 | 247 | 601 | ||||||||||
| Net earnings including noncontrolling interests | 1,508 | 596 | 1,133 | ||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | 11 | (6 | ) | 17 | |||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. | $ | 1,497 | $ | 602 | $ | 1,116 | |||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per basic common share | $ | 2.78 | $ | 1.01 | $ | 1.75 | |||||||
| Average number of common shares used in basic calculation | 533 | 590 | 635 | ||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per diluted common share | $ | 2.77 | $ | 1.01 | $ | 1.74 | |||||||
| Average number of common shares used in diluted calculation | 537 | 593 | 638 | ||||||||||
| Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.53 | $ | 0.44 | $ | 0.40 | |||||||
| (In millions) | 2015 (52 weeks) | 2014 (52 weeks) | 2013 (52 weeks) | ||||||||||||||
| Cash Flows From Operating Activities: | |||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings including noncontrolling interests | $ | 2,049 | $ | 1,747 | $ | 1,531 | |||||||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 2,089 | 1,948 | 1,703 | ||||||||||||||
| Asset impairment charge | 46 | 37 | 39 | ||||||||||||||
| LIFO charge | 28 | 147 | 52 | ||||||||||||||
| Stock-based employee compensation | 165 | 155 | 107 | ||||||||||||||
| Expense for Company-sponsored pension plans | 103 | 55 | 74 | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 317 | 73 | 72 | ||||||||||||||
| Other | 54 | 72 | 47 | ||||||||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities net of effects from mergers of businesses: | |||||||||||||||||
| Store deposits in-transit | 95 | (27 | ) | 25 | |||||||||||||
| Receivables | (59 | ) | (141 | ) | (8 | ) | |||||||||||
| Inventories | (184 | ) | (147 | ) | (131 | ) | |||||||||||
| Prepaid and other current assets | (28 | ) | 2 | (49 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Trade accounts payable | 440 | 135 | 196 | ||||||||||||||
| Accrued expenses | 191 | 197 | 77 | ||||||||||||||
| Income taxes receivable and payable | (359 | ) | (68 | ) | (47 | ) | |||||||||||
| Contribution to Company-sponsored pension plans | (5 | ) | — | (100 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Other | (109 | ) | (22 | ) | (15 | ) | |||||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 4,833 | 4,163 | 3,573 | ||||||||||||||
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities: | |||||||||||||||||
| Payments for property and equipment, including payments for lease buyouts | (3,349 | ) | (2,831 | ) | (2,330 | ) | |||||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of assets | 45 | 37 | 24 | ||||||||||||||
| Payments for mergers | (168 | ) | (252 | ) | (2,344 | ) | |||||||||||
| Other | (98 | ) | (14 | ) | (121 | ) | |||||||||||
| Net cash used by investing activities | (3,570 | ) | (3,060 | ) | (4,771 | ) | |||||||||||
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities: | |||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt | 1,181 | 576 | 3,548 | ||||||||||||||
| Payments on long-term debt | (1,245 | ) | (375 | ) | (1,060 | ) | |||||||||||
| Net (payments) borrowings on commercial paper | (285 | ) | 25 | (395 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | (385 | ) | (338 | ) | (319 | ) | |||||||||||
| Excess tax benefits on stock based awards | 97 | 52 | 32 | ||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of capital stock | 120 | 110 | 196 | ||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchases | (703 | ) | (1,283 | ) | (609 | ) | |||||||||||
| Investment in the remaining equity of a noncontrolling interest | (26 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Other | (8 | ) | (3 | ) | (32 | ) | |||||||||||
| Net cash provided (used) by financing activities | (1,254 | ) | (1,236 | ) | 1,361 | ||||||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and temporary cash investments | 9 | (133 | ) | 163 | |||||||||||||
| Cash and temporary cash investments: | |||||||||||||||||
| Beginning of year | 268 | 401 | 238 | ||||||||||||||
| End of year | $ | 277 | $ | 268 | $ | 401 | |||||||||||
| Reconciliation of capital investments: | |||||||||||||||||
| Payments for property and equipment, including payments for lease buyouts | $ | (3,349 | ) | $ | (2,831 | ) | $ | (2,330 | ) | ||||||||
| Payments for lease buyouts | 35 | 135 | 108 | ||||||||||||||
| Changes in construction-in-progress payables | (35 | ) | (56 | ) | (83 | ) | |||||||||||
| Total capital investments, excluding lease buyouts | $ | (3,349 | ) | $ | (2,752 | ) | $ | (2,305 | ) | ||||||||
| Disclosure of cash flow information: | |||||||||||||||||
| Cash paid during the year for interest | $ | 474 | $ | 477 | $ | 401 | |||||||||||
| Cash paid during the year for income taxes | $ | 1,001 | $ | 941 | $ | 679 | |||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
A-34
THE KROGER CO.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive IncomeCONSOLIDATED STATEMENTOF CHANGESIN SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Years Ended January 30, 2016, January 31, 2015 and February 2, 2013, January 28, 2012 and January 29, 20111, 2014
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | (53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings including noncontrolling interests | $ | 1,508 | $ | 596 | $ | 1,133 | ||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized gain on available for sale securities, net of income tax (1) | — | 2 | 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Change in pension and other postretirement defined benefit plans, net | ||||||||||||||||||
| of income tax (2) | 75 | (271 | ) | 36 | ||||||||||||||
| Unrealized gain (loss) on cash flow hedging activities, net of | ||||||||||||||||||
| income tax (3) | 13 | (26 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
| Amortization of unrealized gains and losses on cash flow hedging | ||||||||||||||||||
| activities, net of income tax (4) | 3 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Total other comprehensive income (loss) | 91 | (294 | ) | 43 | ||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income | 1,599 | 302 | 1,176 | |||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | 11 | (6 | ) | 17 | ||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income attributable to The Kroger Co. | $ | 1,588 | $ | 308 | $ | 1,159 | ||||||||||||
| (In millions, except per share amounts) | Common Stock | Additional Paid-In Capital | Treasury Stock | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Gain (Loss) | Accumulated Earnings | Noncontrolling Interest | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at February 2, 2013 | 1,918 | $ | 1,918 | $ | 2,492 | 890 | $ | (9,237 | ) | $ | (753 | ) | $ | 9,787 | $ | 7 | $ | 4,214 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exercised | — | — | — | (18 | ) | 196 | — | — | — | 196 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock issued | — | — | (60 | ) | (5 | ) | 26 | — | — | — | (34 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock activity: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchases, at cost | — | — | — | 18 | (338 | ) | — | — | — | (338 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exchanged | — | — | — | 17 | (271 | ) | — | — | — | (271 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based employee compensation | — | — | 107 | — | — | — | — | — | 107 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive gain net of | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| income tax of $168 | — | — | — | — | — | 289 | — | — | 289 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | — | — | 51 | — | (17 | ) | — | — | (8 | ) | 26 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($0.315 per common share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (325 | ) | — | (325 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings including | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| non-controlling interests | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,519 | 12 | 1,531 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at February 1, 2014 | 1,918 | $ | 1,918 | $ | 2,590 | 902 | $ | (9,641 | ) | $ | (464 | ) | $ | 10,981 | $ | 11 | $ | 5,395 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exercised | — | — | — | (10 | ) | 110 | — | — | — | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock issued | — | — | (91 | ) | (5 | ) | 40 | — | — | — | (51 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock activity: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchases, at cost | — | — | — | 51 | (1,129 | ) | — | — | — | (1,129 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exchanged | — | — | — | 6 | (154 | ) | — | — | — | (154 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based employee compensation | — | — | 155 | — | — | — | — | — | 155 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss net of income | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| tax of ($204) | — | — | — | — | — | (348 | ) | — | — | (348 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | — | — | 94 | — | (35 | ) | — | — | — | 59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($0.350 per common share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (342 | ) | — | (342 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings including | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| non-controlling interests | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,728 | 19 | 1,747 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at January 31, 2015 | 1,918 | $ | 1,918 | $ | 2,748 | 944 | $ | (10,809 | ) | $ | (812 | ) | $ | 12,367 | $ | 30 | $ | 5,442 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exercised | — | — | — | (9 | ) | 120 | — | — | — | 120 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock issued | — | — | (122 | ) | (5 | ) | 37 | — | — | — | (85 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock activity: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchases, at cost | — | — | — | 14 | (500 | ) | — | — | — | (500 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exchanged | — | — | — | 7 | (203 | ) | — | — | — | (203 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based employee compensation | — | — | 165 | — | — | — | — | — | 165 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive gain net of income | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| tax of $77 | — | — | — | — | — | 132 | — | — | 132 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Investment in the remaining equity of a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| non-controlling interest | — | — | 26 | — | — | — | — | (57 | ) | (31 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | — | — | 163 | — | (54 | ) | — | — | (5 | ) | 104 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($0.408 per common share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (395 | ) | — | (395 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings including | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| non-controlling interests | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2,039 | 10 | 2,049 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at January 30, 2016 | 1,918 | $ | 1,918 | $ | 2,980 | 951 | $ | (11,409 | ) | $ | (680 | ) | $ | 14,011 | $ | (22 | ) | $ | 6,798 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
A-35
THE KROGER CO.NOTESTO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Years Ended February 2, 2013, January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | (53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | |||||||||||||||
| Cash Flows From Operating Activities: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings including noncontrolling interests | $ | 1,508 | $ | 596 | $ | 1,133 | ||||||||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 1,652 | 1,638 | 1,600 | |||||||||||||||
| Goodwill impairment charge | — | — | 18 | |||||||||||||||
| Asset impairment charge | 18 | 37 | 25 | |||||||||||||||
| LIFO charge | 55 | 216 | 57 | |||||||||||||||
| Stock-based employee compensation | 82 | 81 | 79 | |||||||||||||||
| Expense for Company-sponsored pension plans | 89 | 70 | 65 | |||||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 176 | 31 | 37 | |||||||||||||||
| Other | 17 | 8 | 8 | |||||||||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities net of effects from acquisitions | ||||||||||||||||||
| of businesses: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Store deposits in-transit | (169 | ) | (120 | ) | (12 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Inventories | (78 | ) | (361 | ) | (88 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Receivables | (126 | ) | (63 | ) | (11 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Prepaid expenses | (257 | ) | 52 | 290 | ||||||||||||||
| Trade accounts payable | 58 | 82 | 315 | |||||||||||||||
| Accrued expenses | 76 | 216 | 71 | |||||||||||||||
| Income taxes receivable and payable | 164 | (106 | ) | 133 | ||||||||||||||
| Contribution to Company-sponsored pension plans | (71 | ) | (52 | ) | (141 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Other | (361 | ) | 333 | (213 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 2,833 | 2,658 | 3,366 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Payments for capital investments | (2,062 | ) | (1,898 | ) | (1,919 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of assets | 49 | 51 | 55 | |||||||||||||||
| Payments for acquisitions | (122 | ) | (51 | ) | (7 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Other | (48 | ) | (10 | ) | (90 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net cash used by investing activities | (2,183 | ) | (1,908 | ) | (1,961 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt | 863 | 453 | 381 | |||||||||||||||
| Payments on long-term debt | (1,445 | ) | (547 | ) | (553 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net borrowings of commercial paper | 1,275 | 370 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of capital stock | 110 | 118 | 29 | |||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchases | (1,261 | ) | (1,547 | ) | (545 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | (267 | ) | (257 | ) | (250 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Investment in the remaining interest of a variable interest entity | — | — | (86 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Other | 125 | 23 | 20 | |||||||||||||||
| Net cash used by financing activities | (600 | ) | (1,387 | ) | (1,004 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and temporary cash investments | 50 | (637 | ) | 401 | ||||||||||||||
| Cash and temporary cash investments: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Beginning of year | 188 | 825 | 424 | |||||||||||||||
| End of year | $ | 238 | $ | 188 | $ | 825 | ||||||||||||
| Reconciliation of capital investments: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Payments for capital investments | $ | (2,062 | ) | $ | (1,898 | ) | $ | (1,919 | ) | |||||||||
| Changes in construction-in-progress payables | (1 | ) | (60 | ) | 22 | |||||||||||||
| Total capital investments | $ | (2,063 | ) | $ | (1,958 | ) | $ | (1,897 | ) | |||||||||
| Disclosure of cash flow information: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cash paid during the year for interest | $ | 438 | $ | 457 | $ | 486 | ||||||||||||
| Cash paid during the year for income taxes | $ | 468 | $ | 296 | $ | 664 | ||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part ofAll amounts in the consolidated financial statements.
A-36
THE KROGER CO.
Consolidated Statement of Changes in Shareowners’ Equity
Years Ended February 2, 2013, January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011
| Accumulated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Additional | Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock | Paid-In | TreasuryStock | Comprehensive | Accumulated | Noncontrolling | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions, except per share amounts) | Shares | Amount | Capital | Shares | Amount | Gain (Loss) | Earnings | Interest | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at January 30, 2010 | 958 | $ | 958 | $ | 3,361 | 316 | $ | (6,238 | ) | $ | (593 | ) | $ | 7,364 | $ | 74 | $ | 4,926 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exercised | 1 | 1 | 9 | (2 | ) | 19 | — | — | — | 29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock issued | — | — | (54 | ) | (1 | ) | 37 | — | — | — | (17 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock activity: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchases, at cost | — | — | — | 24 | (505 | ) | — | — | — | (505 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exchanged | — | — | — | 2 | (40 | ) | — | — | — | (40 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Investment in the remaining interest of a variable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| interest entity net of income tax of $(14) | — | — | (8 | ) | — | — | — | — | (67 | ) | (75 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based employee compensation | — | — | 79 | — | — | — | — | — | 79 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive gain net of income | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| tax of $26 | — | — | — | — | — | 43 | — | — | 43 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | — | — | 7 | — | (5 | ) | — | — | (22 | ) | (20 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($0.40 per common share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (255 | ) | — | (255 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings including non-controlling interests | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,116 | 17 | 1,133 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at January 29, 2011 | 959 | $ | 959 | $ | 3,394 | 339 | $ | (6,732 | ) | $ | (550 | ) | $ | 8,225 | $ | 2 | $ | 5,298 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exercised | — | — | — | (6 | ) | 118 | — | — | — | 118 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock issued | — | — | (55 | ) | (2 | ) | 34 | — | — | — | (21 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock activity: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchases, at cost | — | — | — | 61 | (1,420 | ) | — | — | — | (1,420 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exchanged | — | — | — | 6 | (127 | ) | — | — | — | (127 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based employee compensation | — | — | 81 | — | — | — | — | — | 81 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss net of income tax | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| of $(167) | — | — | — | — | — | (294 | ) | — | — | (294 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | — | — | 7 | — | (5 | ) | — | — | (11 | ) | (9 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($0.44 per common share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (256 | ) | — | (256 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) including non-controlling | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| interests | — | — | — | — | — | — | 602 | (6 | ) | 596 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at January 28, 2012 | 959 | $ | 959 | $ | 3,427 | 398 | $ | (8,132 | ) | $ | (844 | ) | $ | 8,571 | $ | (15 | ) | $ | 3,966 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exercised | — | — | — | (7 | ) | 110 | — | — | — | 110 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock issued | — | — | (59 | ) | (2 | ) | 40 | — | — | — | (19 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock activity: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchases, at cost | — | — | — | 51 | (1,165 | ) | — | — | — | (1,165 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exchanged | — | — | — | 5 | (96 | ) | — | — | — | (96 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based employee compensation | — | — | 82 | — | — | — | — | — | 82 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive gain net of income | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| tax of $54 | — | — | — | — | — | 91 | — | — | 91 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | — | — | 1 | — | 6 | — | — | 11 | 18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($0.53 per common share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (281 | ) | — | (281 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings including non-controlling interests | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,497 | 11 | 1,508 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at February 2, 2013 | 959 | $ | 959 | $ | 3,451 | 445 | $ | (9,237 | ) | $ | (753 | ) | $ | 9,787 | $ | 7 | $ | 4,214 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
A-37
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
All dollar amounts are in millions except share and per share amounts.
Certain prior-year amounts have been reclassified to conform to current year presentation.
1. Accounting Policies ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The following is a summary of the significant accounting policies followed in preparing these financial statements.
Description of Business, Basis of Presentation and Principles of Consolidation
The Kroger Co. (the “Company”) was founded in 1883 and incorporated in 1902. As of February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, the Company was one of the largest retailers in the United Statesnation based on annual sales. The Company also manufactures and processes food for sale by its supermarkets. The accompanying financial statements include the consolidated accounts of the Company, its wholly-owned subsidiaries and the Variable Interest Entities (“VIEs”)variable interest entities in which the Company is the primary beneficiary. Significant intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated.
On June 25, 2015, the Company’s Board of Directors approved a two-for-one stock split of The Kroger Co.’s common shares in the form of a 100% stock dividend, which was effective July 13, 2015. All share and per share amounts in the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements and related notes have been retroactively adjusted to reflect the stock split for all periods presented.
Refer to Note 17 for an additional change to the Consolidated Balance Sheets for a recently adopted accounting standard regarding the presentation of debt issuance costs.
Fiscal Year
The Company’s fiscal year ends on the Saturday nearest January 31. The last three fiscal years consist of the 53-week period ended February 2, 2013 and the 52-week periods ended January 28, 201230, 2016, January 31, 2015 and January 29, 2011.February 1, 2014.
Pervasiveness of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities. Disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of consolidated revenues and expenses during the reporting period is also is required. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
InventoriesCash, Temporary Cash Investments and Book Overdrafts
Cash and temporary cash investments represent store cash and short-term investments with original maturities of less than three months. Book overdrafts are included in “Trade accounts payable” and “Accrued salaries and wages” in the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Deposits In-Transit
Deposits in-transit generally represent funds deposited to the Company’s bank accounts at the end of the year related to sales, a majority of which were paid for with debit cards, credit cards and checks, to which the Company does not have immediate access but settle within a few days of the sales transaction.
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost (principally on a last-in, first-out “LIFO” basis) or market. In total, approximately 96% and 97%95% of inventories for 2012in 2015 and 2011, respectively,2014 were valued using the LIFO method. Cost for the balance of the inventories, including substantially all fuel inventories, was determined using the first-in, first-out (“FIFO”) method. Replacement cost was higher than the carrying amount by $1,098 at February 2, 2013 and $1,043$1,272 at January 28, 2012.30, 2016 and $1,245 at January 31, 2015. The Company follows the Link-Chain, Dollar-Value LIFO method for purposes of calculating its LIFO charge or credit.
A-36
The item-cost method of accounting to determine inventory cost before the LIFO adjustment is followed for substantially all store inventories at the Company’s supermarket divisions. This method involves counting each item in inventory, assigning costs to each of these items based on the actual purchase costs (net of vendor allowances and cash discounts) of each item and recording the cost of items sold. The item-cost method of accounting allows for more accurate reporting of periodic inventory balances and enables management to more precisely manage inventory when compared to the retail method of accounting.inventory. In addition, substantially all of the Company’s inventory consists of finished goods and is recorded at actual purchase costs (net of vendor allowances and cash discounts).
The Company evaluates inventory shortages throughout the year based on actual physical counts in its facilities. Allowances for inventory shortages are recorded based on the results of these counts to provide for estimated shortages as of the financial statement date.
A-38
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are recorded at cost.cost or, in the case of assets acquired in a business combination, at fair value. Depreciation and amortization expense, which includes the amortizationdepreciation of assets recorded under capital leases, is computed principally using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of individual assets. Buildings and land improvements are depreciated based on lives varying from 10 to 40 years. All new purchases of store equipment are assigned lives varying from three to nine years. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of the lease term to which they relate, which generally varies from four to 25 years, or the useful life of the asset. ManufacturingFood production plant and distribution center equipment is depreciated over lives varying from three to 15 years. Information technology assets are generally depreciated over five years. Depreciation and amortization expense was $1,652$2,089 in 2012, $1,6382015, $1,948 in 20112014 and $1,600$1,703 in 2010.2013.
Interest costs on significant projects constructed for the Company’s own use are capitalized as part of the costs of the newly constructed facilities. Upon retirement or disposal of assets, the cost and related accumulated depreciation and amortization are removed from the balance sheet and any gain or loss is reflected in net earnings. Refer to Note 4 for further information regarding the Company’s property, plant and equipment.
Deferred Rent
The Company recognizes rent holidays, including the time period during which the Company has access to the property for construction of buildings or improvements and escalating rent provisions on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease. The deferred amount is included in Other Current Liabilities“Other current liabilities” and Other Long-Term Liabilities“Other long-term liabilities” on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Goodwill
The Company reviews goodwill for impairment during the fourth quarter of each year, and also upon the occurrence of trigger events.a triggering event. The Company performs reviews are performed at theof each of its operating division level.divisions and variable interest entities (collectively, “reporting units”) that have goodwill balances. Generally, fair value is determined using a multiple of earnings, or discounted projected future cash flows, and is compared to the carrying value of a divisionreporting unit for purposes of identifying potential impairment. Projected future cash flows are based on management’s knowledge of the current operating environment and expectations for the future. If potential for impairment is identified, the fair value of a divisionreporting unit is measured against the fair value of its underlying assets and liabilities, excluding goodwill, to estimate an implied fair value of the division’sreporting unit’s goodwill. Goodwill impairment is recognized for any excess of the carrying value of the division’sreporting unit’s goodwill over the implied fair value. Results of the goodwill impairment reviews performed during 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 20102013 are summarized in Note 2 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.3.
A-37
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The Company monitors the carrying value of long-lived assets for potential impairment each quarter based on whether certain triggertriggering events have occurred. These events include current period losses combined with a history of losses or a projection of continuing losses or a significant decrease in the market value of an asset. When a triggertriggering event occurs, an impairment calculation is performed, comparing projected undiscounted future cash flows, utilizing current cash flow information and expected growth rates related to specific stores, to the carrying value for those stores. If the Company identifies impairment for long-lived assets to be held and used, the Company compares the assets’ current carrying value to the assets’ fair value. Fair value is based on current market values or discounted future cash flows. The Company records impairment when the carrying value exceeds fair market value. With respect to owned property and equipment held for sale,disposal, the value of the property and equipment is adjusted to reflect recoverable values based on previous efforts to dispose of similar assets and current economic conditions. Impairment is recognized for the excess of the carrying value over the estimated fair market value, reduced by estimated direct costs of disposal. The Company recorded asset impairments in the normal course of business totaling $18,$46, $37 and $25$39 in 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 2010,2013, respectively. Costs to reduce the carrying value of long-lived assets for each of the years presented have been included in the Consolidated Statements of Operations as “Operating, general and administrative” expense.
A-39
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
Store Closing Costs
The Company provides for closed store liabilities relating to the present value of the estimated remaining non-cancellable lease payments after the closing date, net of estimated subtenant income. The Company estimates the net lease liabilities using a discount rate to calculate the present value of the remaining net rent payments on closed stores. The closed store lease liabilities usually are paid over the lease terms associated with the closed stores, which generally have remaining terms ranging from one to 20 years. Adjustments to closed store liabilities primarily relate to changes in subtenant income and actual exit costs differing from original estimates. Adjustments are made for changes in estimates in the period in which the change becomes known. Store closing liabilities are reviewed quarterly to ensure that any accrued amount that is not a sufficient estimate of future costs or that no longer is needed for its originally intended purpose, is adjusted to income in the proper period.
Owned stores held for disposal are reduced to their estimated net realizable value. Costs to reduce the carrying values of property, equipment and leasehold improvements are accounted for in accordance with the Company’s policy on impairment of long-lived assets. Inventory write-downs, if any, in connection with store closings, are classified in the Consolidated Statements of Operations as “Merchandise costs.” Costs to transfer inventory and equipment from closed stores are expensed as incurred.
The following table summarizes accrual activity forcurrent portion of the future lease obligations of stores that were closedis included in “Other current liabilities,” and the long-term portion is included in “Other long-term liabilities” in the normal course of business:Consolidated Balance Sheets.
| Future Lease | ||||||
| Obligations | ||||||
| Balance at January 29, 2011 | $ | 52 | ||||
| Additions | 9 | |||||
| Payments | (11 | ) | ||||
| Other | 5 | |||||
| Balance at January 28, 2012 | 55 | |||||
| Additions | 6 | |||||
| Payments | (10 | ) | ||||
| Other | (7 | ) | ||||
| Balance at February 2, 2013 | $ | 44 | ||||
Interest Rate Risk Management
The Company uses derivative instruments primarily to manage its exposure to changes in interest rates. The Company’s current program relative to interest rate protection and the methods by which the Company accounts for its derivative instruments are described in Note 6.7.
Commodity Price Protection
The Company enters into purchase commitments for various resources, including raw materials utilized in its manufacturing facilitiesfood production plants and energy to be used in its stores, manufacturing facilitiesfood production plants and administrative offices. The Company enters into commitments expecting to take delivery of and to utilize those resources in the conduct of the normal course of business. The Company’s current program relative to commodity price protection and the methods by which the Company accounts for its purchase commitments are described in Note 6.7.
A-40A-38
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
Benefit Plans and Multi-Employer Pension Plans
The Company recognizes the funded status of its retirement plans on the Consolidated Balance Sheet.Sheets. Actuarial gains or losses, prior service costs or credits and transition obligations that have not yet been recognized as part of net periodic benefit cost are required to be recorded as a component of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (“AOCI”). All plans are measured as of the Company’s fiscal year end.
The determination of the obligation and expense for Company-sponsored pension plans and other post-retirement benefits is dependent on the selection of assumptions used by actuaries and the Company in calculating those amounts. Those assumptions are described in Note 1315 and include, among others, the discount rate, the expected long-term rate of return on plan assets, mortality and the rates of increase in compensation and health care costs. Actual results that differ from the assumptions are accumulated and amortized over future periods and, therefore, generally affect the recognized expense and recorded obligation in future periods. While the Company believes that the assumptions are appropriate, significant differences in actual experience or significant changes in assumptions may materially affect the pension and other post-retirement obligations and future expense.
The Company also participates in various multi-employer plans for substantially all union employees. Pension expense for these plans is recognized as contributions are funded. Refer to Note 1416 for additional information regarding the Company’s participation in these various multi-employer plans and the United Food and Commercial Workers International Union (“UFCW”) consolidated fund.plans.
The Company administers and makes contributions to the employee 401(k) retirement savings accounts. Contributions to the employee 401(k) retirement savings accounts are expensed when contributed. Refer to Note 1315 for additional information regarding the Company’s benefit plans.
StockShare Based Compensation
The Company accounts for stock options under fair value recognition provisions. Under this method, the Company recognizes compensation expense for all share-based payments granted. The Company recognizes share-based compensation expense, net of an estimated forfeiture rate, over the requisite service period of the award. In addition, the Company records expense for restricted stock awards in an amount equal to the fair market value of the underlying stock on the grant date of the award, over the period the awards lapse. Refer to Note 12 for additional information regarding the Company’s stock based compensation.
Deferred Income Taxes
Deferred income taxes are recorded to reflect the tax consequences of differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their financial reporting basis. Refer to Note 45 for the types of differences that give rise to significant portions of deferred income tax assets and liabilities. Deferred income taxes are classified as a net current or noncurrent asset or liability based on the classification of the related asset or liability for financial reporting purposes. A deferred tax asset or liability that is not related to an asset or liability for financial reporting is classified according to the expected reversal date.
Uncertain Tax Positions
The Company reviews the tax positions taken or expected to be taken on tax returns to determine whether and to what extent a benefit can be recognized in its consolidated financial statements. Refer to Note 45 for the amount of unrecognized tax benefits and other related disclosures related to uncertain tax positions.
A-39
Various taxing authorities periodically audit the Company’s income tax returns. These audits include questions regarding the Company’s tax filing positions, including the timing and amount of deductions and the allocation of income to various tax jurisdictions. In evaluating the exposures connected with these various tax filing positions, including state and local taxes, the Company records allowances for probable exposures. A number of years may elapse before a particular matter, for which an allowance has been established, is audited and fully resolved. As of February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, the Internal Revenue Service had concluded its field examination
A-41
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
of the Company’s 20082010 and 20092011 federal tax returns. The Company has filed an administrative appeal within the Internal Revenue Service protesting certain adjustments proposed by the Internal Revenue Service as a result of their field work.Tax years 2012 and 2013 remain under examination.
The assessment of the Company’s tax position relies on the judgment of management to estimate the exposures associated with the Company’s various filing positions.
Self-Insurance Costs
The Company is primarily self-insured for costs related to workers’ compensation and general liability claims. Liabilities are actuarially determined and are recognized based on claims filed and an estimate of claims incurred but not reported. The liabilities for workers’ compensation claims are accounted for on a present value basis. The Company has purchased stop-loss coverage to limit its exposure to any significant exposure on a per claim basis. The Company is insured for covered costs in excess of these per claim limits.
The following table summarizes the changes in the Company’s self-insurance liability through February 2, 2013.January 30, 2016.
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | 529 | $ | 514 | $ | 485 | $ | 599 | $ | 569 | $ | 537 | ||||||||||||
| Expense | 215 | 215 | 210 | 234 | 246 | 220 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Claim payments | (207 | ) | (200 | ) | (181 | ) | (225 | ) | (216 | ) | (215 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Assumed from Roundy’s or Harris Teeter | 31 | — | 27 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Ending balance | 537 | 529 | 514 | 639 | 599 | 569 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Less: Current portion | (205 | ) | (197 | ) | (181 | ) | (223 | ) | (213 | ) | (224 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Long-term portion | $ | 332 | $ | 332 | $ | 333 | $ | 416 | $ | 386 | $ | 345 | ||||||||||||
The current portion of the self-insured liability is included in “Other current liabilities,” and the long-term portion is included in “Other long-term liabilities” in the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
The Company maintains surety bonds related to self-insured workers’ compensation claims. These bonds are required by most states in which the Company is self-insured for workers’ compensation and are placed with third-party insurance providers to insure payment of the Company’s obligations in the event the Company is unable to meet its claim payment obligations up to its self-insured retention levels. These bonds do not represent liabilities of the Company, as the Company has recorded reserves for the claim costs.
The Company is also similarly self-insured for property-related losses. The Company maintains stop loss coverage to limit its property loss exposures including coverage for earthquake, wind, flood and other catastrophic events.
A-40
Revenue Recognition
Revenues from the sale of products are recognized at the point of sale. Discounts provided to customers by the Company at the time of sale, including those provided in connection with loyalty cards, are recognized as a reduction in sales as the products are sold. Discounts provided by vendors, usually in the form of paper coupons, are not recognized as a reduction in sales provided the coupons are redeemable at any retailer that accepts coupons. The Company records a receivable from the vendor for the difference in sales price and cash received. Pharmacy sales are recorded when product is provided to the customer. Sales taxes are recorded as other accrued liabilities and not as a component of sales. The Company does not recognize a sale when it sells its own gift cards and gift certificates. Rather, it records a deferred liability equal to the amount received. A sale is then recognized when the gift card or gift certificate is redeemed to purchase the Company’s products. Gift card and certificate breakage is recognized when redemption is deemed remote and there is no legal obligation to remit the value of the unredeemed gift card. The amount of breakage has not been material for 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 2010.2013.
Merchandise Costs
The “Merchandise costs” line item of the Consolidated Statements of Operations includes product costs, net of discounts and allowances; advertising costs (see separate discussion below); inbound freight charges; warehousing costs, including receiving and inspection costs; transportation costs; and manufacturingfood production and operational costs. Warehousing, transportation and manufacturing management salaries
A-42
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
are also included in the “Merchandise costs” line item; however, purchasing management salaries and administration costs are included in the “Operating, general and administrative” line item along with most of the Company’s other managerial and administrative costs. Rent expense and depreciation and amortization expense are shown separately in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Warehousing and transportation costs include distribution center direct wages, transportation direct wages, repairs and maintenance, utilities, inbound freight and, where applicable, third party warehouse management fees, as well as transportation direct wages and repairs and maintenance.fees. These costs are recognized in the periods the related expenses are incurred.
The Company believes the classification of costs included in merchandise costs could vary widely throughout the industry. The Company’s approach is to include in the “Merchandise costs” line item the direct, net costs of acquiring products and making them available to customers in its stores. The Company believes this approach most accurately presents the actual costs of products sold.
The Company recognizes all vendor allowances as a reduction in merchandise costs when the related product is sold. When possible, vendor allowances are applied to the related product cost by item and, therefore, reduce the carrying value of inventory by item. When the items are sold, the vendor allowance is recognized. When it is not possible, due to systems constraints, to allocate vendor allowances to the product by item, vendor allowances are recognized as a reduction in merchandise costs based on inventory turns and, therefore, recognized as the product is sold.
Advertising Costs
The Company’s advertising costs are recognized in the periods the related expenses are incurred and are included in the “Merchandise costs” line item of the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The Company’s pre-tax advertising costs totaled $553$679 in 2012, $5322015, $648 in 20112014 and $533$587 in 2010.2013. The Company does not record vendor allowances for co-operative advertising as a reduction of advertising expense.
Deposits In-Transit
Deposits in-transit generally represent funds deposited to the Company’s bank accounts at the end of the year related to sales, a majority of which were paid for with credit cards and checks, to which the Company does not have immediate access but that settle within a few days of the sales transaction.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
For purposes of the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, the Company considers all highly liquid debt instruments purchased with an original maturity of three months or less to be temporary cash investments. Book overdrafts, which are included in accounts payable, represent disbursements that are funded as the item is presented for payment. Book overdrafts totaled $839, $718 and $699 as of February 2, 2013, January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011, respectively, and are reflected as a financing activity in the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows.
Accumulated Other Comprehensive (Loss) Income
Accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income, net of applicable taxes, consisted of the following at year-end:
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| Unrealized gain on available for sale securities | $ | 7 | $ | 7 | $ | 5 | ||||||
| Pension and other postretirement defined benefit plans | (746 | ) | (821 | ) | (550 | ) | ||||||
| Unrealized gain (loss) on cash flow hedging activities | (14 | ) | (30 | ) | (5 | ) | ||||||
| Total | $ | (753 | ) | $ | (844 | ) | $ | (550 | ) | |||
A-43A-41
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, ContinuedSegments
Segments
The Company operates retail food and drug stores, multi-department stores, jewelry stores, and convenience stores throughout the United States. The Company’s retail operations, which represent over 99% of the Company’s consolidated sales and EBITDA, are its only reportable segment. The Company’s retail operating divisions have been aggregated into one reportable segment due to the operating divisions having similar economic characteristics with similar long-term financial performance. In addition, the Company’s operating divisions offer to its customers similar products, have similar distribution methods, operate in similar regulatory environments, purchase the majority of the Company’s merchandise for retail sale from similar (and in many cases identical) vendors on a coordinated basis from a centralized location, serve similar types of customers, and are allocated capital from a centralized location. The Company’s operating divisions reflect the manner in which the business is managed and how the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, and Chief Operating Officer, who actacts as the Company’s chief operating decision makers,maker, assess performance internally. All of the Company’s operations are domestic.
The following table presents sales revenue by type of product for 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 2010.2013.
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of total | Amount | % of total | Amount | % of total | Amount | % of total | Amount | % of total | Amount | % of total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non Perishable (1) | $ | 48,663 | 50.3 | % | $ | 46,494 | 51.4 | % | $ | 44,615 | 54.4 | % | $ | 57,187 | 52.1% | $ | 54,392 | 50.1% | $ | 49,229 | 50.0% | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Perishable (2) | 19,893 | 20.6 | % | 18,693 | 20.7 | % | 17,532 | 21.4 | % | 25,726 | 23.4% | 24,178 | 22.3% | 20,625 | 21.0% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fuel | 18,896 | 19.5 | % | 16,901 | 18.7 | % | 12,081 | 14.7 | % | 14,802 | 13.5% | 18,850 | 17.4% | 18,962 | 19.3% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharmacy | 8,018 | 8.3 | % | 7,322 | 8.1 | % | 6,929 | 8.4 | % | 9,778 | 8.9% | 9,032 | 8.3% | 8,073 | 8.2% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other (3) | 1,281 | 1.3 | % | 964 | 1.1 | % | 892 | 1.1 | % | 2,337 | 2.1% | 2,013 | 1.9% | 1,486 | 1.5% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Sales and other revenue | $ | 96,751 | 100.0 | % | $ | 90,374 | 100.0 | % | $ | 82,049 | 100.0 | % | $ | 109,830 | 100.0% | $ | 108,465 | 100.0% | $ | 98,375 | 100.0% | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Consists primarily of grocery, general merchandise, health and beauty care and natural foods. | |
| (2) | Consists primarily of produce, floral, meat, seafood, deli, bakery and | |
| (3) | Consists primarily of sales related to jewelry | |
2. GoodwillMergers
On December 18, 2015, the Company closed its merger with Roundy’s by purchasing 100% of Roundy’s outstanding common stock for $3.60 per share and assuming Roundy’s outstanding debt, for a purchase price of $866. The merger brings a complementary store base in communities throughout Wisconsin and a stronger presence in the greater Chicagoland area. The merger was accounted for under the purchase method of accounting and was financed through a combination of commercial paper and long-term debt (see Note 6). In a business combination, the purchase price is allocated to assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their fair values, with any excess of purchase price over fair value recognized as goodwill. In addition to recognizing the assets and liabilities on the acquired company’s balance sheet, the Company reviews supply contracts, leases, financial instruments, employment agreements and other significant agreements to identify potential assets or liabilities that require recognition in connection with the application of acquisition accounting under Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 805. Intangible assets are recognized apart from goodwill when the asset arises from contractual or other legal rights, or are separable from the acquired entity such that they may be sold, transferred, licensed, rented or exchanged either on a standalone basis or in combination with a related contract, asset or liability.
TheA-42followingtablesummarizesthechangesintheCompany’snetgoodwillbalancethrough February 2, 2013.
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| Balance beginning of year | ||||||||
| Goodwill | $ | 3,670 | $ | 3,672 | ||||
| Accumulated impairment losses | (2,532 | ) | (2,532 | ) | ||||
| 1,138 | 1,140 | |||||||
| Activity during the year | ||||||||
| Acquisitions | 96 | — | ||||||
| Disposition | — | (2 | ) | |||||
| Balance end of year | ||||||||
| Goodwill | 3,766 | 3,670 | ||||||
| Accumulated impairment losses | (2,532 | ) | (2,532 | ) | ||||
| $ | 1,234 | $ | 1,138 | |||||
Pending finalization of the Company’s valuation and other items, the following table summarizes the preliminary fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed as part of the merger with Roundy’s:
| December 18, 2015 | ||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash and temporary cash investments | $ | 20 | ||||
| Store deposits in-transit | 30 | |||||
| Receivables | 43 | |||||
| FIFO inventory | 323 | |||||
| Prepaid and other current assets | 19 | |||||
| Total current assets | 435 | |||||
| Property, plant and equipment | 342 | |||||
| Intangibles | 324 | |||||
| Other assets | 4 | |||||
| Total Assets, excluding Goodwill | 1,105 | |||||
| LIABILITIES | ||||||
| Current portion of obligations under capital leases and financing obligations | (9 | ) | ||||
| Trade accounts payable | (236 | ) | ||||
| Accrued salaries and wages | (40 | ) | ||||
| Other current liabilities | (89 | ) | ||||
| Total current liabilities | (374 | ) | ||||
| Fair-value of long-term debt | (678 | ) | ||||
| Fair-value of long-term obligations under capital leases and financing obligations | (20 | ) | ||||
| Deferred income taxes | (112 | ) | ||||
| Pension and postretirement benefit obligations | (36 | ) | ||||
| Other long-term liabilities | (111 | ) | ||||
| Total Liabilities | (1,331 | ) | ||||
| Total Identifiable Net Liabilities | (226 | ) | ||||
| Goodwill | 414 | |||||
| Total Purchase Price | $ | 188 | ||||
Of the $324 allocated to intangible assets, $211 relates to the Mariano’s, Pick ’n Save, Metro Market and Copps trade names, to which we assigned an indefinite life and, therefore, will not be amortized. The Company also recorded $69, $38, and $6 related to favorable leasehold interests, pharmacy prescription files and customer lists, respectively. The Company will amortize the favorable leasehold interests over a weighted average of twelve years. The Company will amortize the pharmacy prescription files and customer lists over seven and two years, respectively. The goodwill recorded as part of the merger was attributable to the assembled workforce of Roundy’s and operational synergies expected from the merger, as well as any intangible assets that do not qualify for separate recognition. The transaction was treated as a stock purchase for income tax purposes. The assets acquired and liabilities assumed as part of the merger did not result in a step up of the tax basis and goodwill is not expected to be deductible for tax purposes. The above amounts represent the preliminary allocation of the purchase price, and are subject to revision when the resulting valuations of property and intangible assets are finalized, which will occur prior to December 18, 2016. Due to the timing of the merger closing late in the year, the revenue and earnings of Roundy’s in 2015 were not material.
A-43
On August 18, 2014, the Company closed its merger with Vitacost.com, Inc. (“Vitacost.com”) by purchasing 100% of the Vitacost.com outstanding common stock for $8.00 per share or $287. This merger affords the Company access to Vitacost.com’s extensive e-commerce platform, which can be combined with the Company’s customer insights and loyal customer base, to create new levels of personalization and convenience for customers. The merger was accounted for under the purchase method of accounting and was financed through the issuance of commercial paper (see Note 6).
The Company’s purchase price allocation was finalized in the second quarter of 2015. The changes in the fair values assumed from the preliminary amounts were not material. The table below summarizes the final fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed:
| August 18, 2014 | ||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Total current assets | $ | 80 | ||||
| Property, plant and equipment | 28 | |||||
| Intangibles | 81 | |||||
| Total Assets, excluding Goodwill | 189 | |||||
| LIABILITIES | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | (56 | ) | ||||
| Deferred income taxes | (6 | ) | ||||
| Total Liabilities | (62 | ) | ||||
| Total Identifiable Net Assets | 127 | |||||
| Goodwill | 160 | |||||
| Total Purchase Price | $ | 287 | ||||
Of the $81 allocated to intangible assets, the Company recorded $49, $26 and $6 related to customer relationships, technology and the trade name, respectively. The Company will amortize the technology and the trade name, using the straight line method, over 10 and three years, respectively, while the customer relationships will be amortized over five years using the declining balance method. The goodwill recorded as part of the merger was attributable to the assembled workforce of Vitacost.com and operational synergies expected from the merger, as well as any intangible assets that did not qualify for separate recognition. The transaction was treated as a stock purchase for income tax purposes. The assets acquired and liabilities assumed as part of the merger did not result in a step up of the tax basis and goodwill is not expected to be deductible for tax purposes.
Pro forma results of operations, assuming the Harris Teeter Supermarkets, Inc. (“Harris Teeter”) merger had taken place at the beginning of 2012, the Vitacost.com merger had taken place at the beginning of 2013 and the Roundy’s transaction had taken place at the beginning of 2014, are included in the following table. The pro forma information includes historical results of operations of Harris Teeter, Vitacost.com and Roundy’s, as well as adjustments for interest expense that would have been incurred due to financing the mergers, depreciation and amortization of the assets acquired and excludes the pre-merger transaction related expenses incurred by Harris Teeter, Vitacost.com, Roundy’s and the Company. The pro forma information does not include efficiencies, cost reductions, synergies or investments in lower prices for our customers expected to result from the mergers. The unaudited pro
A-44
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
Informa financial information is not necessarily indicative of the results that actually would have occurred had the Harris Teeter merger been completed at the beginning of 2012, the Vitacost.com merger completed at the beginning of 2013 or the Roundy’s merger completed at the beginning of 2014.
| Fiscal year ended January 30, 2016 | Fiscal year ended January 31, 2015 | Fiscal year ended February 1, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| Sales | $ | 113,308 | $ | 112,458 | $ | 103,584 | |||||||||
| Net earnings including noncontrolling interests | 2,061 | 1,751 | 1,624 | ||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interests | 10 | 19 | 12 | ||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. | $ | 2,051 | $ | 1,732 | $ | 1,612 | |||||||||
3. Goodwill and Intangible Assets
The following table summarizes the changes in the Company’s net goodwill balance through January 30, 2016.
| 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
| Balance beginning of year | |||||||||
| Goodwill | $ | 4,836 | $ | 4,667 | |||||
| Accumulated impairment losses | (2,532 | ) | (2,532 | ) | |||||
| 2,304 | 2,135 | ||||||||
| Activity during the year | |||||||||
| Mergers | 420 | 169 | |||||||
| Balance end of year | |||||||||
| Goodwill | 5,256 | 4,836 | |||||||
| Accumulated impairment losses | (2,532 | ) | (2,532 | ) | |||||
| $ | 2,724 | $ | 2,304 | ||||||
In 2015, the Company acquired an interest in one of its suppliers and all the outstanding shares of Axium Pharmacy,Roundy’s, a leading specialty pharmacy that provides specialized drug therapiessupermarket retailer in the Wisconsin and support services for patients with complex medical conditions,Chicagoland markets, resulting in combinedadditional goodwill totaling $414. Roundy’s is accounted for as a single reporting unit.
In 2014, the Company acquired all the outstanding shares of Vitacost.com, an online retailer, resulting in additional goodwill of $96.$160.
See Note 2 for additional information regarding the Roundy’s and Vitacost.com mergers.
Testing for impairment must be performed annually, or on an interim basis upon the occurrence of a triggering event or a change in circumstances that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying amount. The annual evaluationevaluations of goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets were performed during the fourth quarter of 20122015, 2014 and 20112013 did not result in impairment.
The annual evaluation of goodwill performed during the fourth quarter of 2010 resulted in an impairment charge of $18. Based on the results of the Company’s step one analysis in the fourth quarter of 2010, a supermarket reporting unit with a small number of stores indicated potential impairment. Due to estimated future expected cash flows being lower than in the past, the estimated fair value of the reporting unit decreased. Management concluded that the carrying value of goodwill for this reporting unit exceeded its implied fair value, resulting in a pre-tax impairment charge of $18 ($12 after-tax). In 2009, the Company disclosed that a 10% reduction in fair value of this supermarket reporting unit would indicate a potential for impairment. Subsequent to the impairment, no goodwill remains at this reporting unit.
Based on current and future expected cash flows, the Company believes goodwill impairments are not reasonably possible.likely. A 10% reduction in fair value of the Company’s reporting units would not indicate a potential for impairment of the Company’s remaining goodwill balance.
In 2015, the Company acquired definite and indefinite lived intangible assets totaling approximately $324 as a result of the merger with Roundy’s.
In 2014, the Company acquired definite and indefinite lived intangible assets totaling approximately $81 as a result of the merger with Vitacost.com.
3.A-45
The following table summarizes the Company’s intangible assets balance through January 30, 2016.
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross carrying amount | Accumulated | Gross carrying amount | Accumulated amortization(1) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Definite-lived favorable leasehold interests | $ | 169 | $ | (31 | ) | $ | 101 | $ | (26 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Definite-lived pharmacy prescription files | 127 | (40 | ) | 98 | (41 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Definite-lived customer relationships | 93 | (39 | ) | 87 | (17 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Definite-lived other | 78 | (23 | ) | 74 | (13 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Indefinite-lived trade name | 641 | — | 430 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Indefinite-lived liquor licenses | 78 | — | 64 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 1,186 | $ | (133 | ) | $ | 854 | $ | (97 | ) | ||||||||||||
| (1) | Favorable leasehold interests are amortized to rent expense, pharmacy prescription files are amortized to merchandise costs, customer relationships are amortized to depreciation and amortization expense and other intangibles are amortized to operating, general and administrative (“OG&A”) expense and depreciation and amortization expense. |
Amortization expense associated with intangible assets totaled approximately $51, $41 and $18, during fiscal years 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Future amortization expense associated with the net carrying amount of definite-lived intangible assets for the years subsequent to 2015 is estimated to be approximately:
| 2016 | $ | 57 | |
| 2017 | 48 | ||
| 2018 | 42 | ||
| 2019 | 40 | ||
| 2020 | 35 | ||
| Thereafter | 112 | ||
| Total future estimated amortization associated | |||
| with definite-lived intangible assets | $ | 334 |
4. Property, Plant and Equipment, Net
Property, plant and equipment, net consists of:
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| Land | $ | 2,450 | $ | 2,253 | ||||
| Buildings and land improvements | 8,276 | 7,799 | ||||||
| Equipment | 10,267 | 10,110 | ||||||
| Leasehold improvements | 6,545 | 6,119 | ||||||
| Construction-in-progress | 1,239 | 1,202 | ||||||
| Leased property under capital leases and financing obligations | 593 | 588 | ||||||
| Total property, plant and equipment | 29,370 | 28,071 | ||||||
| Accumulated depreciation and amortization | (14,495 | ) | (13,607 | ) | ||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | $ | 14,875 | $ | 14,464 | ||||
| 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
| Land | $ | 2,997 | $ | 2,819 | |||||
| Buildings and land improvements | 10,524 | 9,639 | |||||||
| Equipment | 12,520 | 11,587 | |||||||
| Leasehold improvements | 8,710 | 8,068 | |||||||
| Construction-in-progress | 2,115 | 1,690 | |||||||
| Leased property under capital leases and financing obligations | 801 | 737 | |||||||
| Total property, plant and equipment | 37,667 | 34,540 | |||||||
| Accumulated depreciation and amortization | (18,048 | ) | (16,628 | ) | |||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | $ | 19,619 | $ | 17,912 | |||||
Accumulated depreciation and amortization for leased property under capital leases was $321 at February 2, 2013 and $327$293 at January 28, 2012.30, 2016 and $332 at January 31, 2015.
A-46
Approximately $236$264 and $220, original cost,$260, net book value, of Property, Plantproperty, plant and Equipmentequipment collateralized certain mortgages at February 2, 2013January 30, 2016 and January 28, 2012,31, 2015, respectively.
A-455. TAXES BASEDON INCOME
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
4. Taxes Based on Income
The provision for taxes based on income consists of:
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||||||||
| Federal | |||||||||||
| Current | $ | 563 | $ | 146 | $ | 697 | |||||
| Deferred | 154 | 78 | (136 | ) | |||||||
| 717 | 224 | 561 | |||||||||
| State and local | |||||||||||
| Current | 46 | 42 | 95 | ||||||||
| Deferred | 31 | (19 | ) | (55 | ) | ||||||
| 77 | 23 | 40 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 794 | $ | 247 | $ | 601 | |||||
| 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
| Federal | |||||||||||
| Current | $ | 723 | $ | 847 | $ | 638 | |||||
| Deferred | 266 | (15 | ) | 81 | |||||||
| Subtotal federal | 989 | 832 | 719 | ||||||||
| State and local | |||||||||||
| Current | 37 | 59 | 42 | ||||||||
| Deferred | 19 | 11 | (10 | ) | |||||||
| Subtotal state and local | 56 | 70 | 32 | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 1,045 | $ | 902 | $ | 751 | |||||
A reconciliation of the statutory federal rate and the effective rate follows:
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||||||
| Statutory rate | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | |||
| State income taxes, net of federal tax benefit | 2.2 | % | 1.8 | % | 1.5 | % | |||
| Credits | (1.4 | )% | (3.6 | )% | (1.3 | )% | |||
| Favorable resolution of issues | (0.5 | )% | (3.4 | )% | (.8 | )% | |||
| Other changes, net | (0.8 | )% | (0.5 | )% | 0.3 | % | |||
| 34.5 | % | 29.3 | % | 34.7 | % | ||||
| 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Statutory rate | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | |||
| State income taxes, net of federal tax benefit | 1.2 | % | 1.7 | % | 0.9 | % | |||
| Credits | (1.2 | )% | (1.2 | )% | (1.3 | )% | |||
| Favorable resolution of issues | (0.2 | )% | (0.4 | )% | — | % | |||
| Domestic manufacturing deduction | (0.7 | )% | (0.7 | )% | (1.1 | )% | |||
| Other changes, net | (0.3 | )% | (0.3 | )% | (0.6 | )% | |||
| 33.8 | % | 34.1 | % | 32.9 | % | ||||
The 20112015 effective tax rate was significantlydiffered from the federal statutory rate primarily as a result of the utilization of tax credits, the Domestic Manufacturing Deduction and other changes, partially offset by the effect of state income taxes. The 2015 rate for state income taxes is lower than 2012 and 20102014 due to the effect on pre-tax incomefiling of the UFCW consolidated pension plan charge of $953 ($591 after-tax)amended returns to claim additional benefits in 2011. The effect of the UFCW consolidated pension plan charge reduced pre-tax income thereby increasing the effect of credits and ofyears still under review, the favorable resolution of state issues and an increase in state credits. The 2013 rate for state income taxes is lower than 2015 and 2014 due to an increase in state credits, including the benefit from filing amended returns to claim additional credits. The 2013 benefit from the Domestic Manufacturing Deduction is greater than 2015 and 2014 due to the amendment of prior years’ tax issues on our 2011 effective tax rate.returns to claim the additional benefit available in years still under review by the Internal Revenue Service.
A-46A-47
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
The tax effects of significant temporary differences that comprise tax balances were as follows:
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| Current deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
| Net operating loss and credit carryforwards | $ | 4 | $ | 1 | ||||
| Compensation related costs | 79 | 171 | ||||||
| Total current deferred tax assets | 83 | 172 | ||||||
| Current deferred tax liabilities: | ||||||||
| Insurance related costs | (116 | ) | (111 | ) | ||||
| Inventory related costs | (234 | ) | (220 | ) | ||||
| Other | (17 | ) | (31 | ) | ||||
| Total current deferred tax liabilities | (367 | ) | (362 | ) | ||||
| Current deferred taxes | $ | (284 | ) | $ | (190 | ) | ||
| Long-term deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
| Compensation related costs | $ | 564 | $ | 749 | ||||
| Lease accounting | 87 | 93 | ||||||
| Closed store reserves | 56 | 66 | ||||||
| Insurance related costs | 77 | 76 | ||||||
| Net operating loss and credit carryforwards | 82 | 86 | ||||||
| Other | 2 | 23 | ||||||
| Subtotal | 868 | 1,093 | ||||||
| Valuation allowance | (32 | ) | (42 | ) | ||||
| Total long-term deferred tax assets | 836 | 1,051 | ||||||
| Long-term deferred tax liabilities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation | (1,636 | ) | (1,698 | ) | ||||
| Long-term deferred taxes | $ | (800 | ) | $ | (647 | ) | ||
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Current deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
| Net operating loss and credit carryforwards | $ | 10 | $ | 5 | ||||
| Compensation related costs | 83 | 88 | ||||||
| Other | 61 | 14 | ||||||
| Subtotal | 154 | 107 | ||||||
| Valuation allowance | (9 | ) | (7 | ) | ||||
| Total current deferred tax assets | 145 | 100 | ||||||
| Current deferred tax liabilities: | ||||||||
| Insurance related costs | (56 | ) | (99 | ) | ||||
| Inventory related costs | (310 | ) | (288 | ) | ||||
| Total current deferred tax liabilities | (366 | ) | (387 | ) | ||||
| Current deferred taxes | $ | (221 | ) | $ | (287 | ) | ||
| Long-term deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
| Compensation related costs | $ | 709 | $ | 721 | ||||
| Lease accounting | 106 | 129 | ||||||
| Closed store reserves | 57 | 50 | ||||||
| Insurance related costs | 29 | 77 | ||||||
| Net operating loss and credit carryforwards | 128 | 115 | ||||||
| Other | 17 | 2 | ||||||
| Subtotal | 1,046 | 1,094 | ||||||
| Valuation allowance | (43 | ) | (42 | ) | ||||
| Total long-term deferred tax assets | 1,003 | 1,052 | ||||||
| Long-term deferred tax liabilities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | (2,755 | ) | (2,261 | ) | ||||
| Total long-term deferred tax liabilities | (2,755 | ) | (2,261 | ) | ||||
| Long-term deferred taxes | $ | (1,752 | ) | $ | (1,209 | ) | ||
On November 19, 2015, the Internal Revenue Service issued implementation guidance for retailers with respect to recently issued tangible property regulations. The adoption of this guidance resulted in the immediate deduction of qualifying costs related to current and prior year store remodels, resulting in an increase in long-term deferred tax liability and current income tax receivable. The adoption of this guidance, along with the impact of the Roundy’s merger, resulted in the increase in the deferred tax liability related to depreciation and amortization from January 31, 2015 to January 30, 2016.
At February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, the Company had net operating loss carryforwards for state income tax purposes of $1,275.$1,460. These net operating loss carryforwards expire from 20142016 through 2032.2036. The utilization of certain of the Company’s state net operating loss carryforwards may be limited in a given year. Further, based on the analysis described below, the Company has recorded a valuation allowance against some of the deferred tax assets resulting from its state net operating losses.
A-48
At February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, the Company had state credit carryforwards of $24, some$65, most of which expire from 20132016 through 2027. The utilization of certain of the Company’s credits may be limited in a given year. Further, based on the analysis described below, the Company has recorded a valuation allowance against some of the deferred tax assets resulting from its state credits.
At January 30, 2016, the Company had federal net operating loss carryforwards of $62. These net operating loss carryforwards expire from 2030 through 2034. The utilization of certain of the Company’s federal net operating loss carryforwards may be limited in a given year. Further, based on the analysis described below, the Company has not recorded a valuation allowance against the deferred tax assets resulting from its federal net operating losses.
The Company regularly reviews all deferred tax assets on a tax filer and jurisdictional basis to estimate whether these assets are more likely than not to be realized based on all available evidence. This evidence includes historical taxable income, projected future taxable income, the expected timing of the reversal of existing temporary differences and the implementation of tax planning strategies. Projected future taxable income is based on expected results and assumptions as to the jurisdiction in which the income will be earned. The expected timing of the reversals of existing temporary differences is based on current tax law and the Company’s tax methods of accounting. Unless deferred tax assets are more likely than not to be realized, a valuation allowance is established to reduce the carrying value of the deferred tax asset until such time that realization becomes more likely than not. Increases and decreases in these valuation allowances are included in “Income tax expense” in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
A-47
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits, including positions impacting only the timing of tax benefits, is as follows:
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | 310 | $ | 285 | $ | 544 | ||||||
| Additions based on tax positions related to the current year | 45 | 24 | 38 | |||||||||
| Reductions based on tax positions related to the current year | (9 | ) | — | (273 | ) | |||||||
| Additions for tax positions of prior years | 1 | 24 | 13 | |||||||||
| Reductions for tax positions of prior years | (27 | ) | (11 | ) | (21 | ) | ||||||
| Settlements | (21 | ) | (12 | ) | (16 | ) | ||||||
| Ending balance | $ | 299 | $ | 310 | $ | 285 | ||||||
| 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | 246 | $ | 325 | $ | 299 | ||||||
| Additions based on tax positions related to the current year | 11 | 17 | 23 | |||||||||
| Reductions based on tax positions related to the current year | (11 | ) | (6 | ) | (10 | ) | ||||||
| Additions for tax positions of prior years | 4 | 9 | 17 | |||||||||
| Reductions for tax positions of prior years | (27 | ) | (36 | ) | (4 | ) | ||||||
| Settlements | (17 | ) | (63 | ) | — | |||||||
| Lapse of statute | (2 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Ending balance | $ | 204 | $ | 246 | $ | 325 | ||||||
In prior periods, the above table included state net operating losses which the Company believed would expire unused. These net operating losses are no longer included in the above table. Instead, the tax benefit of these losses has been included in the deferred tax table shown above and a valuation allowance has been recorded against them as described above.
The Company does not anticipate that changes in the amount of unrecognized tax benefits over the next twelve months will have a significant impact on its results of operations or financial position.
As of January 30, 2016, January 31, 2015 and February 2, 2013, January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011,1, 2014, the amount of unrecognized tax benefits that, if recognized, would impact the effective tax rate was $70, $81$83, $90 and $85$98, respectively. The Company’s disclosure of these amounts for 2011 and 2010 has changed due to the Company reclassifying state operating losses as described above.
To the extent interest and penalties would be assessed by taxing authorities on any underpayment of income tax, such amounts have been accrued and classified as a component of income tax expense. During the years ended January 30, 2016, January 31, 2015 and February 2, 2013, January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011,1, 2014, the Company recognized approximately $(8)$(5), $(24)$3 and $(2),$10, respectively, in interest and penalties (recoveries). The Company had accrued approximately $33$25, $30 and $54$41 for the payment of interest and penalties as of January 30, 2016, January 31, 2015 and February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012,1, 2014, respectively.
As of February 2, 2013,January 31, 2015, the Internal Revenue Service had concluded its field examination of the Company’s 2008our 2010 and 20092011 federal tax returns and is currently auditing tax years 20102012 and 2011.2013. The 20102012 and 2011 audit is2013 audits are expected to be completed in 2014. The Company has filed an administrative appeal within the Internal Revenue Service protesting certain adjustments proposed by the Internal Revenue Service as a result of their field work.2016.
5. Debt Obligations
Long-term debt consists of:
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| 0.40% to 0.48% Commercial paper due through March 2013 | $ | 1,645 | $ | 370 | ||||
| 2.20% to 8.00% Senior notes due through 2042 | 6,587 | 7,078 | ||||||
| 5.00% to 12.75% Mortgages due in varying amounts through 2034 | 60 | 65 | ||||||
| Other | 184 | 230 | ||||||
| Total debt | 8,476 | 7,743 | ||||||
| Less current portion | (2,700 | ) | (1,275 | ) | ||||
| Total long-term debt | $ | 5,776 | $ | 6,468 | ||||
A-48A-49
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued6. DEBT OBLIGATIONS
Long-term debt consists of:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| 0.76% to 8.00% Senior notes due through 2043 | $ | 9,826 | $ | 9,224 | ||||
| 5.00% to 12.75% Mortgages due in varying amounts through 2027 | 58 | 73 | ||||||
| 0.27% to 0.66% Commercial paper due through February 2016 | 990 | 1,275 | ||||||
| Other | 522 | 454 | ||||||
| Total debt | 11,396 | 11,026 | ||||||
| Less current portion | (2,318 | ) | (1,844 | ) | ||||
| Total long-term debt | $ | 9,078 | $ | 9,182 | ||||
In 2011, the Company issued $450 of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 2.20% due in fiscal year 2016. The proceeds of this issuance of senior notes were used to fund a portion of the Company’s obligations under the UFCW consolidated multi-employer pension fund. In 2011, the Company repaid $478 of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 6.80%.
In 2012,2015, the Company issued $500 of senior notes due in fiscal year 20222026 bearing an interest rate of 3.40% and $3503.50%, $300 of senior notes due in fiscal year 20422021 bearing an interest rate of 5.00%. In 2012, the Company repaid upon their maturity $4912.60% and $300 of senior notes due in fiscal year 2019 bearing an interest rate of 6.75%2.00%, $346 of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 6.20% and repaid $500 of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 5.50%.3.90% upon maturity. Due to the merger with Roundy’s, the Company assumed $678 of term loans, which were entirely paid off following the merger.
In 2014, the Company issued $500 of senior notes due in fiscal year 2021 bearing an interest rate of 2.95% and repaid $300 of senior notes bearing an interest rate of 4.95% upon maturity.
On January 25, 2012,June 30, 2014, the Company amended, extended and extendedrestated its $2,000 unsecured revolving credit facility. The Company entered into the amended credit facility to amend, extend and extendrestate the Company’s existing credit facility whichthat would have terminated on May 15, 2014.January 25, 2017. The amended credit facility provides for a $2,000$2,750 unsecured revolving credit facility (the “Credit Agreement”), with a termination date of January 25, 2017,June 30, 2019, unless extended as permitted under the Credit Agreement. The Company has the ability to increase the size of the Credit Agreement by up to an additional $500,$750, subject to certain conditions.
Borrowings under the Credit Agreement bear interest at the Company’s option, at either (i) LIBOR plus a market rate spread, based on the Company’s Leverage Ratio or (ii) the base rate, defined as the highest of (a) the Federal Funds Rate plus 0.5%, (b) the Bank of America prime rate, (b) the Federal Funds rate plus 0.5%, and (c) one-month LIBOR plus 1.0%, plus a market rate spread based on the Company’s Leverage Ratio. The Company will also pay a Commitment Fee based on the Leverage Ratio and Letter of Credit fees equal to a market rate spread based on the Company’s Leverage Ratio. The Credit Agreement contains covenants, which, among other things, require the maintenance of a Leverage Ratio of not greater than 3.50:1.00 and a Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio of not less than 1.70:1.00. In the first quarter of 2012, the covenants were amended to exclude up to $1,000 in expense related to the Company’s commitment to fund the UFCW consolidated pension plan. The Company may repay the Credit Agreement in whole or in part at any time without premium or penalty. The Credit Agreement is not guaranteed by the Company’s subsidiaries.
In addition to the Credit Agreement, the Company maintained two uncommitted money market lines totaling $75 in the aggregate. The money market lines allow the Company to borrow from banks at mutually agreed upon rates, usually at rates below the rates offered under the credit agreement. As of February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, the Company had $1,645$990 of borrowings of commercial paper, with a weighted average interest rate of 0.66%, and no borrowings under its Credit Agreement and money market lines.
Agreement. As of February 2, 2013,January 31, 2015, the Company had $1,275 of borrowings of commercial paper, with a weighted average interest rate of 0.37%, and no borrowings under its Credit Agreement.
As of January 30, 2016, the Company had outstanding letters of credit in the amount of $192,$244, of which $13 reducereduces funds available under the Company’s Credit Agreement. The letters of credit are maintained primarily to support performance, payment, deposit or surety obligations of the Company.
A-50
Most of the Company’s outstanding public debt is subject to early redemption at varying times and premiums, at the option of the Company. In addition, subject to certain conditions, some of the Company’s publicly issued debt will be subject to redemption, in whole or in part, at the option of the holder upon the occurrence of a redemption event, upon not less than five days’ notice prior to the date of redemption, at a redemption price equal to the default amount, plus a specified premium. “Redemption Event” is defined in the indentures as the occurrence of (i) any person or group, together with any affiliate thereof, beneficially owning 50% or more of the voting power of the Company, (ii) any one person or group, or affiliate thereof, succeeding in having a majority of its nominees elected to the Company’s Board of Directors, in each case, without the consent of a majority of the continuing directors of the Company or (iii) both a change of control and a below investment grade rating.
A-49
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
The aggregate annual maturities and scheduled payments of long-term debt, as of year-end 2012,2015, and for the years subsequent to 20122015 are:
| 2013 | $ | 2,700 | |
| 2014 | 320 | ||
| 2015 | 517 | ||
| 2016 | 463 | ||
| 2017 | 607 | ||
| Thereafter | 3,869 | ||
| Total debt | $ | 8,476 |
| 2016 | $ | 2,318 | |
| 2017 | 735 | ||
| 2018 | 1,307 | ||
| 2019 | 774 | ||
| 2020 | 724 | ||
| Thereafter | 5,538 | ||
| Total debt | $ | 11,396 |
6. Derivative Financial Instruments7. DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
GAAP defines derivatives, requires that derivatives be carried at fair value on the balance sheet, and provides for hedge accounting when certain conditions are met. The Company’s derivative financial instruments are recognized on the balance sheet at fair value. Changes in the fair value of derivative instruments designated as “cash flow” hedges, to the extent the hedges are highly effective, are recorded in other comprehensive income, net of tax effects. Ineffective portions of cash flow hedges, if any, are recognized in current period earnings. Other comprehensive income or loss is reclassified into current period earnings when the hedged transaction affects earnings. Changes in the fair value of derivative instruments designated as “fair value” hedges, along with corresponding changes in the fair values of the hedged assets or liabilities, are recorded in current period earnings. Ineffective portions of fair value hedges, if any, are recognized in current period earnings.
The Company assesses, both at the inception of the hedge and on an ongoing basis, whether derivatives used as hedging instruments are highly effective in offsetting the changes in the fair value or cash flow of the hedged items. If it is determined that a derivative is not highly effective as a hedge or ceases to be highly effective, the Company discontinues hedge accounting prospectively.
Interest Rate Risk Management
The Company is exposed to market risk from fluctuations in interest rates. The Company manages its exposure to interest rate fluctuations through the use of a commercial paper program, interest rate swaps (fair value hedges) and forward-starting interest rate swaps (cash flow hedges). The Company’s current program relative to interest rate protection contemplates hedging the exposure to changes in the fair value of fixed-rate debt attributable to changes in interest rates. To do this, the Company uses the following guidelines: (i) use average daily outstanding borrowings to determine annual debt amounts subject to interest rate exposure, (ii) limit the average annual amount subject to interest rate reset and the amount of floating rate debt to a combined total of $2,500 or less, (iii) include no leveraged products, and (iv) hedge without regard to profit motive or sensitivity to current mark-to-market status.
A-51
The Company reviews compliance with these guidelines annually with the Financial Policy Committee of the Board of Directors. These guidelines may change as the Company’s needs dictate.
A-50
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
Fair Value Interest Rate Swaps
The table below summarizes the outstanding interest rate swaps designated as fair value hedges as of February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016 and January 28, 2012.31, 2015.
| 2012 | 2011 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pay | Pay | Pay | Pay | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Floating | Fixed | Floating | Fixed | Pay Floating | Pay Fixed | Pay Floating | Pay Fixed | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Notional amount | $ | 475 | $ | — | $ | 1,625 | $ | — | $ | 100 | $— | $ | 100 | $— | |||||||||||||||
| Number of contracts | 6 | — | 18 | — | 2 | — | 2 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Duration in years | 1.41 | — | 0.74 | — | 2.92 | — | 3.94 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Average variable rate | 3.29 | % | — | 3.84 | % | — | 6.00 | % | — | 5.83 | % | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Average fixed rate | 5.38 | % | — | 5.87 | % | — | 6.80 | % | — | 6.80 | % | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Maturity | Between | Between | December 2018 | December 2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| April 2013 and | April 2012 and | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 2018 | April 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
During 2012, fourteen of the Company’s fair value swaps, with a notional amount of $1,250, matured.
In 2012, the Company entered into two fair value swaps with a total notional amount of $100.
The gain or loss on these derivative instruments as well as the offsetting gain or loss on the hedged items attributable to the hedged risk areis recognized in current incomeearnings as “Interest expense.” These gains and losses for 20122015 and 20112014 were as follows:
| Year-To-Date | Year-To-Date | |||||||||||||||
| February 2, 2013 | January 28, 2012 | January 30, 2016 | January 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||
| Gain/(Loss) on | Gain/(Loss) on | Gain/(Loss) on | Gain/(Loss) on | |||||||||||||
| Income Statement Classification | Swaps | Borrowings | Swaps | Borrowings | ||||||||||||
| Consolidated Statements of Operations Classification | Gain/ (Loss) on Swaps | Gain/ (Loss) on Borrowings | Gain/ (Loss) on Swaps | Gain/ (Loss) on Borrowings | ||||||||||||
| Interest Expense | $(24) | $16 | $(20) | $22 | $1 | $(1) | $2 | $(2) | ||||||||
The following table summarizes the location and fair value of derivative instruments designated as fair value hedges on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets:
| Asset Derivatives | ||||||
| Fair Value | ||||||
| February 2, | January 28, | Balance Sheet | ||||
| Derivatives Designated as Fair Value Hedging Instruments | 2013 | 2012 | Location | |||
| Interest Rate Hedges | $1 | $25 | Other Assets | |||
| Asset Derivatives | ||||||
| Fair Value | ||||||
| Derivatives Designated as Fair Value Hedging Instruments | January 30, 2016 | January 31, 2015 | Balance Sheet Location | |||
| Interest Rate Hedges | $1 | $— | (Other long-term | |||
| liabilities)/Other | ||||||
| assets | ||||||
Cash Flow Forward-Starting Interest Rate Swaps
As of February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, the Company had 17seven forward-starting interest rate swap agreements with maturity dates between April 2013 and January 2014of August 2017 with an aggregate notional amount totaling $850. In 2012, the Company entered into seven of these forward-starting interest rate swap agreements with an aggregate notional amount totaling $350.$400. A forward-starting interest rate swap is an agreement that effectively hedges the variability in future benchmark interest payments attributable to changes in interest rates on the forecasted issuance of fixed-rate debt. The Company entered into these forward-starting interest rate swaps in order to lock in fixed interest rates on its forecasted issuance of debt in August 2017. Accordingly, the forward-starting interest rate swaps were designated as cash-flow hedges as defined by GAAP. As of January 30, 2016, the fair value of the interest rate swaps was recorded in other long-term liabilities for $27 and accumulated other comprehensive loss for $17 net of tax.
A-52
As of January 31, 2015, the Company had four forward-starting interest rate swap agreements with maturity dates of October 2015 with an aggregate notional amount totaling $300 and seven forward-starting interest rate swap agreements with maturity dates of August 2017 with an aggregate notional amount totaling $400. The Company entered into these forward-starting interest rate swaps in order to lock in fixed interest rates on its forecasted issuances of debt in fiscal year 2013. Accordingly, the forward-starting interest rate swaps were designated as cash-flow hedges as defined by GAAP. As of February 2, 2013, the fair value of the interest rates swaps was recorded in other investments for $5October 2015 and accumulated other comprehensive income for $3 net of tax.
A-51
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
As of January 28, 2012, the Company maintained 24 forward-starting interest rate swap derivatives with maturity dates between May 2012 and April 2013 with an aggregate notional amount totaling $1,200. The Company entered into the forward-starting interest rate swaps in order to lock in fixed interest rates on its forecasted issuances of debt in fiscal years 2012 and 2013.August 2017. Accordingly, the forward-starting interest rate swaps were designated as cash-flow hedges as defined by GAAP. As of January 28, 2012,31, 2015, the fair value of the interest ratesrate swaps was recorded in other long-term liabilities for $41$39 and accumulated other comprehensive loss for $26$25 net of tax.
During 2012,2015, the Company terminated 14eight forward-starting interest rate swap agreements with maturity dates of May 2012October 2015 and January 2016 with an aggregate notional amount totaling $700.$600. Four of these forward-starting interest rate swap agreements, with an aggregate notional amount totaling $300, were entered into and terminated in 2015. These forward-starting interest rate swap agreements were hedging the variability in future benchmark interest payments attributable to changing interest rates on the forecasted issuance of fixed-rate debt issued in 2012.2015. As discussed in Note 5,6, the Company issued $850$1,100 of senior notes in 2012.2015. Since these forward-starting interest rate swap agreements were classified as cash flow hedges, the unamortized loss of $27$17, $11 net of tax, has been deferred net of tax in accumulated other comprehensive income (“AOCI”)AOCI and will be amortized to earnings as the interest payments are made.
The following table summarizes the effect of the Company’s derivative instruments designated as cash flow hedges for 20122015 and 2011:2014:
| Year-To-Date | Year-To-Date | |||||||||||||||||||
| Amount of Gain/(Loss) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount of Gain/(Loss) | Reclassified from AOCI | |||||||||||||||||||
| in AOCI on Derivative | into Income (Effective | Location of Gain/(Loss) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives in Cash Flow Hedging | (Effective Portion) | Portion) | Reclassified into Income | |||||||||||||||||
| Relationships | 2012 | 2011 | 2012 | 2011 | (Effective Portion) | |||||||||||||||
| Derivatives in Cash Flow Hedging Relationships | Amount of Gain/ (Loss) in AOCI on Derivative (Effective Portion) | Amount of Gain/ (Loss) Reclassified from AOCI into Income (Effective Portion) | Location of Gain/ (Loss) Reclassified into Income (Effective Portion) | |||||||||||||||||
| 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||
| Forward-Starting Interest Rate | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Swaps, net of tax* | $(14) | $(30) | $(3) | $(1) | Interest expense | $(51) | $(49) | $(1) | $(1) | Interest expense | ||||||||||
| * | The amounts of Gain/(Loss) in AOCI on derivatives include unamortized proceeds and payments from forward-starting interest rate swaps once classified as cash flow hedges that were terminated prior to end of |
For the above fair value and cash flow interest rate swaps, the Company has entered into International Swaps and Derivatives Association master netting agreements that permit the net settlement of amounts owed under their respective derivative contracts. Under these master netting agreements, net settlement generally permits the Company or the counterparty to determine the net amount payable for contracts due on the same date and in the same currency for similar types of derivative transactions. These master netting agreements generally also provide for net settlement of all outstanding contracts with a counterparty in the case of an event of default or a termination event.
Collateral is generally not required of the counterparties or of the Company under these master netting agreements. As of January 30, 2016 and January 31, 2015, no cash collateral was received or pledged under the master netting agreements.
A-53
The effect of the net settlement provisions of these master netting agreements on the Company’s derivative balances upon an event of default or termination event is as follows as of January 30, 2016 and January 31, 2015:
| January 30, 2016 | Gross Amount Recognized | Gross Amounts Offset in the Balance Sheet | Net Amount Presented in the Balance Sheet | Gross Amounts Not Offset in the Balance Sheet | Net Amount | |||||||
| Financial Instruments | Cash Collateral | |||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||
| Fair Value Interest | ||||||||||||
| Rate Swaps | $1 | $— | $1 | $— | $— | $1 | ||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||
| Cash Flow Forward-Starting | ||||||||||||
| Interest Rate Swaps | 27 | — | 27 | — | — | 27 | ||||||
| January 31, 2015 | Gross Amount Recognized | Gross Amounts Offset in the Balance Sheet | Net Amount Presented inthe Balance Sheet | Gross Amounts Not Offset in the Balance Sheet | Net Amount | |||||||
Financial Instruments | Cash Collateral | |||||||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||
| Cash Flow Forward-Starting | ||||||||||||
| Interest Rate Swaps | $39 | $— | $39 | $— | $— | $39 | ||||||
Commodity Price Protection
The Company enters into purchase commitments for various resources, including raw materials utilized in its manufacturing facilitiesfood production plants and energy to be used in its stores, warehouses, manufacturing facilitiesfood production plants and administrative offices. The Company enters into commitments expecting to take delivery of and to utilize those resources in the conduct of normal business. Those commitments for which the Company expects to utilize or take delivery in a reasonable amount of time in the normal course of business qualify as normal purchases and normal sales.
7. Fair Value Measurements8. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
GAAP establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs used to measure fair value. The three levels of the fair value hierarchy defined in the standards are as follows:
Level 1 – Quoted prices are available in active markets for identical assets or liabilities;
Level 2 – Pricing inputs are other than quoted prices in active markets included in Level 1, which are either directly or indirectly observable;
Level 3 – Unobservable pricing inputs in which little or no market activity exists, therefore requiring an entity to develop its own assumptions about the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability.
A-52A-54
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
For items carried at (or adjusted to) fair value in the consolidated financial statements, the following tables summarize the fair value of these instruments at February 2, 2013January 30, 2016 and January 28, 2012:31, 2015:
February 2, 2013January 30, 2016 Fair Value Measurements Using
| Quoted Prices in | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Active Markets | Significant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| for Identical | Significant Other | Unobservable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assets | Observable Inputs | Inputs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trading Securities | $48 | $ — | $— | $ 48 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-Sale Securities | $ | 8 | $ | — | $ | 20 | $ | 28 | 41 | — | — | 41 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-Lived Assets | — | — | 8 | 8 | — | — | 7 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest Rate Hedges | — | 6 | — | 6 | — | (26 | ) | — | (26 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 8 | $ | 6 | $ | 28 | $ | 42 | $89 | $(26 | ) | $ 7 | $ 70 | |||||||||||||||||||||
January 28, 201231, 2015 Fair Value Measurements Using
| Quoted Prices in | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Active Markets | Significant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| for Identical | Significant Other | Unobservable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assets | Observable Inputs | Inputs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trading Securities | $47 | $ — | $— | $ 47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-Sale Securities | $ | 8 | $ | — | $ | 20 | $ | 28 | 36 | — | — | 36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrants | — | 26 | — | 26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-Lived Assets | — | — | 23 | 23 | — | — | 22 | 22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest Rate Hedges | — | (16 | ) | — | (16 | ) | — | (39 | ) | — | (39 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 8 | $ | (16 | ) | $ | 43 | $ | 35 | $83 | $(13 | ) | $22 | $ 92 | ||||||||||||||||||||
In 2015 and 2014, unrealized gains on the Level 1 available-for-sale securities totaled $5 and $8, respectively.
The Company values warrants using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The Black-Scholes option-pricing model is classified as a Level 2 input.
The Company values interest rate hedges using observable forward yield curves. These forward yield curves are classified as Level 2 inputs.
Fair value measurements of non-financial assets and non-financial liabilities are primarily used in the impairment analysis of goodwill, other intangible assets, long-lived assets and in the valuation of store lease exit costs. The Company reviews goodwill and otherindefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment annually, during the fourth quarter of each fiscal year, and as circumstances indicate the possibility of impairment. See Note 23 for further discussion related to the Company’s carrying value of goodwill and its goodwill impairment charge in 2010.goodwill. Long-lived assets and store lease exit costs were measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis using Level 3 inputs as defined in the fair value hierarchy. See Note 1 for further discussion of the Company’s policies and recorded amounts for impairments of long-lived assets and valuation of store lease exit costs. In 2012,2015, long-lived assets with a carrying amount of $26$53 were written down to their fair value of $8,$7, resulting in an impairment charge of $18.$46. In 2011,2014, long-lived assets with a carrying amount of $60$59 were written down to their fair value of $23,$22, resulting in an impairment charge of $37.
A-55
Mergers are accounted for using the acquisition method of accounting, which requires that the purchase price paid for an acquisition be allocated to the assets and liabilities acquired based on their estimated fair values as of the effective date of the acquisition, with the excess of the purchase price over the net assets being recorded as goodwill. See Note 2 for further discussion related to accounting for mergers.
FAIR In 2011, unrealized gains on Level 3 Available-for-Sale Securities totaled $3.VALUEOF OTHER FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Fair Value of Other Financial Instruments
Current and Long-term Debt
The fair value of the Company’s long-term debt, including current maturities, was estimated based on the quoted market prices for the same or similar issues adjusted for illiquidity based on available market evidence. If quoted market prices were not available, the fair value was based upon the net present value of the future cash flow using the forward interest rate yield curve in effect at respective year-ends. At February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, the fair value of total debt was $9,339$12,344 compared to a carrying value of $8,476.$11,396. At January 28, 2012,31, 2015, the fair value of total debt was $8,700$12,378 compared to a carrying value of $7,743.$11,026.
A-53
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
Cash and Temporary Cash Investments, Store Deposits In-Transit, Receivables, Prepaid and Other Current Assets, Trade Accounts Payable, Accrued Salaries and Wages and Other Current Liabilities
The carrying amounts of these items approximated fair value.
Long-term InvestmentsOther Assets
The fair values of these investments were estimated based on quoted market prices for those or similar investments, or estimated cash flows, if appropriate. At February 2, 2013January 30, 2016 and January 28, 2012,31, 2015, the carrying and fair value of long-term investments for which fair value is determinable were $44was $128 and $50,$133, respectively. At January 30, 2016 and January 31, 2015, the carrying value of notes receivable for which fair value is determinable was $145 and $98, respectively.
8. Leases and Lease-Financed Transactions9. ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
The following table represents the changes in AOCI by component for the years ended January 31, 2015 and January 30, 2016:
| Cash Flow Hedging Activities(1) | Available for sale Securities(1) | Pension and Postretirement Defined Benefit Plans(1) | Total(1) | ||||||||||||
| Balance at February 1, 2014 | $ (25 | ) | $12 | $(451 | ) | $(464 | ) | ||||||||
| OCI before reclassifications(2) | (25 | ) | 5 | (351 | ) | (371 | ) | ||||||||
| Amounts reclassified out of AOCI(3) | 1 | — | 22 | 23 | |||||||||||
| Net current-period OCI | (24 | ) | 5 | (329 | ) | (348 | ) | ||||||||
| Balance at January 31, 2015 | (49 | ) | 17 | (780 | ) | (812 | ) | ||||||||
| OCI before reclassifications(2) | (3 | ) | 3 | 78 | 78 | ||||||||||
| Amounts reclassified out of AOCI(3) | 1 | — | 53 | 54 | |||||||||||
| Net current-period OCI | (2 | ) | 3 | 131 | 132 | ||||||||||
| Balance at January 30, 2016 | $ (51 | ) | $20 | $(649 | ) | $(680 | ) | ||||||||
| (1) | All amounts are net of tax. | |
| (2) | Net of tax of $(14), $3 and $(206) for cash flow hedging activities, available for sale securities and pension and postretirement defined benefit plans, respectively, as of January 31, 2015. Net of tax of $(2), $2 and $45 for cash flow hedging activities, available for sale securities and pension and postretirement defined benefit plans, respectively, as of January 30, 2016. | |
A-56
| (3) | Net of tax of $13 for pension and postretirement defined benefit plans, as of January 31, 2015. Net of tax of $32 for pension and postretirement defined benefit plans as of January 30, 2016. |
The following table represents the items reclassified out of AOCI and the related tax effects for the years ended January 30, 2016, January 31, 2015 and February 1, 2014:
| For the year ended January 30, 2016 | For the year ended January 31, 2015 | For the year ended February 1, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Gains on cash flow hedging activities | ||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of unrealized gains and losses | ||||||||||||||||||
| on cash flow hedging activities(1) | $ | 1 | $ | 1 | $ | 2 | ||||||||||||
| Tax expense | — | — | (1 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Net of tax | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Pension and postretirement defined benefit | ||||||||||||||||||
| plan items | ||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of amounts included in net | ||||||||||||||||||
| periodic pension expense(2) | 85 | 35 | 98 | |||||||||||||||
| Tax expense | (32 | ) | (13 | ) | (36 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net of tax | 53 | 22 | 62 | |||||||||||||||
| Total reclassifications, net of tax | $ | 54 | $ | 23 | $ | 63 | ||||||||||||
| (1) | Reclassified from AOCI into interest expense. |
| (2) | Reclassified from AOCI into merchandise costs and OG&A expense. These components are included in the computation of net periodic pension costs (see Note 15 for additional details). |
10. LEASESAND LEASE-FINANCED TRANSACTIONS
While the Company’s current strategy emphasizes ownership of store real estate, the Company operates primarily in leased facilities. Lease terms generally range from 10 to 20 years with options to renew for varying terms. Terms of certain leases include escalation clauses, percentage rent based on sales or payment of executory costs such as property taxes, utilities or insurance and maintenance. Rent expense for leases with escalation clauses or other lease concessions are accounted for on a straight-line basis beginning with the earlier of the lease commencement date or the date the Company takes possession. Portions of certain properties are subleased to others for periods generally ranging from one to 20 years.
Rent expense (under operating leases) consists of:
| 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||||
| Minimum rentals | $ | 807 | $ | 795 | $ | 706 | ||||||||
| Contingent payments | 18 | 16 | 13 | |||||||||||
| Tenant income | (102 | ) | (104 | ) | (106 | ) | ||||||||
| Total rent expense | $ | 723 | $ | 707 | $ | 613 | ||||||||
A-57
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| Minimum rentals | $ | 727 | $ | 715 | $ | 721 | ||||||
| Contingent payments | 13 | 13 | 11 | |||||||||
| Tenant income | (112 | ) | (109 | ) | (109 | ) | ||||||
| Total rent expense | $ | 628 | $ | 619 | $ | 623 | ||||||
Minimum annual rentals and payments under capital leases and lease-financed transactions for the five years subsequent to 20122015 and in the aggregate are:
| Lease- | Capital Leases | Operating Leases | Lease- Financed Transactions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Operating | Financed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Leases | Leases | Transactions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | $ | 51 | $ | 707 | $ | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 47 | 663 | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 | 42 | 601 | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 39 | 540 | 7 | $ | 103 | $ | 967 | $ | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 38 | 467 | 8 | 72 | 922 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 62 | 853 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 57 | 774 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 52 | 674 | 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thereafter | 232 | 2,025 | 87 | 527 | 4,199 | 63 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 449 | $ | 5,003 | $ | 121 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 873 | $ | 8,389 | $ | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Less estimated executory costs included in capital leases | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net minimum lease payments under capital leases | 449 | 873 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Less amount representing interest | 171 | 293 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Present value of net minimum lease payments under capital leases | $ | 278 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Present value of net minimum lease payments under | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| capital leases | $ | 580 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total future minimum rentals under noncancellable subleases at February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016 were $243.$261.
A-5411. E
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, ContinuedARNINGSPERCOMMONSHARE
9. Earnings Per Common Share
Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per basic common share equals net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. less income allocated to participating securities divided by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per diluted common share equals net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. less income allocated to participating securities divided by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding, after giving effect to dilutive stock options. The following table provides a reconciliation of net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. and shares used in calculating net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per basic common share to those used in calculating net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per diluted common share:
| For the year ended | For the year ended | For the year ended | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| February 2, 2013 | January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings | Shares | Per | Earnings | Shares | Per | Earnings | Shares | Per | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions, except | (Numer- | (Denomi- | Share | (Numer- | (Denomi- | Share | (Numer- | (Denomi- | Share | |||||||||||||||
| per share amounts) | ator) | nator) | Amount | ator) | nator) | Amount | ator) | nator) | Amount | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| to The Kroger Co. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| per basic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| common share | $1,485 | 533 | $2.78 | $598 | 590 | $1.01 | $1,109 | 635 | $1.75 | |||||||||||||||
| Dilutive effect of | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| stock options | 4 | 3 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| to The Kroger Co. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| per diluted | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| common share | $1,485 | 537 | $2.77 | $598 | 593 | $1.01 | $1,109 | 638 | $1.74 | |||||||||||||||
| For the year ended | For the year ended | For the year ended | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| January 30, 2016 | January 31, 2015 | February 1, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings | Shares | Per | Earnings | Shares | Per | Earnings | Shares | Per | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions, except | (Numer- | (Denomi- | Share | (Numer- | (Denomi- | Share | (Numer- | (Denomi- | Share | |||||||||||||||
| per share amounts) | ator) | nator) | Amount | ator) | nator) | Amount | ator) | nator) | Amount | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per basic common share | $2,021 | 966 | $2.09 | $1,711 | 981 | $1.74 | $1,507 | 1,028 | $1.47 | |||||||||||||||
| Dilutive effect of stock options | 14 | 12 | 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per diluted common share | $2,021 | 980 | $2.06 | $1,711 | 993 | $1.72 | $1,507 | 1,040 | $1.45 | |||||||||||||||
The Company had combined undistributed and distributed earnings to participating securities totaling $18, $17 and $12 $4in 2015, 2014 and $7 in 2012, 2011 and 2010,2013, respectively.
For the years ended February 2, 2013, January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011, there wereA-58
The Company had options outstanding for approximately 12.21.9 million, 12.24.6 million and 21.24.7 million, common shares, respectively, thatfor the years ended January 30, 2016, January 31, 2015 and February 1, 2014, which were excluded from the computationcomputations of net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per diluted common share. These shares were excludedshare because their inclusion would have had an anti-dilutive effect on EPS.net earnings per diluted share.
10. Stock Option Plans12. STOCK OPTION PLANS
The Company grants options for common shares (“stock options”) to employees as well as to its non-employee directors, under various plans at an option price equal to the fair market value of the stock at the date of grant. The Company accounts for stock options under the fair value recognition provisions.Under this method, the Company recognizes compensation expense for all share-based payments granted. The Company recognizes share-based compensation expense, net of an estimated forfeiture rate, over the requisite service period of the award. Equity awards may be made at one of four meetings of its Board of Directors occurring shortly after the Company’s release of quarterly earnings. The 20122015 primary grant was made in conjunction with the June meeting of the Company’s Board of Directors. Certain changes to the stock option compensation strategy were put into effect in 2015, which resulted in a reduction to the number of stock options granted in 2015, compared to 2014 and 2013.
Stock options typically expire 10 years from the date of grant. Stock options vest between one and five years from the date of grant. At February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, approximately 1537 million common shares were available for future option grants under these plans.
In addition to the stock options described above, the Company awards restricted stock to employees and non-employee directors under various plans. The restrictions on these awards generally lapse between one and five years from the date of the awards. The Company records expense for restricted stock awards in an amount equal to the fair market value of the underlying shares on the grant date of the award, over the period the awards lapse. As of February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, approximately 821 million common shares were available under the 2005, 2008, 2011 and 2011
A-55
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
2014 Long-Term Incentive Plans (the “Plans”) for future restricted stock awards or shares issued to the extent performance criteria are achieved. The Company has the ability to convert shares available for stock options under the Plans to shares available for restricted stock awards. Under some of the Plans, four shares available for option awards can be converted into one share available for restricted stock awards.
All awards become immediately exercisable upon certain changes of control of the Company.
Stock Options
Changes in options outstanding under the stock option plans are summarized below:
| Shares | Weighted- | Shares subject to option (in millions) | Weighted- average exercise price | |||||||||||||||||
| subject | average | |||||||||||||||||||
| to option | exercise | |||||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | price | |||||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2009 | 34.7 | $ | 21.30 | |||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2012 | 53.0 | $ | 11.30 | |||||||||||||||||
| Granted | 3.7 | $ | 20.23 | 8.4 | $ | 18.84 | ||||||||||||||
| Exercised | (2.0 | ) | $ | 16.31 | (17.7 | ) | $ | 11.11 | ||||||||||||
| Canceled or Expired | (0.5 | ) | $ | 22.12 | (0.4 | ) | $ | 12.74 | ||||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2010 | 35.9 | $ | 21.45 | |||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2013 | 43.3 | $ | 12.83 | |||||||||||||||||
| Granted | 3.9 | $ | 24.69 | 8.4 | $ | 24.71 | ||||||||||||||
| Exercised | (5.9 | ) | $ | 20.28 | (10.3 | ) | $ | 11.56 | ||||||||||||
| Canceled or Expired | (2.9 | ) | $ | 24.43 | (0.6 | ) | $ | 15.56 | ||||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2011 | 31.0 | $ | 21.80 | |||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2014 | 40.8 | $ | 15.56 | |||||||||||||||||
| Granted | 4.1 | $ | 22.04 | 3.4 | $ | 38.40 | ||||||||||||||
| Exercised | (6.7 | ) | $ | 18.35 | (8.9 | ) | $ | 13.54 | ||||||||||||
| Canceled or Expired | (1.9 | ) | $ | 23.28 | (0.4 | ) | $ | 19.98 | ||||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2012 | 26.5 | $ | 22.61 | |||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2015 | 34.9 | $ | 18.26 | |||||||||||||||||
A-59
A summary of options outstanding, exercisable and exercisableexpected to vest at February 2, 2013January 30, 2016 follows:
| Weighted- | ||||||||||||||
| average | Weighted- | Weighted- | ||||||||||||
| Range of Exercise | Number | remaining | average | Options | average | |||||||||
| Prices | outstanding | contractual life | exercise price | exercisable | exercise price | |||||||||
| (in millions) | (in years) | (in millions) | ||||||||||||
| $13.78 - $17.30 | 2.8 | 2.22 | $16.38 | 2.8 | $16.38 | |||||||||
| $17.31 - $20.15 | 4.1 | 2.38 | $18.68 | 4.0 | $18.67 | |||||||||
| $20.16 - $22.33 | 6.9 | 8.52 | $21.21 | 1.6 | $20.21 | |||||||||
| $22.34 - $26.13 | 6.4 | 7.45 | $23.71 | 3.6 | $23.32 | |||||||||
| $26.14 - $28.62 | 6.3 | 4.84 | $28.35 | 6.0 | $28.36 | |||||||||
| $13.78 - $28.62 | 26.5 | 5.77 | $22.61 | 18.0 | $22.57 | |||||||||
| Number of shares | Weighted- average remaining contractual life | Weighted- average exercise price | Aggregate | |||||
| (in millions) | (in years) | (in millions) | ||||||
| Options Outstanding | 34.9 | 6.20 | $18.26 | 719 | ||||
| Options Exercisable | 21.4 | 5.05 | $14.24 | 526 | ||||
| Options Expected to Vest | 13.2 | 8.02 | $24.53 | 189 |
The weighted-average remaining contractual life for options exercisable at February 2, 2013, was approximately 4.5 years. The intrinsic value of options outstanding and exercisable at February 2, 2013 was $143 and $99, respectively.
A-56
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
Restricted stock
Changes in restricted stock outstanding under the restricted stock plans are summarized below:
| Restricted | Restricted shares outstanding (in millions) | Weighted- average grant-date fair value | |||||||||||||||
| shares | Weighted-average | ||||||||||||||||
| outstanding | grant-date | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | fair value | ||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2009 | 4.4 | $24.25 | |||||||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2012 | 8.6 | $ | 11.34 | ||||||||||||||
| Granted | 2.4 | $20.25 | 6.3 | $ | 18.84 | ||||||||||||
| Lapsed | (2.3 | ) | $23.62 | (5.1 | ) | $ | 11.49 | ||||||||||
| Canceled or Expired | (0.1 | ) | $23.13 | (0.2 | ) | $ | 13.66 | ||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2010 | 4.4 | $22.39 | |||||||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2013 | 9.6 | $ | 16.16 | ||||||||||||||
| Granted | 2.5 | $24.63 | 6.1 | $ | 24.76 | ||||||||||||
| Lapsed | (2.5 | ) | $21.96 | (5.2 | ) | $ | 16.52 | ||||||||||
| Canceled or Expired | (0.2 | ) | $23.80 | (0.3 | ) | $ | 18.67 | ||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2011 | 4.2 | $23.92 | |||||||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2014 | 10.2 | $ | 21.04 | ||||||||||||||
| Granted | 2.6 | $22.23 | 3.2 | $ | 38.34 | ||||||||||||
| Lapsed | (2.4 | ) | $24.34 | (5.4 | ) | $ | 21.49 | ||||||||||
| Canceled or Expired | (0.1 | ) | $23.28 | (0.4 | ) | $ | 22.80 | ||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2012 | 4.3 | $22.67 | |||||||||||||||
| Outstanding, year-end 2015 | 7.6 | $ | 28.01 | ||||||||||||||
The weighted-average grant date fair value of stock options granted during 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 20102013 was $4.39, $6.00$9.78, $5.98 and $5.12,$4.49, respectively. The fair value of each stock option grant was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model, based on the assumptions shown in the table below. The Black-Scholes model utilizes extensiveaccounting judgment and financial estimates, including the term employeesoption holders are expected to retain their stock options before exercising them, the volatility of the Company’s stockshare price over that expected term, the dividend yield over the term and the number of awards expected to be forfeited before they vest. Using alternative assumptions in the calculation of fair value would produce fair values for stock option grants that could be different than those used to record stock-based compensation expense in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The decreaseincrease in the fair value of the stock options granted during 2012,2015, compared to 2011,2014, resulted primarily from a decreasean increase in the Company’s share price, a decrease in the weighted average risk-free interest rate and an increase inwhich decreased the expected dividend yield. The increase in the fair value of the stock options granted in 2011,during 2014, compared to 2010,2013, resulted primarily from an increase in the Company’s share price.price, which decreased the expected dividend yield, and an increase in the weighted average risk-free interest rate.
A-60
The following table reflects the weighted-average assumptions used for grants awarded to option holders:
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||||
| Weighted average expected volatility | 26.49 | % | 26.31 | % | 26.87 | % | 24.07 | % | 25.29 | % | 26.34 | % | |||||
| Weighted average risk-free interest rate | 0.97 | % | 2.16 | % | 2.57 | % | 2.12 | % | 2.06 | % | 1.87 | % | |||||
| Expected dividend yield | 2.49 | % | 1.90 | % | 2.00 | % | 1.20 | % | 1.51 | % | 1.82 | % | |||||
| Expected term (based on historical results) | 6.9 years | 6.9 years | 6.9 years | 7.2 years | 6.6 years | 6.8 years | |||||||||||
The weighted-average risk-free interest rate was based on the yield of a treasury note as of the grant date, continuously compounded, which matures at a date that approximates the expected term of the options. The dividend yield was based on our history and expectation of dividend payouts. Expected volatility was determined based upon historical stock volatilities; however, implied volatility was also considered. Expected term was determined based upon a combination of historical exercise and cancellation experience as well as estimates of expected future exercise and cancellation experience.
A-57
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
Total stock compensation recognized in 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 20102013 was $82, $81$165, $155 and $79,$107, respectively. Stock option compensation recognized in 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 20102013 was $22, $22$31, $32 and $25,$24, respectively. Restricted shares compensation recognized in 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 20102013 was $60, $59$134, $123 and $54$83, respectively.
The total intrinsic value of options exercised was $44, $24$217, $142 and $11$115 in 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 2010,2013, respectively. The total amount of cash received in 20122015 by the Company from the exercise of options granted under share-based payment arrangements was $110.$120. As of February 2, 2013,January 30, 2016, there was $96$206 of total unrecognized compensation expense remaining related to non-vested share-based compensation arrangements granted under the Company’s equity award plans. This cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of approximately two years. The total fair value of options that vested was $23, $33, $26 and $37$20 in 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 2010,2013, respectively.
Shares issued as a result of stock option exercises may be newly issued shares or reissued treasury shares. Proceeds received from the exercise of options, and the related tax benefit, may be utilized to repurchase the Company’s common shares under a stock repurchase program adopted by the Company’s Board of Directors. During 2012,2015, the Company repurchased approximately fourfive million common shares in such a manner.
11. Commitments and Contingencies13. COMMITMENTSAND CONTINGENCIES
The Company continuously evaluates contingencies based upon the best available evidence.
The Company believes that allowances for loss have been provided to the extent necessary and that its assessment of contingencies is reasonable. To the extent that resolution of contingencies results in amounts that vary from the Company’s estimates, future earnings will be charged or credited.
The principal contingencies are described below:
Insurance — The Company’s workers’ compensation risks are self-insured in most states. In addition, other workers’ compensation risks and certain levels of insured general liability risks are based on retrospective premium plans, deductible plans, and self-insured retention plans. The liability for workers’ compensation risks is accounted for on a present value basis. Actual claim settlements and expenses incident thereto may differ from the provisions for loss. Property risks have been underwritten by a subsidiary and are all reinsured with unrelated insurance companies. Operating divisions and subsidiaries have paid premiums, and the insurance subsidiary has provided loss allowances, based upon actuarially determined estimates.
A-61
Litigation —On October 6, 2006, the Company petitioned the Tax Court (Ralphs Grocery Company and Subsidiaries, formerly known as Ralphs Supermarkets, Inc. v. Commissioner of Internal Revenue, Docket No. 20364-06–) for a redetermination of deficiencies asserted by the Commissioner of Internal Revenue. The dispute at issue involved a 1992 transaction in which Ralphs Holding Company acquired the stock of Ralphs Grocery Company and made an election under Section 338(h)(10) of the Internal Revenue Code. The Commissioner determined that the acquisition of the stock was not a purchase as defined by Section 338(h)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code and that the acquisition therefore did not qualify for a Section 338(h)(10) election. On January 27, 2011, the Tax Court issued its opinion upholding the Company’s position that the acquisition of the stock qualified as a purchase, granting the Company’s motion for partial summary judgment and denying the Tax Commissioner’s motion. All remaining issues in the matter had been resolved and the Tax Court entered its decision on May 2, 2012. On July 24, 2012, the Tax Commissioner filed a notice with the United States Court of Appeals for the 9th Circuit to appeal the decision of the Tax Court.
Subsequent to the filing of the notice to appeal the government requested the dismissal of the case. On November 14, 2012, the United States Court of Appeals for the 9th Circuit issued its dismissal order with prejudice, finally resolving all issues in the matter.
Various claims and lawsuits arising in the normal course of business, including suits charging violations of certain antitrust, wage and hour, or civil rights laws, as well as product liability cases, are pending against the Company. Some of these suits purport or have been determined to be class actions and/or seek substantial damages. Any damages that may be awarded in antitrust cases will be automatically trebled. Although it is not possible at this time to evaluate
A-58
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
the merits of all of these claims and lawsuits, nor their likelihood of success, the Company is of the belief that any resulting liability will not have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial position, results of operations, or cash flows.
The Company continually evaluates its exposure to loss contingencies arising from pending or threatened litigation and believes it has made provisions where it is reasonably possible to estimate and wherewhen an adverse outcome is probable. Nonetheless, assessing and predicting the outcomes of these matters involves substantial uncertainties. Management currently believes that the aggregate range of loss for the Company’s exposure is not material to the Company. It remains possible that despite management’s current belief, material differences in actual outcomes or changes in management’s evaluation or predictions could arise that could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, or cash flows.
Assignments —– The Company is contingently liable for leases that have been assigned to various third parties in connection with facility closings and dispositions. The Company could be required to satisfy the obligations under the leases if any of the assignees is unable to fulfill its lease obligations. Due to the wide distribution of the Company’s assignments among third parties, and various other remedies available, the Company believes the likelihood that it will be required to assume a material amount of these obligations is remote.
12. Stock14. STOCK
Preferred Shares
The Company has authorized five million shares of voting cumulative preferred shares; two million shares were available for issuance at February 2, 2013.January 30, 2016. The shares have a par value of $100 per share and are issuable in series.
Common Shares
The Company has authorized onetwo billion common shares, $1 par value per share.
On May 20, 1999,June 25, 2015, the shareholders authorized an amendment to the Amended Articles of Incorporation to increase the number of authorized common shares from one billion to two billion when theCompany’s Board of Directors determines it to beapproved a two-for-one stock split of The Kroger Co.’s common shares in the best interestform of a 100% stock dividend, which was effective July 13, 2015. All share and per share amounts in the Company.Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements and related notes have been retroactively adjusted to reflect the stock split for all periods presented.
Common Stock Repurchase Program
The Company maintains stock repurchase programs that comply with Rule 10b5-1 of the Securities Exchange Act Rule 10b5-1of 1934 to allow for the orderly repurchase of The Kroger Co. common shares, from time to time. The Company made open market purchases totaling $1,165, $1,420$500, $1,129 and $505$338 under these repurchase programs in 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 2010,2013, respectively. In addition to these repurchase programs, in December 1999, the Company began a program to repurchase common shares to reduce dilution resulting from its employee stock option plans. This program is solely funded by proceeds from stock option exercises and the related tax benefit. The Company repurchased approximately $96, $127$203, $154 and $40$271 under the stock option program during 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 2010,2013, respectively.
13. Company-Sponsored Benefit PlansA-62
15. COMPANY-SPONSORED BENEFIT PLANS
The Company administers non-contributory defined benefit retirement plans for substantially allsome non-union employees and some union-represented employees as determined by the terms and conditions of collective bargaining agreements. These include several qualified pension plans (the “Qualified Plans”) and a non-qualified planpension plans (the “Non-Qualified Plan”Plans”). The Non-Qualified Plan paysPlans pay benefits to any employee that earns in excess of the maximum allowed for the Qualified Plans by Section 415 of the Internal Revenue Code. The Company only funds obligations under the Qualified Plans. Funding for the Company-sponsored pension plans is based on a review of the specific requirements and on evaluation of the assets and liabilities of each plan.
A-59
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
In addition to providing pension benefits, the Company provides certain health care benefits for retired employees. The majority of the Company’s employees may become eligible for these benefits if they reach normal retirement age while employed by the Company. Funding of retiree health care benefits occurs as claims or premiums are paid.
The Company recognizes the funded status of its retirement plans on the Consolidated Balance Sheet.Sheets. Actuarial gains or losses, prior service costs or credits and transition obligations that have not yet been recognized as part of net periodic benefit cost are required to be recorded as a component of AOCI. All plans are measured as of the Company’s fiscal year end.
Amounts recognized in AOCI as of February 2, 2013January 30, 2016 and January 28, 2012 consist31, 2015 consists of the following (pre-tax):
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2012 | 2011 | 2012 | 2011 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net actuarial loss (gain) | $ | 1,206 | $ | 1,329 | $ | (15 | ) | $ | (21 | ) | $ | 1,191 | $ | 1,308 | |||||||||
| Prior service cost (credit) | 3 | 3 | (8 | ) | (12 | ) | (5 | ) | (9 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Transition obligation | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 1,209 | $ | 1,333 | $ | (23 | ) | $ | (33 | ) | $ | 1,186 | $ | 1,300 | |||||||||
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net actuarial loss (gain) | $ | 1,213 | $ | 1,398 | $ | (121 | ) | $ | (89 | ) | $ | 1,092 | $ | 1,309 | ||||||||||||
| Prior service cost (credit) | 1 | 1 | (66 | ) | (75 | ) | (65 | ) | (74 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 1,214 | $ | 1,399 | $ | (187 | ) | $ | (164 | ) | $ | 1,027 | $ | 1,235 | ||||||||||||
Amounts in AOCI expected to be recognized as components of net periodic pension or postretirement benefit costs in the next fiscal year are as follows (pre-tax):
| Pension | Other | |||||||||||||||||
| Benefits | Benefits | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | 2013 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net actuarial loss | $ | 101 | $ | — | $ | 101 | ||||||||||||
| Prior service cost (credit) | 1 | (4 | ) | (3 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 102 | $ | (4 | ) | $ | 98 | |||||||||||
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | Total | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2016 | 2016 | |||||||||||||||
| Net actuarial loss (gain) | $ | 62 | $ | (9 | ) | $ | 53 | ||||||||||
| Prior service credit | — | (8 | ) | (8 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 62 | $ | (17 | ) | $ | 45 | ||||||||||
Other changes recognized in other comprehensive income in 2012, 2011,2015, 2014 and 20102013 were as follows (pre-tax):
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incurred net actuarial loss (gain) | $ | (33 | ) | $ | 451 | $ | (18 | ) | $ | 5 | $ | 32 | $ | 4 | $ | (28 | ) | $ | 483 | $ | (14 | ) | |||||||||||
| Amortization of prior service | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| credit (cost) | — | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of net actuarial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| gain (loss) | (97 | ) | (64 | ) | (50 | ) | — | 2 | 3 | (97 | ) | (62 | ) | (47 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total recognized in other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| comprehensive income | (130 | ) | 386 | (69 | ) | 10 | 39 | 12 | (120 | ) | 425 | (57 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total recognized in net periodic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| benefit cost and other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| comprehensive income | $ | (41 | ) | $ | 456 | $ | (4 | ) | $ | 38 | $ | 62 | $ | 33 | $ | (3 | ) | $ | 518 | $ | 29 | ||||||||||||
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incurred net actuarial loss (gain) | $ | (83 | ) | $ | 590 | $ | (243 | ) | $ | (39 | ) | $ | 14 | $ | (97 | ) | $ | (122 | ) | $ | 604 | $ | (340 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Amortization of prior service credit | — | — | — | 11 | 7 | 4 | 11 | 7 | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of net actuarial gain (loss) | (102 | ) | (50 | ) | (102 | ) | 7 | 8 | — | (95 | ) | (42 | ) | (102 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | — | — | — | (2 | ) | (47 | ) | (30 | ) | (2 | ) | (47 | ) | (30 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Total recognized in other | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| comprehensive income (loss) | (185 | ) | 540 | (345 | ) | (23 | ) | (18 | ) | (123 | ) | (208 | ) | 522 | (468 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total recognized in net periodic benefit cost | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| and other comprehensive income | $ | (82 | ) | $ | 595 | $ | (271 | ) | $ | (22 | ) | $ | (9 | ) | $ | (95 | ) | $ | (104 | ) | $ | 586 | $ | (366 | ) | |||||||||||
A-60A-63
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
Information with respect to change in benefit obligation, change in plan assets, the funded status of the plans recorded in the Consolidated Balance Sheets, net amounts recognized at the end of fiscal years, weighted average assumptions and components of net periodic benefit cost follow:
| Pension Benefits | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Benefits | Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Qualified Plans | Non-Qualified Plan | Other Benefits | Qualified Plans | Non-Qualified Plans | Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2012 | 2011 | 2012 | 2011 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change in benefit obligation: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefit obligation at beginning of | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| fiscal year | $ | 3,348 | $ | 2,923 | $ | 217 | $ | 192 | $ | 378 | $ | 330 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefit obligation at beginning of fiscal year | $ | 4,102 | $ | 3,509 | $ | 304 | $ | 263 | $ | 275 | $ | 294 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Service cost | 44 | 41 | 3 | 3 | 16 | 13 | 62 | 48 | 3 | 3 | 10 | 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest cost | 146 | 158 | 9 | 10 | 16 | 17 | 154 | 169 | 12 | 13 | 9 | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plan participants’ contributions | — | — | — | — | 9 | 9 | — | — | — | — | 10 | 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial loss | 33 | 344 | 3 | 21 | 6 | 32 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial (gain) loss | (411 | ) | 539 | (17 | ) | 40 | (39 | ) | 14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefits paid | (131 | ) | (122 | ) | (11 | ) | (9 | ) | (23 | ) | (23 | ) | (162 | ) | (163 | ) | (17 | ) | (15 | ) | (19 | ) | (21 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 3 | 4 | — | — | — | — | (17 | ) | — | 3 | — | (2 | ) | (47 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assumption of Roundy’s benefit obligation | 194 | — | 2 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefit obligation at end of fiscal year | $ | 3,443 | $ | 3,348 | $ | 221 | $ | 217 | $ | 402 | $ | 378 | $ | 3,922 | $ | 4,102 | $ | 290 | $ | 304 | $ | 244 | $ | 275 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change in plan assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets at beginning of | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| fiscal year | $ | 2,523 | $ | 2,472 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 3,189 | $ | 3,135 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actual return on plan assets | 278 | 117 | — | — | — | — | (124 | ) | 217 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Employer contributions | 71 | 52 | 11 | 9 | 14 | 14 | 5 | — | 17 | 15 | 9 | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plan participants’ contributions | — | — | — | — | 9 | 9 | — | — | — | — | 10 | 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefits paid | (131 | ) | (122 | ) | (11 | ) | (9 | ) | (23 | ) | (23 | ) | (162 | ) | (163 | ) | (17 | ) | (15 | ) | (19 | ) | (21 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 5 | 4 | — | — | — | — | (18 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assumption of Roundy’s plan assets | 155 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets at end of fiscal year | $ | 2,746 | $ | 2,523 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 3,045 | $ | 3,189 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funded status at end of fiscal year | $ | (697 | ) | $ | (825 | ) | $ | (221 | ) | $ | (217 | ) | $ | (402 | ) | $ | (378 | ) | $ | (877 | ) | $ | (913 | ) | $ | (290 | ) | $ | (304 | ) | $ | (244 | ) | $ | (275 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net liability recognized at end of fiscal year | $ | (697 | ) | $ | (825 | ) | $ | (221 | ) | $ | (217 | ) | $ | (402 | ) | $ | (378 | ) | $ | (877 | ) | $ | (913 | ) | $ | (290 | ) | $ | (304 | ) | $ | (244 | ) | $ | (275 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
As of February 2, 2013January 30, 2016 and January 28, 2012,31, 2015, other current liabilities include $29$31 and $27,$29, respectively, of net liability recognized for the above benefit plans.
As of February 2, 2013January 30, 2016 and January 28, 2012,31, 2015, pension plan assets do not include common shares of The Kroger Co.
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Weighted average assumptions | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||||
| Discount rate – Benefit obligation | 4.29% | 4.55% | 5.60% | 4.11% | 4.40% | 5.40% | 4.62% | 3.87% | 4.99% | 4.44% | 3.74% | 4.68% | ||||||||||||
| Discount rate – Net periodic benefit cost | 4.55% | 5.60% | 6.00% | 4.40% | 5.40% | 5.80% | 3.87% | 4.99% | 4.29% | 3.74% | 4.68% | 4.11% | ||||||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets | 8.50% | 8.50% | 8.50% | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Expected long-term rate of return on | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| plan assets | 7.44% | 7.44% | 8.50% | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Rate of compensation increase – | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net periodic benefit cost | 2.82% | 2.88% | 2.92% | 2.85% | 2.86% | 2.77% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Rate of compensation increase – | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefit Obligation | 2.77% | 2.82% | 2.88% | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefit obligation | 2.71% | 2.85% | 2.86% | |||||||||||||||||||||
A-64
The Company’s discount rate assumptions were intended to reflect the rates at which the pension benefits could be effectively settled. They take into account the timing and amount of benefits that would be available under the plans. The Company’s policy for selecting the discount rates as of year-end 2012 changed from the policy as of year-end 2011 and 2010. In 2012, the Company’s policy wasis to match the plan’s cash flows to that of a hypothetical bond portfolio whose cash flow from coupons and maturities match the plan’s projected
A-61
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
benefit cash flows. The discount rates are the single rates that produce the same present value of cash flows. The selection of the 4.29%4.62% and 4.11%4.44% discount rates as of year-end 20122015 for pension and other benefits, respectively, represents the hypothetical bond portfolio using bonds with an AA or better rating constructed with the assistance of an outside consultant. In 2011 and 2010, the Company’s policy was to match the plan’s cash flows to that of a yield curve that provides the equivalent yields on zero-coupon corporate bonds for each maturity. Benefit cash flows due in a particular year can theoretically be “settled” by “investing” them in the zero-coupon bond that matures in the same year. The discount rates are the single rates that produce the same present value of cash flows. The selection of the 4.55% and 4.40% discount rates as of year-end 2011 for pension and other benefits, respectively, represents the equivalent single rates constructed under a broad-market AA yield curve constructed with the assistance of an outside consultant. A 100 basis point increase in the discount rate would decrease the projected pension benefit obligation as of February 2, 2013,January 31, 2016, by approximately $412.$438.
To determine the expected rate of return on pension plan assets held by the Company considersfor 2015, the Company considered current and anticipatedforecasted plan asset allocations as well as historical and forecasted rates of return on various asset categories. For 2012, 2011In 2015 and 2010,2014, the Company decreased the assumed a pension plan investment return rate of 8.5%.to 7.44% compared to 8.50% in 2013. The Company pension plan’s average rate of return was 9.7%6.47% for the 10 calendar years ended December 31, 2012,2015, net of all investment management fees and expenses. The ratevalue of return forall investments in the Company-sponsored defined benefit pension plans forQualified Plans during the calendar year ending December 31, 2012 was 15.0%2015 decreased 0.80%, net of investment management fees and expenses. For the past 20 years, the Company’s average annual rate of return has been 9.9%, and the average annual rate of return for the S&P 500 has been 8.5%7.99%. Based on the above information and forward looking assumptions for investments made in a manner consistent with the Company’s target allocations, the Company believes an 8.5%a 7.44% rate of return assumption is reasonable.
The Company calculates its expected return on plan assets by using the market-related value of plan assets. The market-related value of plan assets is determined by adjusting the actual fair value of plan assets for gains or losses on plan assets. Gains or losses represent the difference between actual and expected returns on plan investments for each plan year. Gains or losses on plan assets are recognized evenly over a five year period. Using a different method to calculate the market-related value of plan assets would provide a different expected return on plan assets.
On January 31, 2015, the Company adopted new mortality tables based on mortality experience and assumptions for generational mortality improvement in calculating the Company’s 2015 and 2014 Company sponsored benefit plans obligations. The tables assume an improvement in life expectancy and increase our current year benefit obligation and future net periodic benefit cost. The Company used the RP-2000 projected 2021 mortality table in calculating the Company’s 2013 Company sponsored benefit plans obligations and the 2014 and 2013 Company-sponsored net periodic benefit cost.
The funded status increased in 2012,2015, compared to 2011,2014, due mostlyprimarily to the return on plan assets, offset slightly by a decreasean increase in the discount rate used to calculateand a decrease in plan assets.
The following table provides the present valuecomponents of the Company’s net periodic benefit obligation.costs for 2015, 2014 and 2013:
The Company uses the RP-2000 projected 2018 mortality table in calculating the pension obligation.
| Pension Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Benefits | Non-Qualified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Qualified Plans | Non-Qualified Plan | Other Benefits | Qualified Plans | Plans | Other Benefits | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components of net periodic benefit cost: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Service cost | $ | 44 | $ | 41 | $ | 40 | $ | 3 | $ | 3 | $ | 2 | $ | 16 | $ | 13 | $ | 12 | $ | 62 | $ | 48 | $ | 40 | $ | 3 | $ | 3 | $ | 3 | $ | 10 | $ | 11 | $ | 17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest cost | 146 | 158 | 158 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 16 | 17 | 17 | 154 | 169 | 144 | 12 | 13 | 9 | 9 | 13 | 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets | (210 | ) | (207 | ) | (196 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (230 | ) | (228 | ) | (224 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prior service cost (credit) | — | — | — | — | 1 | (1 | ) | (4 | ) | (5 | ) | (5 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prior service credit | — | — | — | — | — | — | (11 | ) | (7 | ) | (4 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial (gain) loss | 88 | 57 | 44 | 9 | 7 | 6 | — | (2 | ) | (3 | ) | 93 | 46 | 93 | 9 | 4 | 9 | (7 | ) | (8 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net periodic benefit cost | $ | 68 | $ | 49 | $ | 46 | $ | 21 | $ | 21 | $ | 19 | $ | 28 | $ | 23 | $ | 21 | $ | 79 | $ | 35 | $ | 53 | $ | 24 | $ | 20 | $ | 21 | $ | 1 | $ | 9 | $ | 28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A-62A-65
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
The following table provides the projected benefit obligation (“PBO”), accumulated benefit obligation (“ABO”) and the fair value of plan assets for all Company-sponsored pension plans.
| Qualified Plans | Non-Qualified Plan | ||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2012 | 2011 | ||||||||||||
| PBO at end of fiscal year | $3,443 | $3,348 | $ | 221 | $ | 217 | |||||||||
| ABO at end of fiscal year | $3,278 | $3,147 | $ | 211 | $ | 209 | |||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets at end of year | $2,746 | $2,523 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||
| Non-Qualified | |||||||||||||||
| Qualified Plans | Plans | ||||||||||||||
| 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||
| PBO at end of fiscal year | $ | 3,922 | $ | 4,102 | $ | 290 | $ | 304 | |||||||
| ABO at end of fiscal year | $ | 3,786 | $ | 3,947 | $ | 280 | $ | 297 | |||||||
| Fair value of plan assets at end of year | $ | 3,045 | $ | 3,189 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||
The following table provides information about the Company’s estimated future benefit payments.
| Pension | Other | |||||||||||
| Benefits | Benefits | |||||||||||
| 2013 | $ | 151 | $ | 18 | ||||||||
| 2014 | $ | 160 | $ | 20 | ||||||||
| 2015 | $ | 170 | $ | 22 | ||||||||
| 2016 | $ | 181 | $ | 23 | ||||||||
| 2017 | $ | 193 | $ | 26 | ||||||||
| 2018 – 2022 | $ | 1,121 | $ | 157 | ||||||||
| Pension | Other | |||||||||
| Benefits | Benefits | |||||||||
| 2016 | $ | 234 | $ | 15 | ||||||
| 2017 | $ | 221 | $ | 16 | ||||||
| 2018 | $ | 230 | $ | 17 | ||||||
| 2019 | $ | 238 | $ | 18 | ||||||
| 2020 | $ | 248 | $ | 19 | ||||||
| 2021 – 2025 | $ | 1,346 | $ | 105 | ||||||
The following table provides information about the weighted average target and actual pension plan asset allocations.
| Target | Actual | ||||||||||||||||||||
| allocations | Allocations | Target allocations | Actual Allocations | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2012 | 2011 | 2015 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Pension plan asset allocation | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Global equity securities | 18.5 | % | 19.2 | % | 20.9 | % | 16.0 | % | 14.9 | % | 13.4 | % | |||||||||
| Emerging market equity securities | 8.8 | 8.9 | 8.8 | 5.4 | 5.2 | 5.8 | |||||||||||||||
| Investment grade debt securities | 9.5 | 8.1 | 10.8 | 13.1 | 11.3 | 11.2 | |||||||||||||||
| High yield debt securities | 16.4 | 17.3 | 14.1 | 12.1 | 11.9 | 12.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Private equity | 6.3 | 6.0 | 6.3 | 5.2 | 7.4 | 6.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Hedge funds | 27.5 | 27.2 | 23.3 | 34.6 | 36.0 | 37.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Real estate | 3.0 | 3.3 | 3.2 | 3.4 | 3.9 | 3.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Other | 10.0 | 10.0 | 12.6 | 10.2 | 9.4 | 9.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Total | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | |||||||||
Investment objectives, policies and strategies are set by the Pension Investment CommitteeCommittees (the “Committee”“Committees”) appointed by the CEO. The primary objectives include holding and investing the assets and distributing benefits to participants and beneficiaries of the pension plans. Investment objectives have been established based on a comprehensive review of the capital markets and each underlying plan’s current and projected financial requirements. The time horizon of the investment objectives is long-term in nature and plan assets are managed on a going-concern basis.
Investment objectives and guidelines specifically applicable to each manager of assets are established and reviewed annually. Derivative instruments may be used for specified purposes, including rebalancing exposures to certain asset classes. Any use of derivative instruments for a purpose or in a manner not specifically authorized is prohibited, unless approved in advance by the Committee.Committees.
A-66
The current target allocations shown represent 2012the 2015 targets that were established in 2011.2014. The Company will rebalance by liquidating assets whose allocation materially exceeds target, if possible, and investing in assets whose allocation is materially below target. If markets are illiquid, the Company may not be able to rebalance to target quickly. To maintain actual asset allocations consistent with target allocations, assets are reallocated or rebalanced periodically. In addition, cash flow from employer contributions and participant benefit payments can be used to fund underweight asset classes and divest overweight asset classes, as appropriate. The Company expects that cash flow will be sufficient to meet most rebalancing needs.
A-63
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
In February 2013, theThe Company contributed $100 to the Company-sponsored defined benefit pension plansis not required and does not expect to make additionalany contributions to the Qualified Plans in 2016. If the Company does make any contributions in 2013. The2016, the Company expects these contributions made during 2013 will decrease its required contributions in future years. Among other things, investment performance of plan assets, the interest rates required to be used to calculate the pension obligations, and future changes in legislation, will determine the amounts of any additional contributions. The Company expects 20132016 expense for Company-sponsored defined benefit pension plans to be approximately $80. In addition, the Company expects 401(k) Retirement Savings Account Planretirement savings account plans cash contributions and expense from automatic and matching contributions to participants to increase slightlybe approximately $200 in 2013, compared to 2012.2016.
Assumed health care cost trend rates have a significant effect on the amounts reported for the health care plans. The Company used a 7.20%6.90% initial health care cost trend rate, andwhich is assumed to decrease on a linear basis to a 4.50% ultimate health care cost trend rate in 2028, to determine its expense. A one-percentage-point change in the assumed health care cost trend rates would have the following effects:
| 1% Point | 1% Point | |||||||||||||||||
| Increase | Decrease | 1% Point Increase | 1% Point Decrease | |||||||||||||||
| Effect on total of service and interest cost components | $ | 5 | $ | (4 | ) | $ | 3 | $ | (2 | ) | ||||||||
| Effect on postretirement benefit obligation | $ | 46 | $ | (44 | ) | $ | 23 | $ | (20 | ) | ||||||||
The following table setstables set forth by level, within the fair value hierarchy, the Plan’sQualified Plans’ assets at fair value as of February 2, 2013January 30, 2016 and January 28, 2012:31, 2015:
Assets at Fair Value as of February 2, 2013
| Quoted Prices in | Significant | |||||||||||||||||
| Active Markets | Other | Significant | ||||||||||||||||
| for Identical | Observable | Unobservable | ||||||||||||||||
| Assets | Inputs | Inputs | ||||||||||||||||
| (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | Total | |||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 17 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 17 | ||||||||||
| Corporate Stocks | 375 | — | — | 375 | ||||||||||||||
| Corporate Bonds | — | 72 | — | 72 | ||||||||||||||
| U.S. Government Securities | — | 66 | — | 66 | ||||||||||||||
| Mutual Funds/Collective Trusts | 130 | 559 | — | 689 | ||||||||||||||
| Partnerships/Joint Ventures | — | 378 | — | 378 | ||||||||||||||
| Hedge Funds | — | — | 739 | 739 | ||||||||||||||
| Private Equity | — | — | 180 | 180 | ||||||||||||||
| Real Estate | — | — | 91 | 91 | ||||||||||||||
| Other | — | 139 | — | 139 | ||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 522 | $ | 1,214 | $ | 1,010 | $ | 2,746 | ||||||||||
A-64
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
Assets at Fair Value as of January 28, 201230, 2016
Quoted | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | Total | |||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 27 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 27 | ||||||||||
| Corporate Stocks | 231 | — | — | 231 | ||||||||||||||
| Corporate Bonds | — | 76 | — | 76 | ||||||||||||||
| U.S. Government Securities | — | 75 | — | 75 | ||||||||||||||
| Mutual Funds/Collective Trusts | 89 | 861 | 40 | 990 | ||||||||||||||
| Partnerships/Joint Ventures | — | 118 | — | 118 | ||||||||||||||
| Hedge Funds | — | — | 1,104 | 1,104 | ||||||||||||||
| Private Equity | — | — | 225 | 225 | ||||||||||||||
| Real Estate | — | — | 103 | 103 | ||||||||||||||
| Other | — | 96 | — | 96 | ||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 347 | $ | 1,226 | $ | 1,472 | $ | 3,045 | ||||||||||
A-67
| Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Stocks | 306 | — | — | 306 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Bonds | — | 82 | — | 82 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Government Securities | — | 91 | — | 91 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mutual Funds/Collective Trusts | 143 | 476 | — | 619 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Partnerships/Joint Ventures | — | 454 | — | 454 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Hedge Funds | — | — | 579 | 579 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Private Equity | — | — | 159 | 159 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Real Estate | — | — | 81 | 81 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | — | 152 | — | 152 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 449 | $ | 1,255 | $ | 819 | $ | 2,523 | ||||||||||||||||
Assets at Fair Value as of January 31, 2015
| Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | Total | |||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 73 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 73 | ||||||||||
| Corporate Stocks | 294 | — | — | 294 | ||||||||||||||
| Corporate Bonds | — | 80 | — | 80 | ||||||||||||||
| U.S. Government Securities | — | 78 | — | 78 | ||||||||||||||
| Mutual Funds/Collective Trusts | 123 | 503 | 40 | 666 | ||||||||||||||
| Partnerships/Joint Ventures | — | 468 | — | 468 | ||||||||||||||
| Hedge Funds | — | — | 1,158 | 1,158 | ||||||||||||||
| Private Equity | — | — | 210 | 210 | ||||||||||||||
| Real Estate | — | — | 105 | 105 | ||||||||||||||
| Other | — | 57 | — | 57 | ||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 490 | $ | 1,186 | $ | 1,513 | $ | 3,189 | ||||||||||
For measurements using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) during 20122015 and 2011,2014, a reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances is as follows:
| Hedge Funds | Private Equity | Real Estate | Hedge Funds | Private Equity | Real Estate | Collective Trusts | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ending balance, January 29, 2011 | $ | 580 | $ | 150 | $ | 62 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ending balance, February 1, 2014 | $ | 1,073 | $ | 243 | $ | 96 | $ | 39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contributions into Fund | 6 | 27 | 17 | 220 | 47 | 17 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Realized gains | — | 18 | 3 | 47 | 35 | 14 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized gains (losses) | (7 | ) | 3 | 8 | 18 | (1 | ) | 4 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distributions | — | (45 | ) | (10 | ) | (257 | ) | (54 | ) | (25 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reclass(1) | 58 | (58 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | — | 6 | 1 | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | (1 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ending balance, January 28, 2012 | 579 | 159 | 81 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ending balance, January 31, 2015 | 1,158 | 210 | 105 | 40 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contributions into Fund | 175 | 49 | 23 | 239 | 47 | 13 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Realized gains | 11 | 15 | 3 | 49 | 23 | 9 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized gains | 55 | — | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized (losses) gains | (49 | ) | (3 | ) | 3 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distributions | (81 | ) | (49 | ) | (22 | ) | (294 | ) | (50 | ) | (26 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | — | 6 | 4 | 1 | (2 | ) | (1 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ending balance, February 2, 2013 | $ | 739 | $ | 180 | $ | 91 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ending balance, January 30, 2016 | $ | 1,104 | $ | 225 | $ | 103 | $ | 40 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | In 2014, the Company reclassified $58 of Level 3 assets from Private Equity to Hedge Funds. |
See Note 78 for a discussion of the levels of the fair value hierarchy. The assets’ fair value measurement level above is based on the lowest level of any input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
A-68
The following is a description of the valuation methods used for the plan’sQualified Plans’ assets measured at fair value in the above tables:
| ● | Cash and cash equivalents: The carrying value approximates fair value. |
| ● | Corporate Stocks: The fair values of these securities are based on observable market quotations for identical assets and are valued at the closing price reported on the active market on which the individual securities are traded. |
| ● | Corporate Bonds: The fair values of these securities are primarily based on observable market quotations for similar bonds, valued at the closing price reported on the active market on which the individual securities are traded. When such quoted prices are not available, the bonds are valued using a discounted cash flow approach using current yields on similar instruments of issuers with similar credit ratings, including adjustments for certain risks that may not be observable, such as credit and liquidity risks. |
| ● | U.S. Government Securities: Certain U.S. Government securities are valued at the closing price reported in the active market in which the security is traded. Other U.S. government securities are valued based on yields currently available on comparable securities of issuers with similar credit ratings. When quoted prices are not available for similar securities, the security is valued under a discounted cash flow approach that maximizes observable inputs, such as current yields of similar instruments, but includes adjustments for certain risks that may not be observable, such as credit and liquidity risks. |
| ● | Mutual Funds/Collective Trusts: The mutual funds/collective trust funds are public investment vehicles valued using a Net Asset Value (NAV) provided by the manager of each fund. The NAV is based on the underlying net assets owned by the fund, divided by the number of shares outstanding. The NAV’s unit price is quoted on a private market that is not active. However, the NAV is based on the fair value of the underlying securities within the fund, which are traded on an active market, and valued at the closing price reported on the active market on which those individual securities are traded. |
| ● | Partnerships/Joint Ventures: These funds consist primarily of U.S. government securities, Corporate Bonds, Corporate Stocks, and derivatives, which are valued in a manner consistent with these types of investments, noted above. |
| ● | Hedge Funds: Hedge funds are private investment vehicles valued using a Net Asset Value (NAV) provided by the manager of each fund. The NAV is based on the underlying net assets owned by the fund, divided by the number of shares outstanding. The NAV’s unit price is quoted on a private market that is not active. The NAV is based on the fair value of the underlying securities within the funds, which may be traded on an active market, and valued at the closing price reported on the active market on which those individual securities are traded. For investments not traded on an active market, or for which a quoted price is not publicly available, a variety of unobservable valuation methodologies, including discounted cash flow, market multiple and cost valuation approaches, are employed by the fund manager to value investments. Fair values of all investments are adjusted annually, if necessary, based on audits of the Hedge Fund financial statements; such adjustments are reflected in the fair value of the plan’s assets. |
A-65A-69
| ● | Private Equity: Private Equity investments are valued based on the fair value of the underlying securities within the fund, which include investments both traded on an active market and not traded on an active market. For those investments that are traded on an active market, the values are based on the closing price reported on the active market on which those individual securities are traded. For investments not traded on an active market, or for which a quoted price is not publicly available, a variety of unobservable valuation methodologies, including discounted cash flow, market multiple and cost valuation approaches, are employed by the fund manager to value investments. Fair values of all investments are adjusted annually, if necessary, based on audits of the private equity fund financial statements; such adjustments are reflected in the fair value of the plan’s assets. Real Estate: Real estate investments include investments in real estate funds managed by a fund manager. These investments are valued using a variety of unobservable valuation methodologies, including discounted cash flow, market multiple and cost valuation approaches. |
| ● | The methods described above may produce a fair value calculation that may not be indicative of net realizable value or reflective of future fair values. Furthermore, while the Company believes its valuation methods are appropriate and consistent with other market participants, the use of different methodologies or assumptions to determine the fair value of certain financial instruments could result in a different fair value measurement. |
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
The methods described above may produce a fair value calculation that may not be indicative of net realizable value or reflective of future fair values. Furthermore, while the plan believes its valuation methods are appropriate and consistent with other market participants, the use of different methodologies or assumptions to determine the fair value of certain financial instruments could result in a different fair value measurement.
A-66
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
The Company contributed and expensed $140, $130$196, $177 and $119$148 to employee 401(k) retirement savings accounts in 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 2010,2013, respectively. The 401(k) retirement savings account plan providesplans provide to eligible employees both matching contributions and automatic contributions from the Company based on participant contributions, compensation as defined by the plan, and length of service.
The Company also administers other defined contribution plans for eligible employees. The cost of these plans was $7, $6$5 for 2015, 2014 and $7 for 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively.2013.
14.16. Multi-Employer Pension Plans
The Company contributes to various multi-employer pension plans, including the UFCW Consolidated Pension Plan, based on obligations arising from collective bargaining agreements. The Company is designated as the named fiduciary of the UFCW Consolidated Pension Plan and has sole investment authority over these assets. These plans provide retirement benefits to participants based on their service to contributing employers. The benefits are paid from assets held in trust for that purpose. Trustees are appointed in equal number by employers and unions. The trustees typically are responsible for determining the level of benefits to be provided to participants as well as for such matters as the investment of the assets and the administration of the plans.
In the fourth quarter of 2011, the Company entered into a memorandum of understanding (“MOU”) with 14 locals of the UFCW that participated in four multi-employer pension funds. The MOU established a process that amended each of the collective bargaining agreements between the Company and the UFCW locals under which the Company made contributions to these funds and consolidated the four multi-employer pension funds into one multi-employer pension fund.
Under the terms of the MOU, the locals of the UFCW agreed to a future pension benefit formula through 2021. The Company was designated as the named fiduciary of the new consolidated pension plan with sole investment authority over the assets. The Company committed to contribute sufficient funds to cover the actuarial cost of current accruals and to fund the pre-consolidation Unfunded Actuarial Accrued Liability (“UAAL”) that existed as of December 31, 2011, in a series of installments on or before March 31, 2018. At January 1, 2012, the UAAL was estimated to be $911 (pre-tax). In accordance with GAAP, the Company expensed $911 in 2011 related to the UAAL. The expense was based on a preliminary estimate of the contractual commitment. In 2012, the Company finalized the UAAL contractual commitment and recorded an adjustment that reduced the 2011 estimated commitment by $53 (pre-tax). The final UAAL contractual commitment, at January 1, 2012, was $858 (pre-tax). In the fourth quarter of 2011,2015, the Company contributed $650$190 to the consolidated multi-employerUFCW Consolidated Pension Plan. The Company had previously accrued $60 of the total contributions at January 31, 2015 and recorded expense for the remaining $130 at the time of payment in 2015.
In 2014, the Company incurred a charge of $56 (after-tax) related to commitments and withdrawal liabilities associated with the restructuring of pension plan agreements, of which $600$15 was allocatedcontributed to the UAAL and $50 was allocatedUFCW Consolidated Pension Plan in 2014.
Refer to service and interest costs and expensed in 2011. In the fourth quarter of 2012, the Company contributed $258 to the consolidated multi-employer pension plan to fully fund the Company’s UAAL contractual commitment. Future contributions will be dependent, among other things,Note 19 for additional details on the investment performanceeffect of assets in the plan. The funding commitments under the MOU replace the prior commitments under the four existing funds to pay an agreed upon amount per hour worked by eligible employees.certain contributions on quarterly results for 2015 and 2014.
The Company recognizes expense in connection with theseits multi-employer pension plans as contributions are funded, or in the case of the UFCW consolidated pension plan, when commitments are made. The Company made contributions to thesemulti-employer funds of $492$426 in 2012, $9462015, $297 in 20112014 and $262$228 in 2010. The cash contributions for 2012 and 2011 include the Company’s $258 and $650 contributions described above, respectively, to the UFCW consolidated pension plan in the fourth quarter of each year.2013.
A-70
The risks of participating in multi-employer pension plans are different from the risks of participating in single-employer pension plans in the following respects:
| a. | Assets contributed to the multi-employer plan by one employer may be used to provide benefits to employees of other participating employers. | |||||
| b. | If a participating employer stops contributing to the plan, the unfunded obligations of the plan allocable to such withdrawing employer may be borne by the remaining participating employers. | |||||
A-67
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
| c. | If the Company stops participating in some of its multi-employer pension plans, the Company may be required to pay those plans an amount based on its allocable share of the | ||
The Company’s participation in thesemulti-employer plans is outlined in the following tables. The EIN / Pension Plan Number column provides the Employer Identification Number (“EIN”) and the three-digit pension plan number. The most recent Pension Protection Act Zone Status available in 20122015 and 20112014 is for the plan’s year-end at December 31, 20112014 and December 31, 2010,2013, respectively. Among other factors, generally, plans in the red zone are less than 65 percent funded, plans in the yellow zone are less than 80 percent funded and plans in the green zone are at least 80 percent funded. The FIP/RP Status Pending / Implemented Column indicates plans for which a funding improvement plan (“FIP”) or a rehabilitation plan (“RP”) is either pending or has been implemented. Unless otherwise noted, the information for these tables was obtained from the Forms 5500 filed for each plan’s year-end at December 31, 20112014 and December 31, 2010.2013. The multi-employer contributions listed in the table below are the Company’s multi-employer contributions made in fiscal years 2012, 20112015, 2014 and 2010.2013.
A-68A-71
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
The following table contains information about the Company’s multi-employer pension plans:
| EIN / Pension | Pension Protection Act Zone Status | FIP/RP Status Pending/ | Multi-Employer Contributions | Surcharge | |||||||||||||||
| Pension Fund | Plan Number | 2012 | 2011 | Implemented | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | Imposed (7) | |||||||||||
| SO CA UFCW Unions & Food | |||||||||||||||||||
| Employers Joint Pension | |||||||||||||||||||
| Trust Fund (1) (2) | 95-1939092 - 001 | Red | Red | Implemented | $ | 43 | $ | 40 | $ | 41 | No | ||||||||
| BD of Trustees of UNTD Food | |||||||||||||||||||
| and Commercial (1) (5) | 58-6101602 - 001 | Red | Red | Implemented | — | 59 | 47 | No | |||||||||||
| Desert States Employers & UFCW | |||||||||||||||||||
| Unions Pension Plan (1) | 84-6277982 - 001 | Green | Yellow | Implemented | 22 | 20 | 17 | No | |||||||||||
| UFCW Unions and Food | |||||||||||||||||||
| Employers Pension Plan of | |||||||||||||||||||
| Central Ohio (1) (5) | 31-6089168 - 001 | Green | Red | Implemented | — | 23 | 21 | No | |||||||||||
| Sound Retirement Trust | |||||||||||||||||||
| (formerly Retail Clerks | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Plan) (1) (3) | 91-6069306 – 001 | Red | Green | Implemented | 12 | 10 | 9 | No | |||||||||||
| Rocky Mountain UFCW | |||||||||||||||||||
| Unions and Employers | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Plan (1) | 84-6045986 - 001 | Green | Red | Implemented | 17 | 16 | 16 | No | |||||||||||
| Indiana UFCW Unions and | |||||||||||||||||||
| Retail Food Employers | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Plan (1) (5) | 35-6244695 - 001 | Red | Red | Implemented | — | 5 | 5 | No | |||||||||||
| Oregon Retail Employees | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Plan (1) | 93-6074377 - 001 | Red | Red | Implemented | 7 | 6 | 6 | No | |||||||||||
| Bakery and Confectionary Union | |||||||||||||||||||
| & Industry International | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Fund (1) | 52-6118572 - 001 | Red | Green | Pending | 10 | 9 | 6 | Yes | |||||||||||
| Washington Meat Industry | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Trust (1) (4) | 91-6134141 - 001 | Red | Red | Implemented | 3 | 2 | 2 | No | |||||||||||
| Retail Food Employers & UFCW | |||||||||||||||||||
| Local 711 Pension (1) | 51-6031512 - 001 | Red | Red | Implemented | 8 | 7 | 7 | No | |||||||||||
| Denver Area Meat Cutters and | |||||||||||||||||||
| Employers Pension Plan (1) | 84-6097461 - 001 | Green | Red | Implemented | 8 | 8 | 8 | No | |||||||||||
| United Food & Commercial | |||||||||||||||||||
| Workers Intl Union – Industry | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Fund (1) (4) | 51-6055922 - 001 | Green | Green | No | 33 | 33 | 30 | No | |||||||||||
| Northwest Ohio UFCW Union | |||||||||||||||||||
| and Employers Joint | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Fund (1) (5) | 34-0947187 - 001 | Green | Red | Implemented | — | 2 | 2 | No | |||||||||||
| Western Conference of | |||||||||||||||||||
| Teamsters Pension Plan | 91-6145047 - 001 | Green | Green | No | 30 | 31 | 30 | No | |||||||||||
| Central States, Southeast & | |||||||||||||||||||
| Southwest Areas | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Plan | 36-6044243 - 001 | Red | Red | Implemented | 12 | 14 | 8 | No | |||||||||||
| UFCW Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Plan (1) (6) | 58-6101602 – 001 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 275 | 650 | — | No | |||||||||||
| Other | 12 | 11 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total Contributions | $ | 492 | $ | 946 | $ | 262 | |||||||||||||
| Pension | |||||||||||||||||||
| Protection | FIP/RP | ||||||||||||||||||
| Act Zone | Status | Multi-Employer | |||||||||||||||||
| EIN / Pension | Status | Pending/ | Contributions | Surcharge | |||||||||||||||
| Pension Fund | Plan Number | 2015 | 2014 | Implemented | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | Imposed(6) | |||||||||||
| SO CA UFCW Unions & Food | |||||||||||||||||||
| Employers Joint Pension | |||||||||||||||||||
| Trust Fund(1) (2) | 95-1939092 - 001 | Red | Red | Implemented | $ | 55 | $ | 48 | $ | 45 | No | ||||||||
| Desert States Employers | |||||||||||||||||||
| & UFCW Unions | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Plan(1) | 84-6277982 - 001 | Green | Green | No | 18 | 21 | 23 | No | |||||||||||
| Sound Retirement Trust | |||||||||||||||||||
| (formerly Retail Clerks | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Plan)(1) (3) | 91-6069306 - 001 | Red | Red | Implemented | 17 | 15 | 13 | No | |||||||||||
| Rocky Mountain UFCW | |||||||||||||||||||
| Unions and Employers | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Plan(1) | 84-6045986 - 001 | Green | Green | No | 17 | 17 | 17 | No | |||||||||||
| Oregon Retail Employees | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Plan(1) | 93-6074377 - 001 | Green | Red | No | 9 | 7 | 7 | No | |||||||||||
| Bakery and Confectionary Union | |||||||||||||||||||
| & Industry International | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Fund(1) | 52-6118572 - 001 | Red | Red | Implemented | 11 | 11 | 12 | No | |||||||||||
| Washington Meat Industry | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Trust(1) (4) (5) | 91-6134141 - 001 | Red | Red | Implemented | — | 1 | 3 | No | |||||||||||
| Retail Food Employers & UFCW | |||||||||||||||||||
| Local 711 Pension(1) | 51-6031512 - 001 | Red | Red | Implemented | 9 | 9 | 8 | No | |||||||||||
| Denver Area Meat Cutters | |||||||||||||||||||
| and Employers | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Plan(1) | 84-6097461 - 001 | Green | Green | No | 7 | 8 | 8 | No | |||||||||||
| United Food & Commercial | |||||||||||||||||||
| Workers Intl Union – Industry | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Fund(1) (4) | 51-6055922 - 001 | Green | Green | No | 35 | 33 | 33 | No | |||||||||||
| Western Conference of | |||||||||||||||||||
| Teamsters Pension Plan | 91-6145047 - 001 | Green | Green | No | 31 | 30 | 31 | No | |||||||||||
| Central States, Southeast | |||||||||||||||||||
| & Southwest Areas | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Plan | 36-6044243 - 001 | Red | Red | Implemented | 16 | 15 | 15 | No | |||||||||||
| UFCW Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Plan(1) | 58-6101602 - 001 | Green | Green | No | 190 | 70 | — | No | |||||||||||
| Other | 11 | 12 | 13 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total Contributions | $ | 426 | $ | 297 | $ | 228 | |||||||||||||
| (1) | The Company’s multi-employer contributions to these respective funds represent more than 5% of the total contributions received by the pension funds. |
A-69
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
| (2) | The information for this fund was obtained from the Form 5500 filed for the plan’s year-end at March 31, | |||
| (3) | The information for this fund was obtained from the Form 5500 filed for the plan’s year-end at September 30, | |||
| (4) | The information for this fund was obtained from the Form 5500 filed for the plan’s year-end at June 30, | |||
A-72
| (5) | As of | |
| (6) | ||
| Under the Pension Protection Act, a surcharge may be imposed when employers make contributions under a collective bargaining agreement that is not in compliance with a rehabilitation plan. As of | ||
The following table describes (a) the expiration date of the Company’s collective bargaining agreements and (b) the expiration date of the Company’s most significant collective bargaining agreements for each of the material multi-employer funds in which the Company participates.
A-70
| Expiration Date | Most Significant Collective | |||||
| of Collective | Bargaining Agreements(1) | |||||
| Bargaining | (not in millions) | |||||
| Pension Fund | Agreements | Count | Expiration | |||
| SO CA UFCW Unions & Food Employers Joint | March 2016 to | March 2016 to | ||||
| Pension Trust Fund | June 2017 | 2 | June 2017 | |||
| March 2016 to | April 2016 to | |||||
| UFCW Consolidated Pension Plan | August 2020 | 8 | August 2020 | |||
| Desert States Employers & UFCW Unions | October 2016 to | |||||
| Pension Plan | June 2018 | 1 | October 2016 | |||
| Sound Retirement Trust (formerly Retail | April 2016 to | May 2016 to | ||||
| Clerks Pension Plan) | January 2018 | 2 | August 2016 | |||
| Rocky Mountain UFCW Unions and | January 2019 to | |||||
| Employers Pension Plan | February 2019 | 1 | January 2019 | |||
| August 2015(2)to | August 2015(2)to | |||||
| Oregon Retail Employees Pension Plan | April 2017 | 3 | June 2016 | |||
| Bakery and Confectionary Union & Industry | June 2016 to July | August 2016 to | ||||
| International Pension Fund | 2018 | 4 | July 2018 | |||
| Retail Food Employers & | April 2017 to | |||||
| UFCW Local 711 Pension | November 2019 | 1 | March 2019 | |||
| Denver Area Meat Cutters and | January 2019 to | |||||
| Employers Pension Plan | February 2019 | 1 | January 2019 | |||
| United Food & Commercial Workers Intl Union – | March 2014(2)to | March 2017 to | ||||
| Industry Pension Fund | April 2019 | 2 | April 2019 | |||
| April 2017 to | July 2017 to | |||||
| Western Conference of Teamsters Pension Plan | September 2020 | 5 | September 2020 | |||
| Central States, Southeast & Southwest | September 2017 to | September 2017 to | ||||
| Areas Pension Plan | November 2018 | 3 | November 2018 | |||
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, Continued
| (1) | This column represents the number of significant collective bargaining agreements and their expiration date for each of the Company’s pension funds listed above. For purposes of this table, the “significant collective bargaining agreements” are the largest based on covered employees that, when aggregated, cover the majority of the employees for which we make multi-employer contributions for the referenced pension fund. | |||
| (2) | Certain collective bargaining agreements for each of these pension funds are operating under an extension. | |||
A-73
Based on the most recent information available to it, the Company believes that the present value of actuarial accrued liabilities in most of these multi-employer plans substantially exceeds the value of the assets held in trust to pay benefits. Moreover, if the Company were to exit certain markets or otherwise cease making contributions to these funds, the Company could trigger a substantial withdrawal liability. Any adjustment for withdrawal liability will be recorded when it is probable that a liability exists and can be reasonably estimated.
The Company also contributes to various other multi-employer benefit plans that provide health and welfare benefits to active and retired participants. Total contributions made by the Company to these other multi-employer benefithealth and welfare plans were approximately $1,192 in 2015, $1,200 in 2014 and $1,100 in 2012, $1,000 in 2011 and $900 in 2010.2013.
15.17. Recently Adopted Accounting Standards
In June 2011,2015, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) amended its rules regardingAccounting Standards Codification 835, “Interest-Imputation of Interest.” The amendment simplifies the presentation of comprehensive income.debt issuance costs related to a recognized debt liability by requiring it be presented in the balance sheet as a direct deduction from the carrying amount of that debt liability, consistent with debt discounts. This amendment became effective for the Company beginning February 1, 2015, and was adopted retrospectively in accordance with the standard. The objectiveadoption of this amendment resulted in amounts previously reported in other assets to now be reported within long-term debt including obligations under capital leases and financing obligations in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. These amounts were not material to the prior year. The adoption of this amendment did not have an effect on the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Operations.
18. Recently Issued Accounting Standards
In May 2014, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers,” which provides guidance for revenue recognition. The standard’s core principle is that a company will recognize revenue when it transfers promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. Per ASU 2015-14, “Deferral of Effective Date,” this guidance will be effective for the Company in the first quarter of its fiscal year ending February 2, 2019. Early adoption is permitted as of the first quarter of the Company’s fiscal year ending February 3, 2018. The Company is currently in the process of evaluating the effect of adoption of this ASU on the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements.
In April 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-04, “Retirement Benefits (Topic 715): Practical Expedient for the Measurement Date of an Employer’s Defined Benefit Obligation and Plan Assets.” This amendment permits an entity to measure defined benefit plan assets and obligations using the month end that is closest to the entity’s fiscal year end for all plans. This guidance will be effective for the Company in the fiscal year ending January 28, 2017. The implementation of this amendment will not have an effect on the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Operations, and will not have a significant effect on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets.
In April 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-07, “Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosures for Investments in Certain Entities That Calculate Net Asset Value per Share (or Its Equivalent).” This amendment removes the requirement to categorize within the fair value hierarchy all investments for which fair value is measured using the net asset value per share. This guidance will be effective for the Company in the fiscal year ending January 28, 2017. The implementation of this amendment will have an effect on the Company’s Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements and will not have an effect on the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Operations or Consolidated Balance Sheets.
A-74
In September 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-16, “Business Combinations (Topic 805): Simplifying the Accounting for Measurement-Period Adjustments.” This amendment eliminates the requirement to retrospectively account for adjustments made to provisional amounts recognized in a business combination. This guidance will be effective for the Company in its fiscal year ending January 28, 2017. The implementation of this amendment is to improve the comparability, consistency and transparency of financial reporting and to increase the prominence of items reported in other comprehensive income. Specifically, this amendment requires that all non-owner changes in shareholders’ equity be presented either in a single continuous statement of comprehensive income or in two separate but consecutive statements. The new rules became effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2011. In December 2011, the FASB deferred certain aspects of this standard beyond the December 15, 2011 effective date, specifically the provisions dealing with reclassification adjustments. The Company adopted this amended standard effective January 29, 2012 by presenting separate Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income immediately following the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Because this standard only affects the display of comprehensive income and does not affect what is included in comprehensive income, this standard did notexpected to have a materialsignificant effect on the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements.
In May 2011,November 2015, the FASB amended its rules for disclosure requirements for common fair value measurement. These amendments,issued ASU 2015-17, “Income Taxes (Topic 740): Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes.” This amendment requires deferred tax liabilities and assets be classified as noncurrent in a classified statement of financial position. This guidance will be effective for the interim and annual periods beginning on or after December 15, 2011 (earlyfiscal year ending January 28, 2017. Early adoption was prohibited), result in a common definition of fair value and common requirements for fair value measurement and disclosure between GAAP and International Financial Accounting Standards. Consequently, the amendments change some fair value measurement principles and disclosure requirements.is permitted. The implementation of the amended accounting guidance didthis amendment will not have a materialan effect on the Company’s consolidated financial position or resultsConsolidated Statements of operations.
16. Recently Issued Accounting Standards
In February 2013, the FASB amended its standards on comprehensive income by requiring disclosure in the footnotes of information about amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by component. Specifically, the amendment will require disclosure of the line items of net income in which the item was reclassified only if it is reclassified to net income in its entirety in the same reporting period. It will also require cross reference to other disclosures for amounts that are not reclassified in their entirety in the same reporting period. The new disclosures will be required for the Company prospectively only for annual periods beginning February 3, 2013Operations and interim periods within those annual periods. The implementation of the amended accounting guidance will not have a materialsignificant effect on the Company’s consolidated financial position or resultsConsolidated Balance Sheets.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, “Leases”, which provides guidance for the recognition of operations.
A-71
Noteslease agreements. The standard’s core principle is that a company will now recognize most leases on its balance sheet as lease liabilities with corresponding right-of-use assets. This guidance will be effective in the first quarter of fiscal year ending February 1, 2020. Early adoption is permitted currently. The adoption of this ASU will result in a significant increase to the Company’s balance sheet for lease liabilities and right-of-use assets, and the Company is currently evaluating the other effects of adoption of this ASU on its Consolidated Financial Statements, ContinuedStatements.
17.19. Quarterly Data (Unaudited)
The two tables that follow reflect the unaudited results of operations for 20122015 and 2011.2014.
| Quarter | Quarter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | First (16 Weeks) | Second (12 Weeks) | Third (12 Weeks) | Fourth (13 Weeks) | Total Year (53 Weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First | Second | Third | Fourth | Total Year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 | (16 Weeks) | (12 Weeks) | (12 Weeks) | (12 Weeks) | (52 Weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales | $ | 29,065 | $ | 21,726 | $ | 21,807 | $ | 24,153 | $ | 96,751 | $ | 33,051 | $ | 25,539 | $ | 25,075 | $ | 26,165 | $ | 109,830 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merchandise costs, including advertising, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| warehousing, and transportation, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| excluding items shown separately below | 23,095 | 17,278 | 17,383 | 19,102 | 76,858 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating, general, and administrative | 4,464 | 3,391 | 3,305 | 3,689 | 14,849 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| warehousing, and transportation, excluding | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| items shown separately below | 25,760 | 20,065 | 19,478 | 20,193 | 85,496 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating, general and administrative | 5,354 | 4,068 | 4,169 | 4,355 | 17,946 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rent | 191 | 139 | 141 | 157 | 628 | 215 | 155 | 172 | 181 | 723 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 501 | 383 | 382 | 386 | 1,652 | 620 | 477 | 484 | 508 | 2,089 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating profit | 814 | 535 | 596 | 819 | 2,764 | 1,102 | 774 | 772 | 928 | 3,576 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 141 | 106 | 103 | 112 | 462 | 148 | 114 | 107 | 113 | 482 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings before income tax expense | 673 | 429 | 493 | 707 | 2,302 | 954 | 660 | 665 | 815 | 3,094 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense | 232 | 148 | 175 | 239 | 794 | 330 | 227 | 238 | 250 | 1,045 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings including noncontrolling interests | 441 | 281 | 318 | 468 | 1,508 | 624 | 433 | 427 | 565 | 2,049 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| interests | 2 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| noncontrolling interests | 5 | — | (1 | ) | 6 | 10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. | $ | 439 | $ | 279 | $ | 317 | $ | 462 | $ | 1,497 | $ | 619 | $ | 433 | $ | 428 | $ | 559 | $ | 2,039 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per basic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| common share | $ | 0.78 | $ | 0.52 | $ | 0.61 | $ | 0.89 | $ | 2.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average number of shares used in basic calculation | 556 | 538 | 518 | 514 | 533 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. per | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| diluted common share | $ | 0.78 | $ | 0.51 | $ | 0.60 | $ | 0.88 | $ | 2.77 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average number of shares used in diluted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| calculation | 559 | 541 | 522 | 518 | 537 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| basic common share | $ | 0.63 | $ | 0.44 | $ | 0.44 | $ | 0.57 | $ | 2.09 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average number of shares used | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| in basic calculation | 969 | 963 | 965 | 966 | 966 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| per diluted common share | $ | 0.62 | $ | 0.44 | $ | 0.43 | $ | 0.57 | $ | 2.06 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average number of shares used in | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| diluted calculation | 983 | 977 | 979 | 980 | 980 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.115 | $ | 0.115 | $ | 0.15 | $ | 0.15 | $ | 0.53 | $ | 0.093 | $ | 0.105 | $ | 0.105 | $ | 0.105 | $ | 0.408 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Annual amounts may not sum due to rounding.
In the third quarter of 2015, the Company incurred a $80 charge to OG&A expenses for contributions to the UFCW Consolidated Pension Plan.
A-72A-75
NotesIn the fourth quarter of 2015, the Company incurred a $30 charge to OG&A expenses for contributions to the UFCW Consolidated Financial Statements, ConcludedPension Plan.
| Quarter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 | First (16 Weeks) | Second (12 Weeks) | Third (12 Weeks) | Fourth (12 Weeks) | Total Year (52 Weeks) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales | $ | 27,461 | $ | 20,913 | $ | 20,594 | $ | 21,406 | $ | 90,374 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merchandise costs, including advertising, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| warehousing, and transportation, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| excluding items shown separately below | 21,624 | 16,555 | 16,358 | 16,957 | 71,494 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating, general, and administrative | 4,335 | 3,353 | 3,318 | 4,339 | 15,345 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rent | 192 | 143 | 141 | 143 | 619 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 499 | 374 | 372 | 393 | 1,638 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating profit (loss) | 811 | 488 | 405 | (426 | ) | 1,278 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 138 | 97 | 99 | 101 | 435 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) before income tax | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| expense (benefit) | 673 | 391 | 306 | (527 | ) | 843 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) | 252 | 108 | 108 | (221 | ) | 247 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) including | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| noncontrolling interests | 421 | 283 | 198 | (306 | ) | 596 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| noncontrolling interests | (11 | ) | 2 | 2 | 1 | (6 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to The Kroger Co | $ | 432 | $ | 281 | $ | 196 | $ | (307 | ) | $ | 602 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to The Kroger Co. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| per basic common share | $ | 0.71 | $ | 0.47 | $ | 0.33 | $ | (0.54 | ) | $ | 1.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average number of shares used in basic calculation. | 608 | 596 | 583 | 565 | 590 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to The Kroger Co. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| per diluted common share | $ | 0.70 | $ | 0.46 | $ | 0.33 | $ | (0.54 | ) | $ | 1.01 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average number of shares used in | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| diluted calculation | 612 | 600 | 586 | 565 | 593 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.105 | $ | 0.105 | $ | 0.115 | $ | 0.115 | $ | 0.44 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quarter | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First | Second | Third | Fourth | Total Year | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | (16 Weeks) | (12 Weeks) | (12 Weeks) | (12 Weeks) | (52 Weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales | $ | 32,961 | $ | 25,310 | $ | 24,987 | $ | 25,207 | $ | 108,465 | |||||||||||||||
| Merchandise costs, including advertising, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| warehousing, and transportation, excluding | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| items shown separately below | 26,065 | 20,136 | 19,764 | 19,547 | 85,512 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating, general and administrative | 5,168 | 3,920 | 3,954 | 4,119 | 17,161 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Rent | 217 | 166 | 162 | 162 | 707 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 581 | 444 | 456 | 467 | 1,948 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating profit | 930 | 644 | 651 | 912 | 3,137 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 147 | 112 | 114 | 115 | 488 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings before income tax expense | 783 | 532 | 537 | 797 | 2,649 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense | 274 | 182 | 172 | 274 | 902 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings including noncontrolling interests | 509 | 350 | 365 | 523 | 1,747 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| noncontrolling interests | 8 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 19 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. | $ | 501 | $ | 347 | $ | 362 | $ | 518 | $ | 1,728 | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| per basic common share | $ | 0.50 | $ | 0.35 | $ | 0.37 | $ | 0.53 | $ | 1.74 | |||||||||||||||
| Average number of shares used in | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| basic calculation | 1,002 | 970 | 972 | 972 | 981 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to The Kroger Co. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| per diluted common share | $ | 0.49 | $ | 0.35 | $ | 0.36 | $ | 0.52 | $ | 1.72 | |||||||||||||||
| Average number of shares used in diluted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| calculation | 1,014 | 982 | 984 | 987 | 993 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.083 | $ | 0.083 | $ | 0.093 | $ | 0.093 | $ | 0.350 | |||||||||||||||
Annual amounts may not sum due to rounding.
In the first quarter of 2014, the Company incurred a $87 charge to OG&A expenses due to commitments and withdrawal liabilities arising from restructuring of certain pension plan agreements to help stabilize associates’ future benefits.
In the third quarter of 2014, the Company incurred a $25 charge to OG&A expenses due to contributions to the Company’s charitable foundation and a $17 benefit to income tax expense due to certain tax items.
In the fourth quarter of 2014, the Company incurred a $60 charge to OG&A expenses due to contributions to the Company’s charitable foundation and a $55 charge to OG&A expenses for contributions to the UFCW Consolidated Pension Plan.
20. Subsequent Event
In anticipation of future debt refinancing in fiscal years 2017 and 2018, the Company, in the first quarter of 2016, entered into additional forward-starting interest rate swap agreements with an aggregate notional amount totaling $1,300. After entering into these additional forward-starting interest rate swaps, the Company has a total of $1,700 notional amount of forward-starting interest rate swaps outstanding. The forward-starting interest rate swaps entered into in the first quarter of 2016 were designated as cash-flow hedges as defined by GAAP.
18. Subsequent Event
In February 2013, the Company made a $100 contribution to the Company-sponsored defined benefit pension plans and does not expect to make additional contributions in 2013.
A-73A-76
|
|
Executive Officers
|
|
|
Operating Unit Heads
|
|
|
The Kroger Co. • 1014 Vine Street • Cincinnati, Ohio 45202 • (513) 762-4000


VOTE BY INTERNET -www.proxyvote.com
Use the Internet to transmit your voting instructions and for electronic delivery of information up until 11:59 P.M. Eastern Time the day before the meeting date. Have your proxy card in hand when you access the web site and follow the instructions to obtain your records and to create an electronic voting instruction form.
ELECTRONIC DELIVERY OF FUTURE PROXY MATERIALS
If you would like to reduce the costs incurred byour companyin mailing proxy materials, you can consent to receiving all future proxy statements, proxy cards and annual reports electronically via e-mail or the Internet. To sign up for electronic delivery, please follow the instructions above to vote using the Internet and, when prompted, indicate that you agree to receive or access proxy materials electronically in future years.
VOTE BY PHONE - 1-800-690-6903
Use any touch-tone telephone to transmit your voting instructions up until 11:59 P.M. Eastern Time the day before the meeting date. Have your proxy card in hand when you call and then follow the instructions.
VOTE BY MAIL
Mark, sign and date your proxy card and return it in the postage-paid envelope we have provided or return it to Vote Processing, c/o Broadridge, 51 Mercedes Way, Edgewood, NY 11717. If you vote your proxy by Internet or by telephone, you do NOT need to mail back your proxy card.
| TO VOTE, MARK BLOCKS BELOW IN BLUE OR BLACK INK AS FOLLOWS: | |
| KEEP THIS PORTION FOR YOUR RECORDS | |
| DETACH AND RETURN THIS PORTION ONLY | |
| THIS PROXY CARD IS VALID ONLY WHEN SIGNED AND DATED. | |
| THE KROGER CO. | |||||||||||||
| | |||||||||||||
| The Board of Directors recommends you vote FOR the following: | |||||||||||||
| 1. | Election of Directors | ||||||||||||
| Nominees: | For | Against | Abstain | ||||||||||
| 1a. | |||||||||||||
| 1b. | Robert D. Beyer | ||||||||||||
| 1c. | |||||||||||||
| 1d. | Susan J. Kropf | ||||||||||||
| 1e. | |||||||||||||
| 1f. | |||||||||||||
| 1g. | |||||||||||||
| 1h. | |||||||||||||
| 1i. | |||||||||||||
| 1j. | |||||||||||||
| 1k. | |||||||||||||
| The Board of Directors recommends that you vote FOR proposals 2 and 3. | For | Against | Abstain | ||||
| 2. | Advisory vote to approve executive compensation. | ||||||
| 3. | |||||||
| The Board of Directors recommends that you vote AGAINST proposals 4, 5, 6 and 7. | For | Against | Abstain | ||||
| 4. | A shareholder proposal, if properly presented, to publish a report on human rights risks | ||||||
| 5. | A shareholder proposal, if properly presented, to | ||||||
| 6. | A shareholder proposal, if properly presented, to issue a report | ||||||
| 7. | A shareholder proposal, if properly presented, to adopt | ||||||
| NOTE: | |||||||
Please sign exactly as your name(s) appear(s) hereon. When signing as attorney, executor, administrator, or other fiduciary, please give full title as such. Joint owners should each sign personally. All holders must sign. If a corporation or partnership, please sign in full corporate or partnership name by authorized officer. | ||||||
| | ||||||
| Signature [PLEASE SIGN WITHIN BOX] | Date | Signature (Joint Owners) | Date | |||
Important Notice Regarding the Availability of Proxy Materials for the Annual Meeting:
The Combined Notice, Proxy Statement, and Annual Report are available atwww.proxyvote.com.
THE KROGER CO.
2016 Annual Meeting of Shareholders
June 27, 201323, 2016 11:00 AM Eastern Time
This proxy is solicited by the Board of Directors
The undersigned hereby appoints each of DAVID B. DILLON, JOHN T. LAMACCHIAROBERT D. BEYER, W. RODNEY McMULLEN, and BOBBY S. SHACKOULSRONALD L. SARGENT, or if more than one is present and acting then a majority thereof, proxies, with full power of substitution and revocation, to vote the common shares of The Kroger Co. that the undersigned is entitled to vote at the annual meeting of shareholders, and at any adjournment thereof, with all the powers the undersigned would possess if personally present, including authority to vote on the matters shown on the reverse in the manner directed, and upon any other matter that properly may come before the meeting. The undersigned hereby revokes any proxy previously given to vote those shares at the meeting or at any adjournment.
The proxies are directed to vote as specified on the reverse hereof and in their discretion on all other matters coming before the meeting. Except as specified to the contrary on the reverse, the shares represented by this proxy will be voted FOR all nomineeseach nominee listed in Proposal 1, FOR Proposals 2 and 3, and AGAINST Proposals 4, 5, 6 and 7.
If you wish to vote in accordance with the recommendations of the Board of Directors, all you need to do is sign and return this card. The Proxy Committeeabove named proxies cannot vote the shares unless you vote your proxy by Internet or telephone, or sign and return this card.
Only shareholders and persons holding proxies from shareholders may attend the meeting.If you are attending the meeting, pleaseyou must bring either: (1) the notice of the meeting that was separately mailed to you or (2) the top portion of your proxy card, either of which will serve asbe your admission ticket.
YOUR MANAGEMENT DESIRES TO HAVE A LARGE NUMBER OF SHAREHOLDERS REPRESENTED AT THE MEETING, IN PERSON OR BY PROXY. PLEASE VOTE YOUR PROXY ELECTRONICALLY VIA THE INTERNET OR BY TELEPHONE. IF YOU HAVE ELECTED TO RECEIVE PRINTED MATERIALS, YOU MAY SIGN AND DATE THE PROXY AND MAIL IT IN THE SELF-ADDRESSED ENVELOPE PROVIDED. NO POSTAGE IS REQUIRED IF MAILED WITHIN THE UNITED STATES. If you are unable to attend the annual meeting, you may listen to a live webcast of the meeting, which will be accessible through our website, ir.kroger.com, at 11 a.m., eastern time.11:00 AM Eastern Time on June 23, 2016.
Continued and to be signed on reverse side